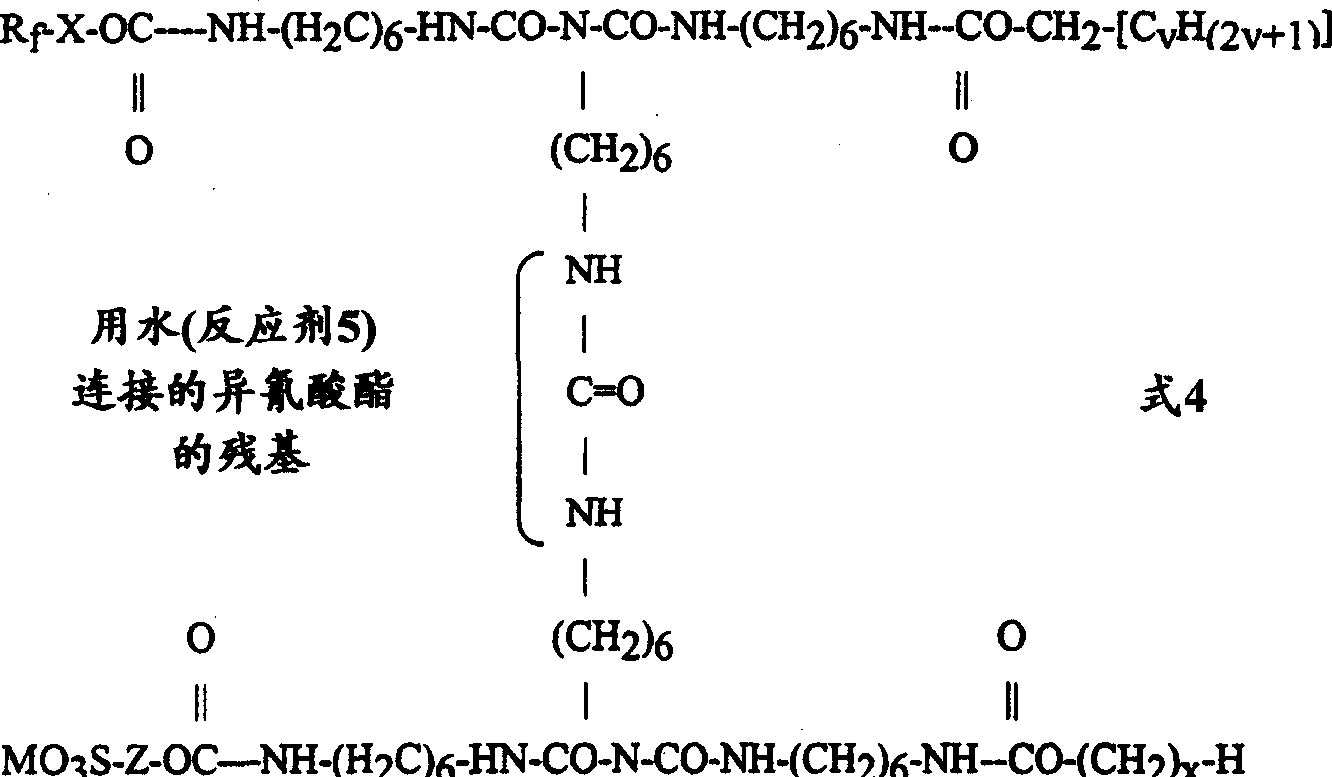
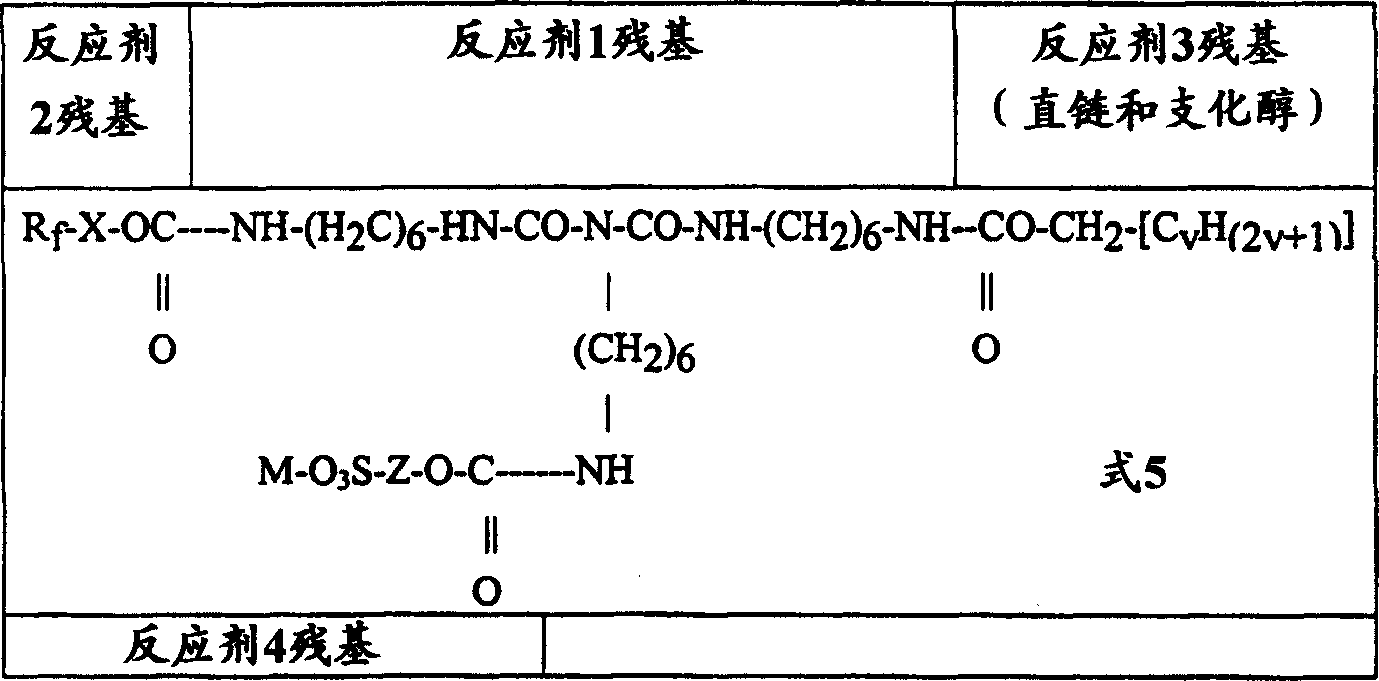
Fluorochemical water and oil repellents
A polymer, fluorocarbon alcohol technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, fabrics, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve problems such as lack of oil repellency and stain resistance of leather
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
test approach 1
[0057] Oil and water repellency ratings give a measure of the theoretical ability of a surface treatment to prevent water and oil from wetting a substrate surface. Typically, Test Methods 1 and 2 are used to test treated Type A substrate samples. These tests are essentially very similar to Test Methods 3 and 4 for Class B substrate samples, with minor changes to accommodate different sample characteristics. Because the surface properties of substrates vary widely within classes, the choice of test method was determined by applying a drop of water to an untreated substrate surface and observing the drop for 30 seconds. If the droplets are absorbed (fibrous substrates, porous surfaces such as biscuit ceramics), use Test Methods 3 and 4 to test the treated substrate. Penetration or wetting of the test surface indicates failure of the test liquid, otherwise the test liquid passes the test. If water droplets are not absorbed in this screening test, as occurs in leather, non-porou...
test approach 2
[0063] * Compositions are calculated by volume at 21°C. Test Method 2 Water Drop Rating Test for Class A Substrates
[0064] A standard test drop is placed on the substrate surface and the wetting and contact angle are observed. The composition of the aqueous test liquid is shown in Table 5 below. The water repellency rating is the highest numbered test fluid that does not wet the substrate surface using the evaluation method above.
