Artificial joint member made of polymeric material
A technology of polymer materials and artificial joints, applied in the field of artificial joint parts made of polymer materials, can solve the problems of lack of elasticity, damage, and load imposed on bones.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0042] Example I: About wettability
[0043] As an index of the wettability of the artificial joint component, the wettability of the liquid is first evaluated.
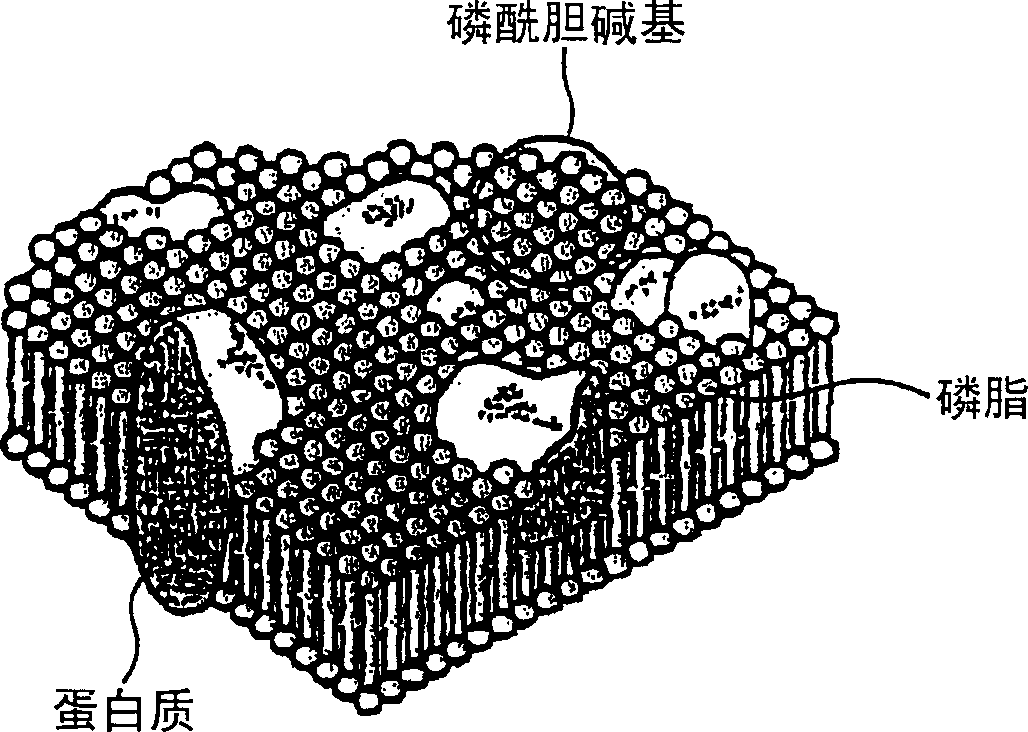
[0044] A polymer layer having phosphorylcholine groups was formed on the surface (only one side) of an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene square bar (cross section: 20 mm×20 mm, length: 50 mm) with a molecular weight of 3 million to 5 million by the following method.
[0045] First, the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene square bar was immersed in an acetone solution containing benzophenone (1.0 g / dL) for 30 seconds, and then immediately taken out to remove the solvent at room temperature.
[0046] After sufficiently degassing an aqueous solution containing 0.5 mol / L of MPC (2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine), the square bar that sufficiently adsorbs benzophenone is immersed in the aqueous solution, and then , The bar is irradiated with ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 300-400nm at a liquid tempe...
