T cell regulatory genes associated with immune disease
a technology of immune disease and regulatory genes, applied in the field of immune disease, can solve the problems of increased asthma prevalence, poor understanding of susceptibility, and direct treatment costs exceeding $11 billion per annum, and achieve the effect of preventing the development of atopy and reducing or terminating immunological disorders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
Identification of Human Tim Sequences
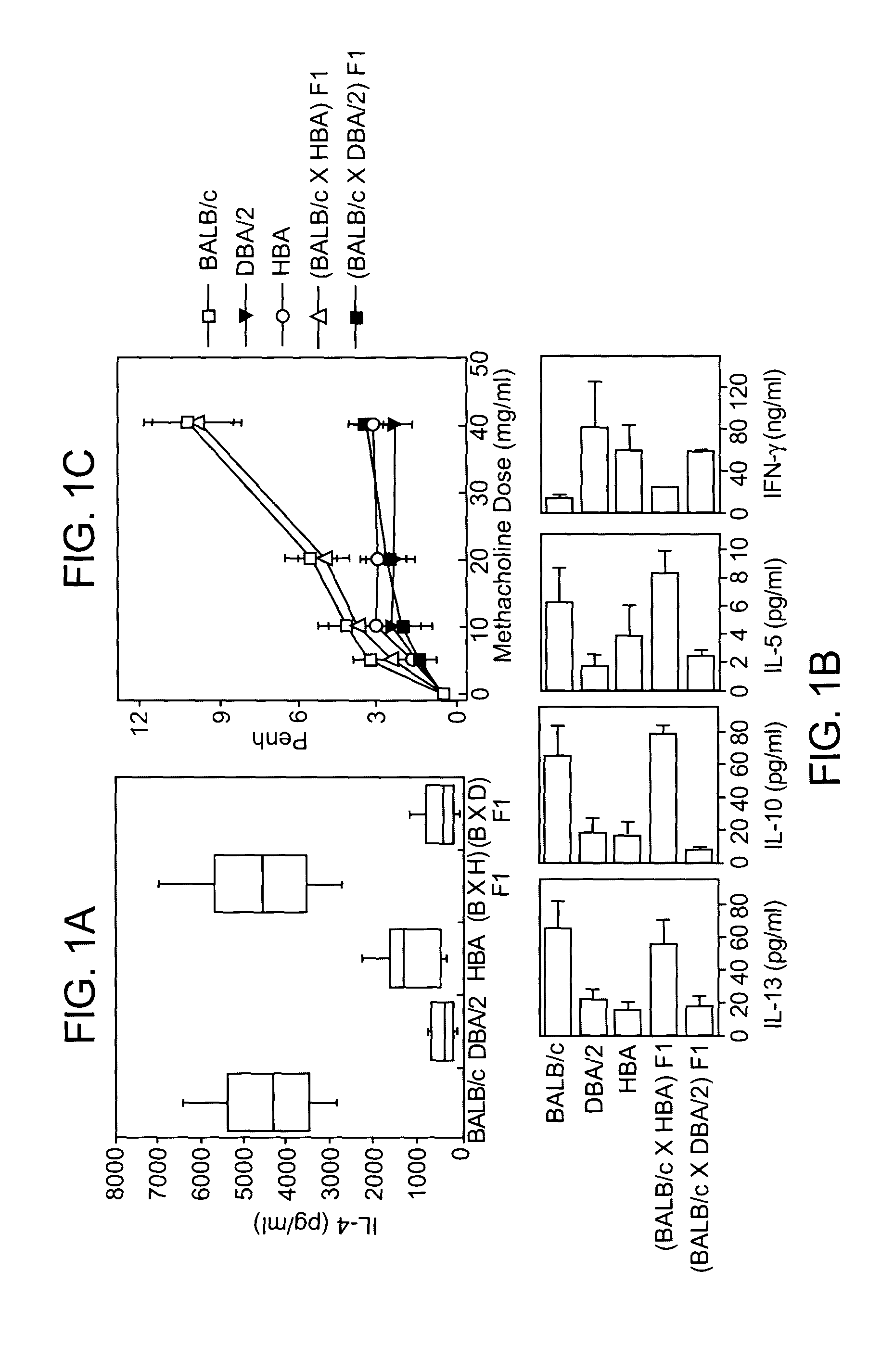
[0164] The positional cloning of the TIM gene family within a locus that confers protection against the development of Th2 responses and allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity provides an opportunity to greatly improve our understanding of the regulation of Th2 driven responses and atopic diseases. In addition, TIM-3 is specifically expressed on murine Th1 cells and anti-TIM-3 mAb leads to increased severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). This emphasizes the importance of the gene family in T helper subset regulation.
[0165] The human Tim cDNAs, which are the orthologues of murine Tim-3 and Tim-4 were cloned by PCR. The human orthologue of TIM-1 was cloned as HAVcr-1, the cellular receptor for hepatitis A virus. The TIM family genes are immediately adjacent to each other on human chromosome 5, in the order TIM-4, TIM-1, TIM-3, with no intervening genes. There are TIM pseudogenes on chromosomes 12 and 19. The gene family mem...
example 3
Expression of Tim Sequences
[0176] Murine TIM-3 protein is expressed on Th1 clones but not on naive T cells or Th2 cells. Using TCR transgenic T cells, TIM-3 protein was not expressed on Th1 cells after one or two rounds of Th1-directed differentiation but was expressed after the third and further rounds of Th1 stimulation. TIM-3 mRNA expression was detected somewhat earlier. In order to determine if TIM-3 gene expression was the same in human, TIM-3 and TIM-1 mRNA expression in human Th1 cells was examined using tetanus toxoid specific T cells generated by stimulation with antigen in the presence of IL-12 and anti IL-4 mAb. Given the association of TIM-1 with asthma, TIM-1 and TIM-3 mRNA expression in human Th2 cells was examined. Th2 cell lines were generated from allergic donors by in vitro stimulation with allergen, IL-4, and anti IL-12 mAb. RNA was analyzed by PCR for TIM gene expression.
[0177] TIM-3 was generally expressed after Th1 differentiation whereas TIM-1 was lost. Con...
example 4
TIM Ligands and Antibodies
[0179] Generation of Antibodies. Generation of monoclonal antibodies against mouse TIM-1 allows examination of the cell surface expression of TIM-1 in different tissues, cell lines and mouse strains. Both alleles of mouse TIM-1 have been cloned into a vector for high protein expression (Invitrogen, pEF6-TOPO). Rats have been immunized and boosted with both Tim1 cDNA constructs to rapidly generate antibodies against cell surface molecules. This method with cDNA vaccination favors the production of mAb against cell surface epitopes since the Tim1 cDNA will be taken up by APC, which will express the TIM-1 as a cell surface molecule. In order to generate mAb that would bind equally well to both the BALB / c and the HBA TIM-1 (by binding to conserved domains of TIM-1 such as the Immunoglobulin domain of TIM-1), both the BALB / c and HBA Tim1 cDNA (pEF6-mTIMbalb and pEF6-mTIMhba) were injected into each rat.
[0180] Further boosting of the Tim1 cDNA-immunized rats wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com