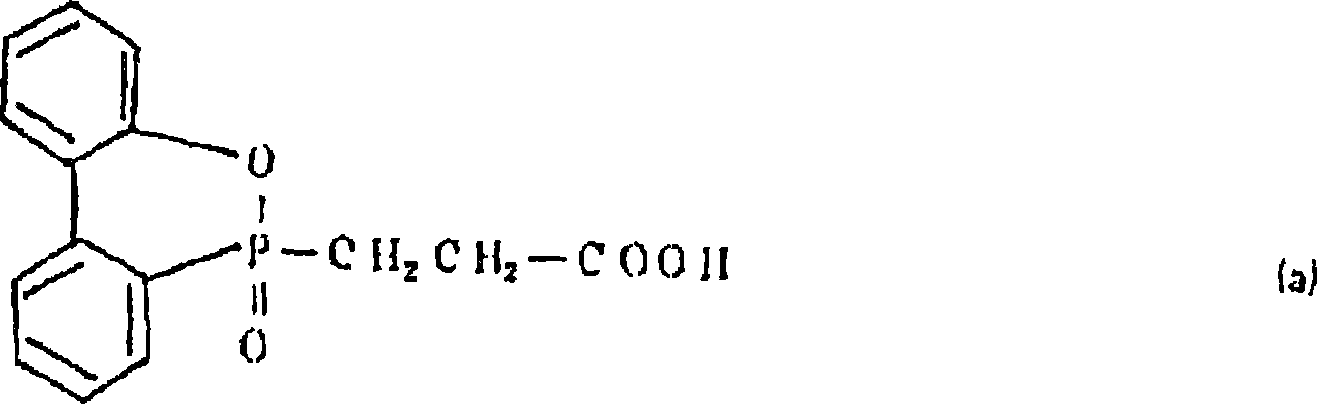Non-woven fabric for manufacturing vehicle formed article and use thereof
A technology of formed body and non-woven fabric, applied in vehicle parts, vehicle safety arrangement, textile and other directions, can solve the problem of weather resistance, flame retardancy, poor folding, flame retardancy, weak weather resistance, nylon non-woven fabric price Advanced problems, to achieve the effect of improving the global environment, good formability, and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~3
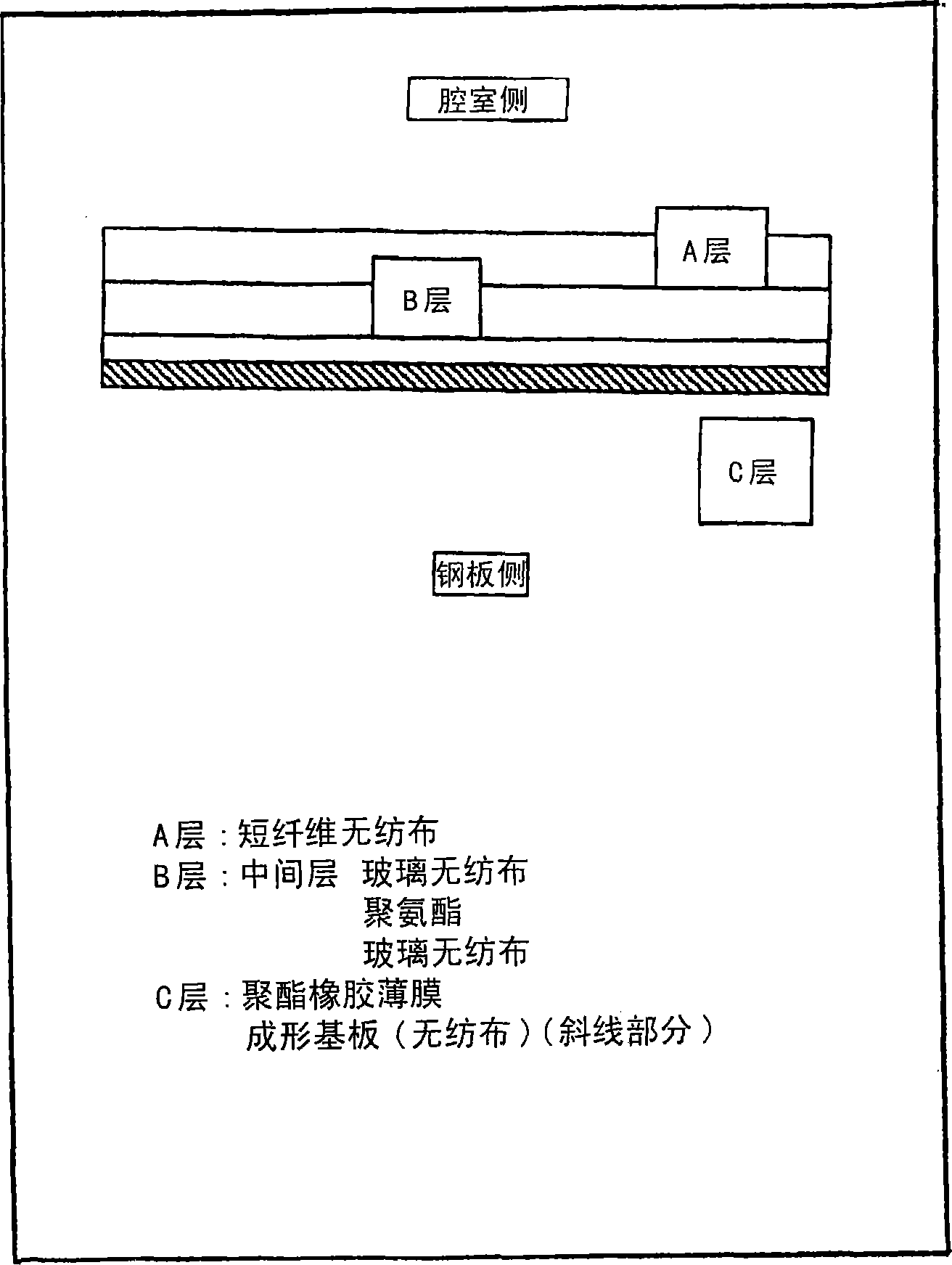
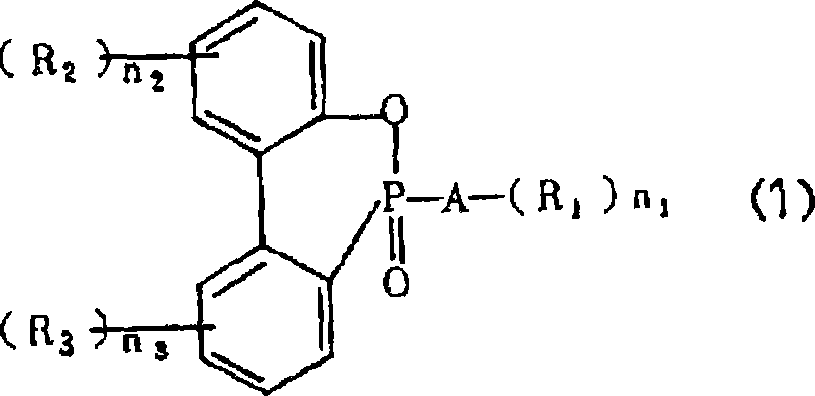
[0190] Manufactured by a spunbond method from the raw materials shown in Table 1 described later, the phosphorus-containing compound (2-carboxyethyl) phenylphosphinic acid ((2-carboxyethyl)phenylphosphinic acid) was polymerized in the amount shown in Table 1, By calendering with a hot roll at 210° C., sheets of the specifications shown in Table 1 having a random loop structure composed of polyester fibers of 1.5 decitex were heat-compressed to obtain molding substrates.
[0191] A 30 μm polyethylene-based film was laminated on the shaped base thus obtained. This laminate was molded at 120° C. together with a polyurethane foam raw material to manufacture an automobile roof material having this laminate as the lowermost layer. The punched waste of the laminate produced at this time was reused as a polyester fiber raw material for the rough felt.
[0192] In addition, a laminate of the above-mentioned nonwoven fabric and the above-mentioned film was used as an air bag wrapping m...
Embodiment 4