Embodiment II
[0051] Example II: Regarding the coefficient of friction
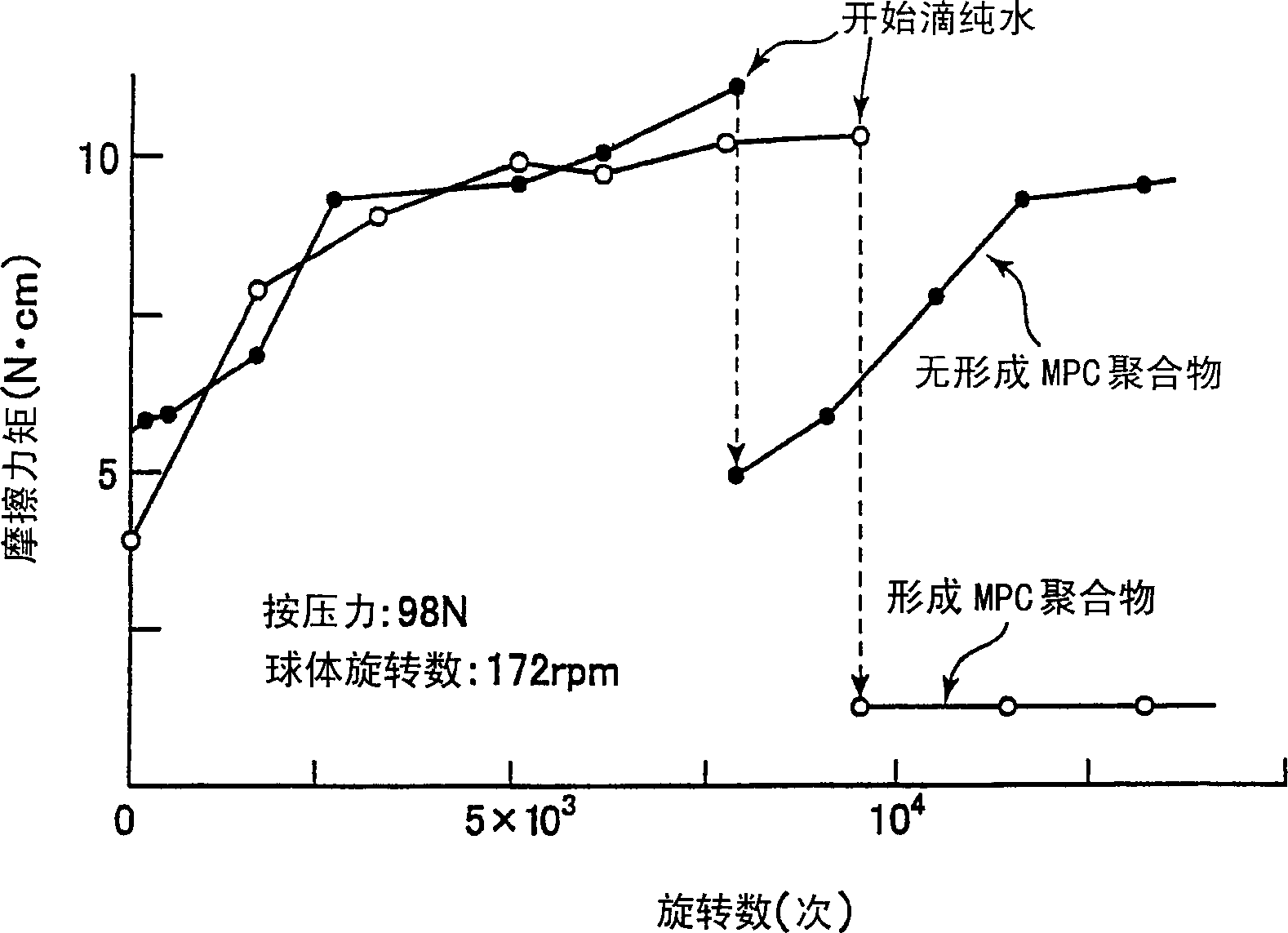
[0052] Next, the lubricity of artificial joint components is evaluated by the coefficient of friction.
[0053] On the test piece obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, the pure water used as a lubricating fluid was pressed against the end surface of the metal round bar with a diameter of 5 mm as shown in Table 2. The vertical pressure applied to the contact surface is 1N / cm 2 Then, at a speed of 100mm / min, the friction coefficient when only the round bar slides on the surface of the square bar is obtained. The results are also recorded in Table 2.
[0054] Type of metal
[0055] It can be seen from Table 2 that when the MPC polymer is formed, the friction coefficient is small and the lubricity is significantly improved. This is because the MPC polymer with a few molecular layers formed on the surface increases the hydrophilicity, thereby forming a molecular layer with a free water content of up to about 90...
