Electric heating composite material for temperature measurement and preparation method thereof
A composite material, temperature measurement technology, applied in the direction of measuring heat, thermometers, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the continuity of polymer matrix materials, poor conductivity of carbon black, performance degradation, etc., to achieve good conductivity, low addition amount , the effect of convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
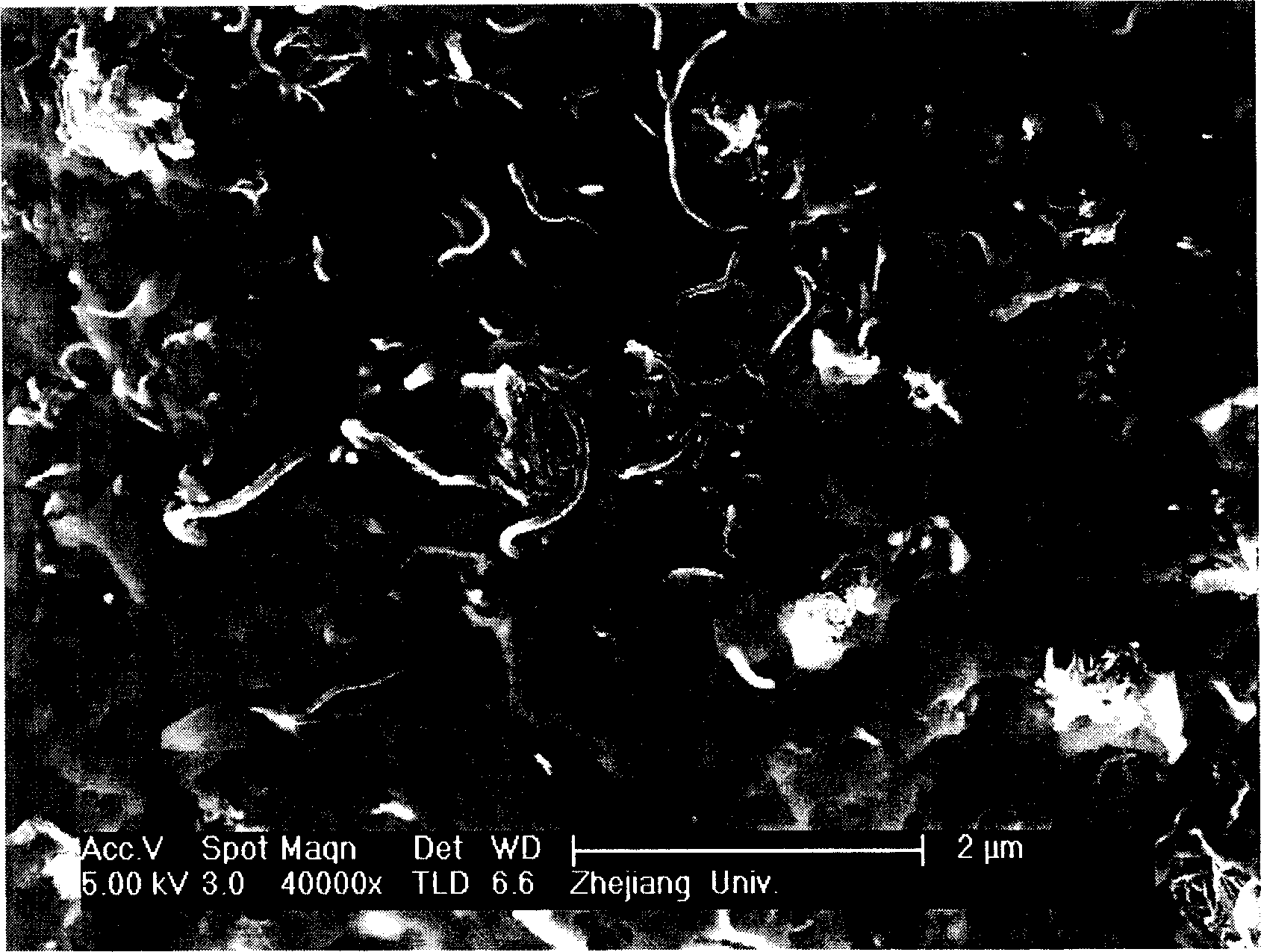
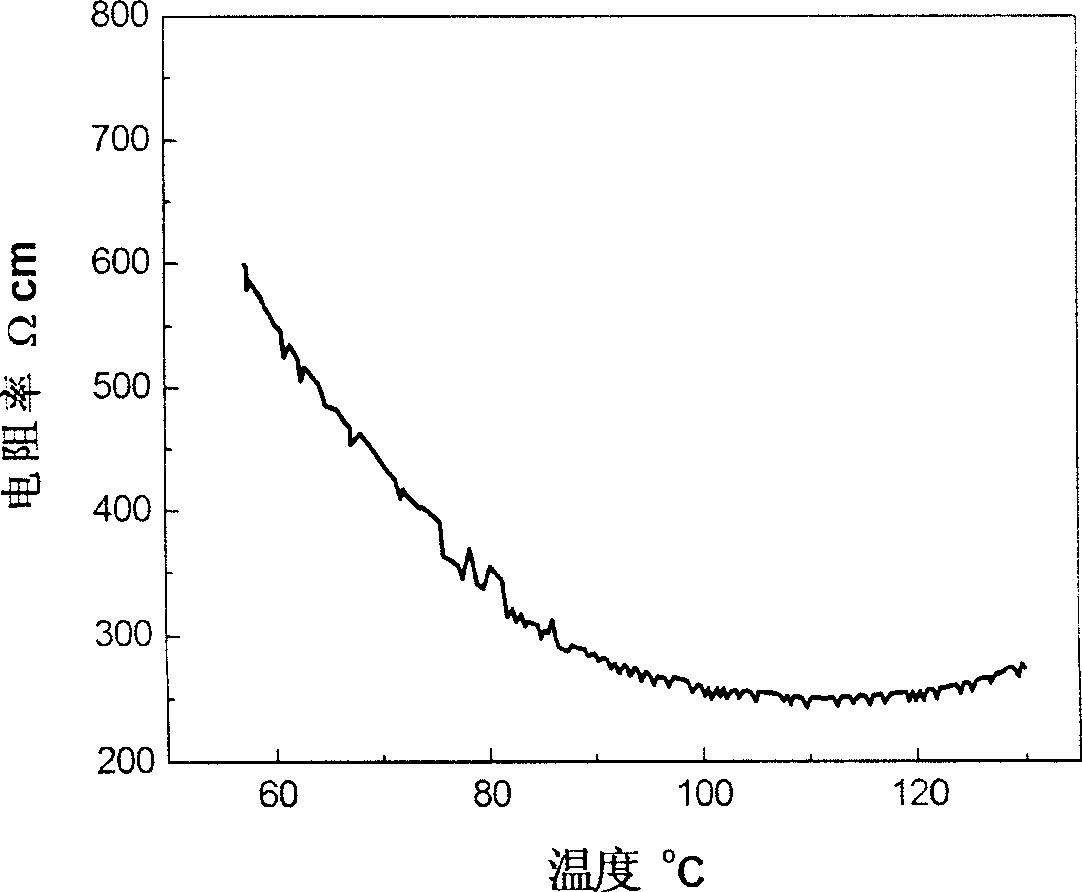
[0016] 6 grams of multi-walled carbon nanotube powder and 94 grams of high-density polyethylene (molecular weight of about 80,000) particles were evenly mixed, and put into a blender for blending at 155° C. for 10 minutes. Take out the homogeneously mixed material and put it into a copper mold, preheat at 160°C for 5 minutes, and then press at 10MPa for 15 minutes. The obtained bulk composite material. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) results of the composite material are as follows: figure 1 shown. figure 2 is the logarithm of resistivity of the composite material as a function of temperature. Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the logarithm of the resistivity of the composite material changes linearly with the temperature below 135°C (the melting point of the polymer matrix material), and this feature of the material can be used in occasions that require temperature measurement. , the resistivity of the material decreases, and the required energy decreases, s...
Embodiment 2
[0018] 8 grams of multi-walled carbon nanotube powder and 92 grams of high-density polyethylene (molecular weight of about 80,000) particles were evenly mixed, and put into a blender for blending at 160° C. for 15 minutes. The homogeneously mixed material was taken out and put into a copper mold, preheated at 170° C. for 10 minutes, and then pressed at 20 MPa for 10 minutes to obtain a block composite material.
Embodiment 3
[0020] 9 grams of carbon nanotube powder and 91 grams of high-density polyethylene (molecular weight of about 80,000) particles were evenly mixed, and then placed in a blender for blending at 165° C. for 10 minutes. The homogeneously mixed material was taken out and put into a copper mold, preheated at 180° C. for 5 minutes, and then pressed at 30 MPa for 5 minutes to obtain a block composite material.
[0021] Tests have shown that the composite materials obtained in Examples 2 and 3 also have a relationship in which the logarithm of resistivity varies substantially linearly with temperature.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com