[0194] Manufactured by the spun-bonding method, the phosphorus-containing compound (2-carboxyethyl) phenylphosphonic acid was copolymerized in the amount shown in Table 1 described later, and processed by calendering with a hot roll at 235°C. 20g / m of random ring structure composed of mixed fiber of polyethylene terephthalate and polyester artificial rubber 2 The thin plates were heat-compressed to obtain a shaped substrate.
[0195] A 30 μm polyethylene film was laminated on the obtained molding base material. This laminated body was molded together with a polyurethane foam raw material, and the automobile roof material which made this laminated body the lowermost layer was manufactured. The punched waste of the laminate produced at this time was reused as a polyester fiber raw material for the rough felt.
Embodiment 5~9
[0197] Manufactured by the spunbond method, the phosphorus-containing compound (2-carboxyethyl) phenylphosphonic acid was copolymerized in the amount shown in Table 1 below, and processed by calendering with a hot roll at 210°C. 20g / m mesh of random annular structure composed of polyester fibers mixed with more than two kinds of raw materials shown in Table 1 2 The thin plates were heat-compressed to obtain a shaped substrate.
[0198] For soft PET, by combining 100 parts of terephthalic acid, 40 parts of ethylene glycol, and 15 parts of neopentyl glycol with a small amount of catalyst, transesterification is performed by the usual method-after polymerization An aromatic copolyester having a melting point of 178° C. and an intrinsic viscosity of 0.780 obtained by pelletizing.
[0199] A 30 μm polyethylene film was laminated on the obtained molding base material. This laminate was molded at 120° C. together with a polyurethane foam raw material to manufacture an automobile ro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com