Embodiment III
[0056] Example III: Rotating and shaking abrasion test (I)
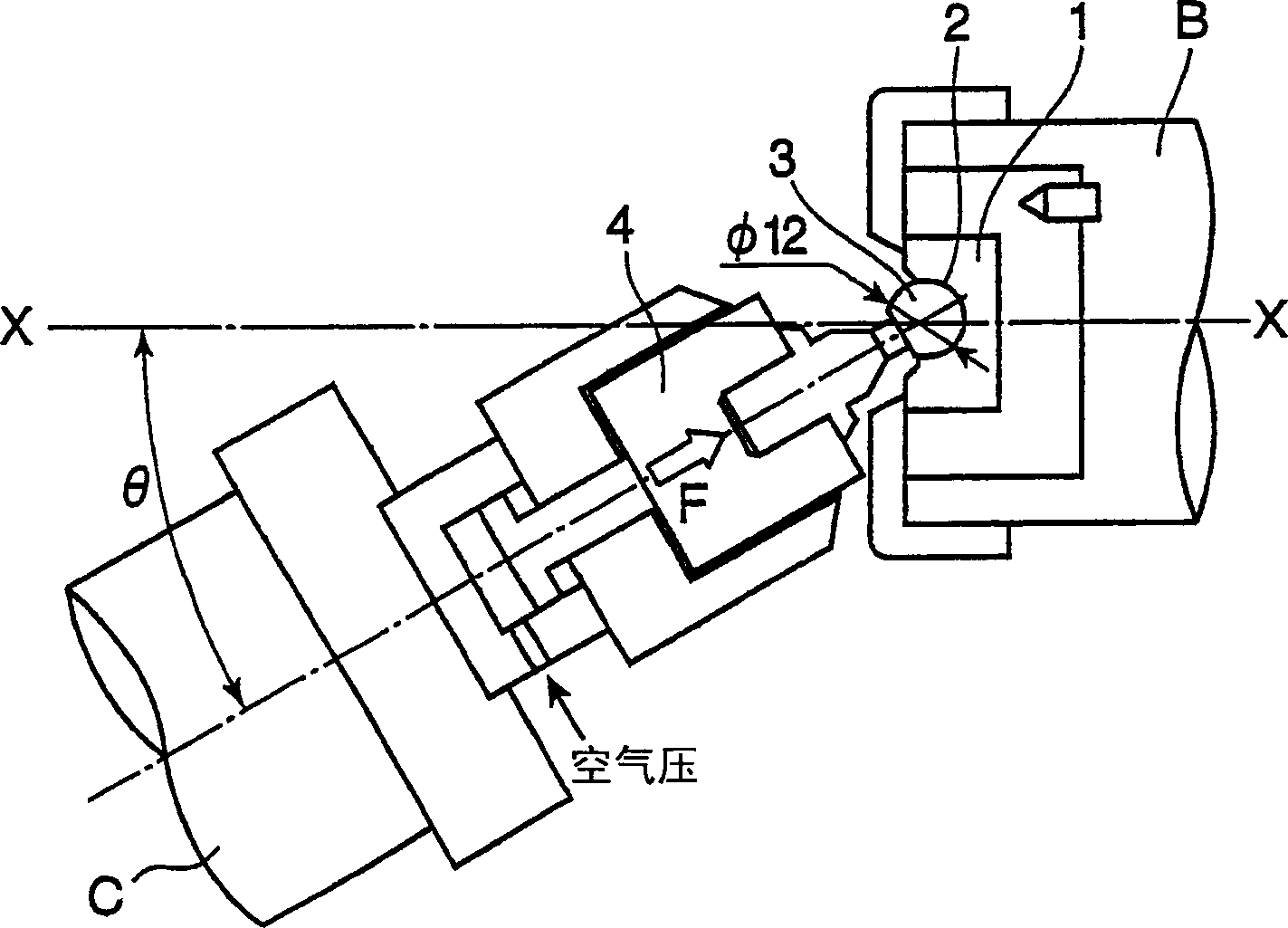
[0057] As a model of the artificial joint, an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene cup was used for the acetabulum, and a stainless steel sphere was used for the bone, and a rotating and shaking abrasion test was performed.
[0058] figure 2 It is a diagram showing the device used in the rotating and shaking wear test. A cup made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (molecular weight 3 to 5 million) 1 having a hemispherical recess 2 with a diameter of 12.10 mm is mounted on the spindle B that freely rotates along the spindle XX. On the one hand, a stainless steel (SUS316) steel ball 3 with a diameter of 12.00mm is installed on the jig, and the steel ball 3 is pressed against the concave surface 2 of the inner wall of the cup 1 by air pressure with a force F. Then, in this state, the steel ball The support shaft of 3 rotates in a state inclined by an arbitrary angle θ with respect to the main shaft XX. In add...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com