Recombinant organophosphate degrading enzyme gene and its expression vector and prepn process
An expression vector and organophosphorus technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of low expression efficiency, and achieve the effects of high enzymatic activity, broad degradation spectrum, and excellent enzymatic properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] [Example 1] Synthesis and cloning of recombinant organophosphate degrading enzyme gene
[0056] 1. According to the codon selection bias of Pichia pastoris, without changing the original organophosphate degrading enzyme gene [see: Wu Ningfeng, Deng Minjie, et al: Cloning and expression ofophc2, a new organophosphorus hydrolase gene.Chinese for the gene sequence Science Bulletin, 2004, 49 (12): 1245-1249] on the premise of the encoded amino acid sequence, the codons of the mature protein coding sequence of the organophosphate degrading enzyme gene were optimized.
[0057] Compared with the original gene, the modified organophosphate degrading enzyme gene has changed 154 bases, involving 135 amino acids, and the G+C content has changed from 62.89% to 50.27%, which is suitable for expression in Pichia pastoris.
[0058] Divide the modified whole gene sequence into three segments A, B, and C, and then further divide the large segment into small segments of about 50bp in siz...
Embodiment 2
[0062] [Example 2] Construction of yeast recombinant plasmid
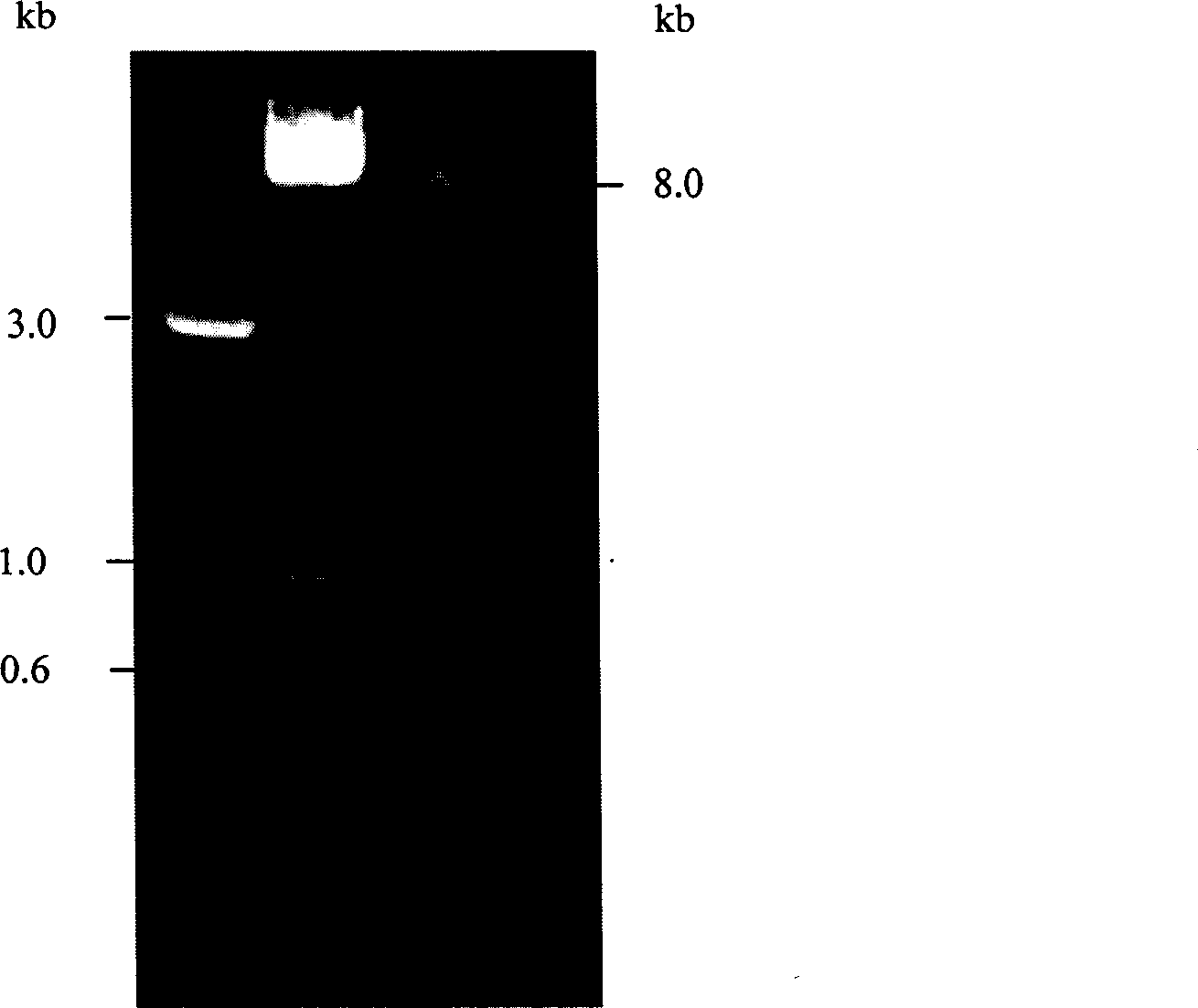
[0063] The correctly detected recombinant plasmid pBS-ophc2-m and plasmid pPIC9 were treated with SnaBI / NotI for double enzyme digestion, and after electrophoresis recovery, they were washed with T 4 DNA ligase (Promega company) ligation. In this way, the gene of interest is inserted between the SnaBI and NotI sites on pPIC9 by using the restriction site to form the recombinant pPIC9-ophc2-m. For the identification of the recombinant, see figure 1 . Thus, the target gene was cloned downstream of the AOX1 promoter, and formed a correct reading frame with the signal peptide coding sequence.
Embodiment 3
[0064] [Example 3] Transformation, detection and screening of highly expressed organophosphate degrading enzyme engineering bacteria
[0065] 1. Transformation of recipient yeast: Extract a large amount of the yeast recombinant expression plasmid pPIC9-ophc2-m prepared in Example 2, take 10 μg and use a slightly excessive amount of BglII for linearization treatment, electrophoresis to detect whether the enzyme digestion is complete, and the linearized plasmid The DNA was extracted once with phenol-chloroform and chloroform respectively, precipitated with ethanol, centrifuged, discarded the supernatant, washed twice with 70% ethanol, and dissolved in sterile water. Then, mix 1-5 μg of linear DNA with 80 μL of yeast GS115 competent cells, pour it into a pre-cooled sterile electric shock cup (0.2 cm, BioRad), tap the electric shock cup to make the mixture fall into the bottom of the electric shock cup, (BioRad) set the voltage at 2.5 kV, the capacitance at 25 μF, and the resistan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com