[0065] Starting with the lowest numbered test liquid, 3 small drops were placed in several places on the surface of the substrate. Observe the droplet from an angle of approximately 45 degrees for 30 seconds. If the water does not wet the substrate around the edge of the drop and the drop maintains the same contact angle, place a drop of the next highest numbered test liquid on the adjacent site on the substrate and observe again for 30 seconds.
[0066] Continue this procedure until a test liquid shows significant wetting of the surface und...
test approach 4
[0069] The oil repellency rating of the substrate is the highest numbered test liquid for which two out of three drops remained spherical to hemispherical and did not wick within 30 seconds. Test Method 4 Water Repellency of Type B Substrates
[0070] The water repellency test measures the ability of a treated substrate to resist wetting by an aqueous liquid. Droplets of water-alcohol mixtures of different surface tensions were placed on the substrate and the degree of surface wetting was determined visually. This test provides a rough index of water stain resistance. The higher the water repellency rating, the better the finished substrate's resistance to contamination by water-based substances. The composition of the standard test liquid is as shown in Table 5 above. Material
[0071] The following materials were used in the examples below:
[0072] 18-CROWN-6 is 1,4,7,10,13,16-hexaoxacyclooctadecane available from Aldrich, Milwaukee, WI.
[0073] DESMODUR N-100 and DE...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com