Super micronization method for botanical medicinal, product obtained thereby and use thereof
A technology of ultra-micronization and medicinal materials, applied in the direction of plant raw materials, pharmaceutical formulations, plant/algae/fungus/moss components, etc., can solve the problem of particle size uniformity and quality control of final products, and weaken the adhesion of dissolved pharmaceutical active ingredients and absorption, unfavorable patients' ability to seek medical treatment and popularization of traditional Chinese medicine, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing dissolution efficiency, enzymatic hydrolysis rate and balanced particle size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1: the influence of the present invention on the dissolution rate of total saponins of Bupleuri
[0041] The comparative experiment on the effect of different treatment methods on the dissolution content of total saponins in Bupleurum bupleuri is carried out as follows:
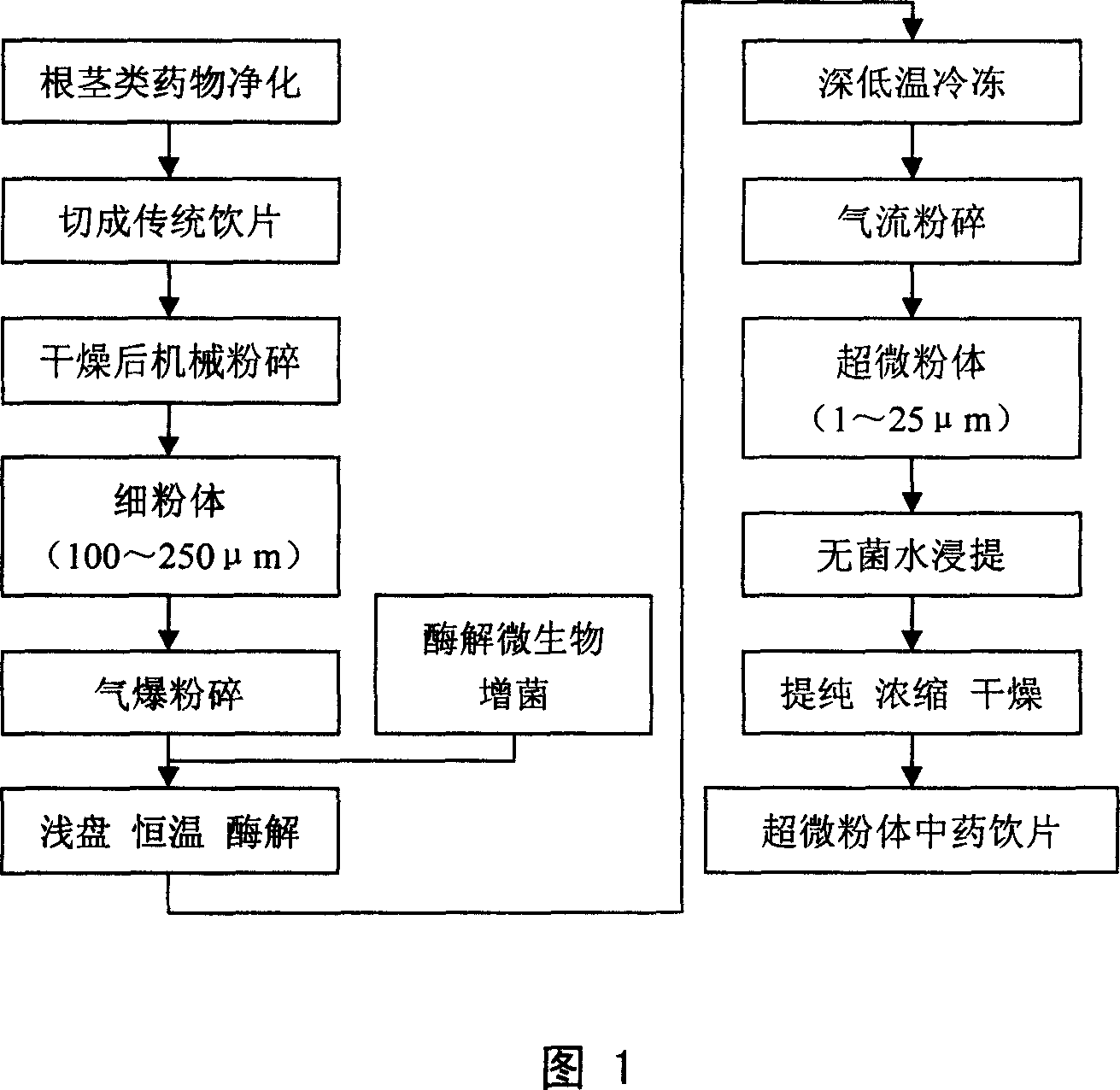
[0042] Firstly, Bupleurum bupleurum is processed as follows: after the Bupleurum bupleurum is purified, cut it into traditional decoction pieces with a slicer, and after proper drying, use a ball mill to pulverize it into a fine powder (average particle size 100-250 μm); Steam explosion crushing is carried out in the explosion tank (flash evaporation under the condition of high pressure 2.2MPa, 180°C, after 5 minutes of action, the pressure is suddenly reduced to form steam explosion), the processed material is swollen and spongy, and the humidity of the material is further adjusted. Reach 70-80%; place the humidified Bupleurum ultrafine powder in a shallow pan, and in a constant temperature...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2: the extraction rate of the total flavonoids of Pueraria lobata (compared with the extraction of Pueraria radici alcohol infusion and Pueraria lobata water infusion) different treatment methods on the comparative experiment of the influence of the dissolution content of total flavonoids of Pueraria lobata in crude drug Pueraria lobata is carried out as follows:
[0047] Pueraria puerariae is purified and cut into traditional decoction pieces, dried and then crushed into fine powder (average particle size 100-250 μm) with a ball mill, and then steam exploded in a steam explosion tank (under the condition of high pressure 2.2MPa, 180°C) Flash steaming, decompression suddenly after 5 minutes of action to form steam explosion), the processed material is bulky and spongy, and the humidity of the material is adjusted to reach 70-80%; the kudzu root powder after further air aeration is placed in a shallow pan, and is successively mixed with The fermented concentrat...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3: Glycyrrhetinic acid conversion rate after glycyrrhizic acid fermentation (compared with physical pulverization ultrafine powder body fermentation) different treatment methods on glycyrrhizic acid fermentation back glycyrrhetinic acid conversion rate The comparative experiment is divided into three steps: firstly, licorice is carried out The test samples were obtained by pretreatment, and then the test samples were fermented, and finally glycyrrhizic acid and glycyrrhetinic acid were detected by high performance liquid phase method, and the conversion rate was calculated.
[0052]Purify the licorice and cut it into traditional decoction pieces, dry it, and then use a ball mill to crush it into a fine powder (average particle size 100-250 μm), and then implement steam explosion crushing in a steam explosion tank (under the condition of high pressure 2.2MPa, 180°C) Flash steaming, depressurization suddenly after 5 minutes to form steam explosion), and adjust t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com