Solar radiation protection composition
A compound, polyphenolic compound technology, used in cosmetics, skin care preparations, cosmetic preparations, etc., to reduce skin cancer and facilitate separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1 Identification of sun-shielding compounds
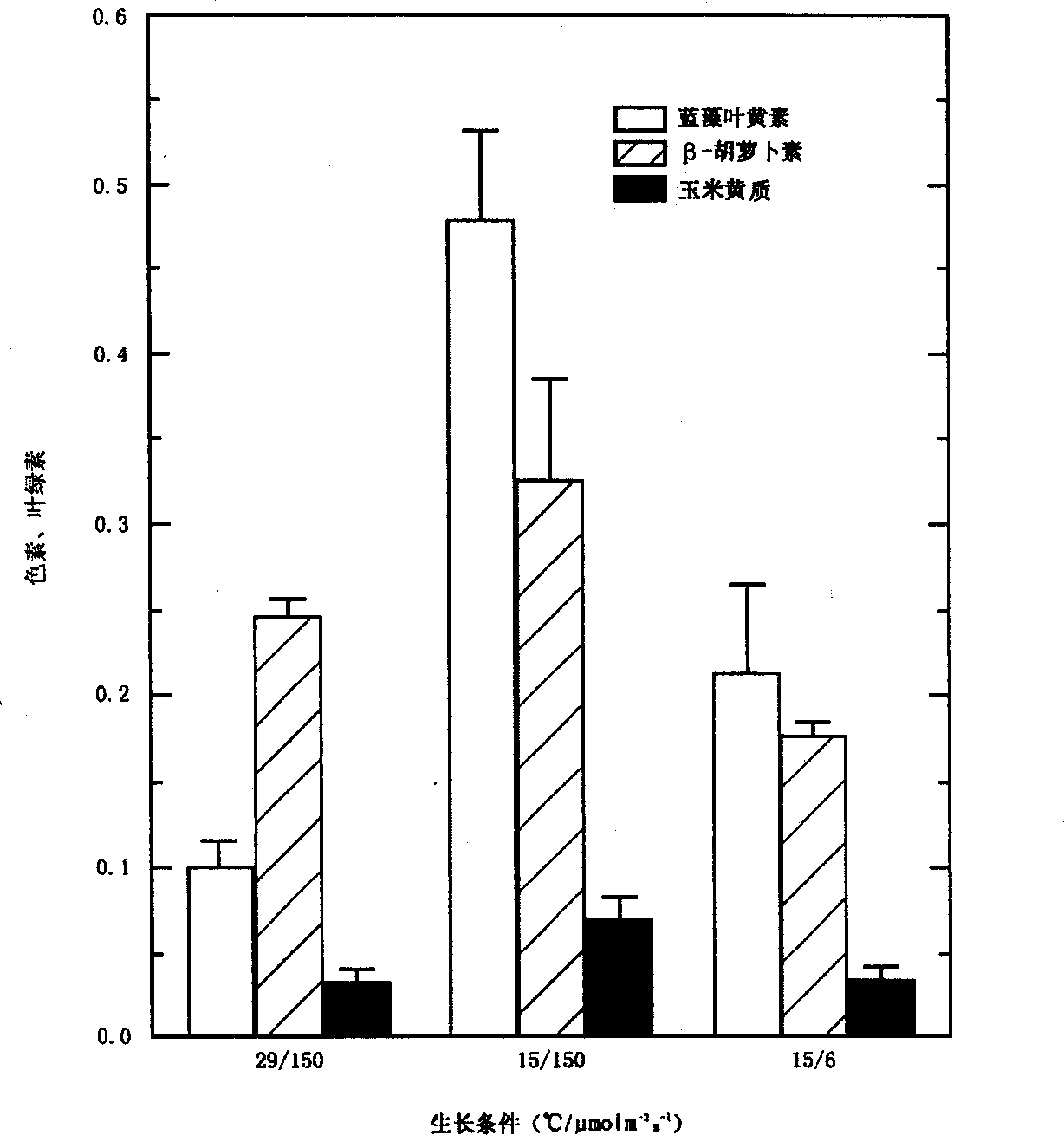
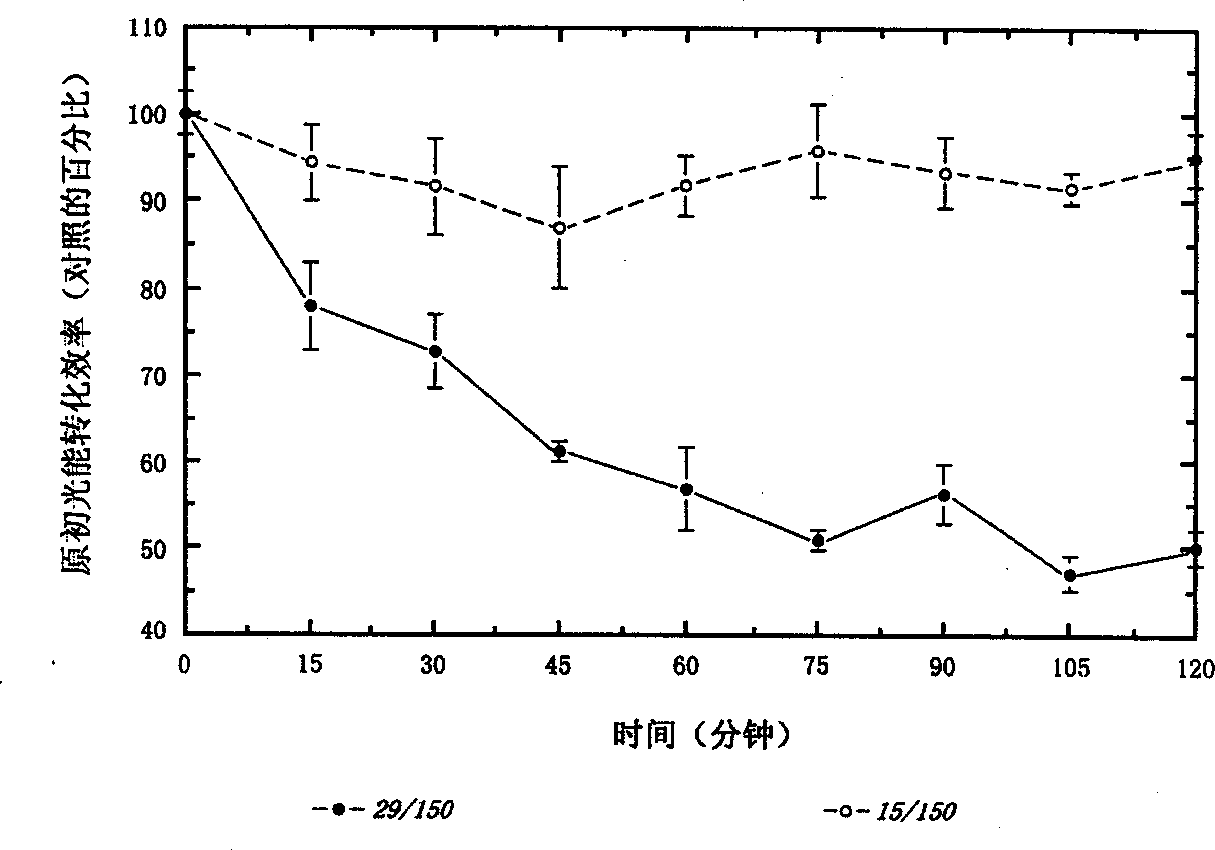
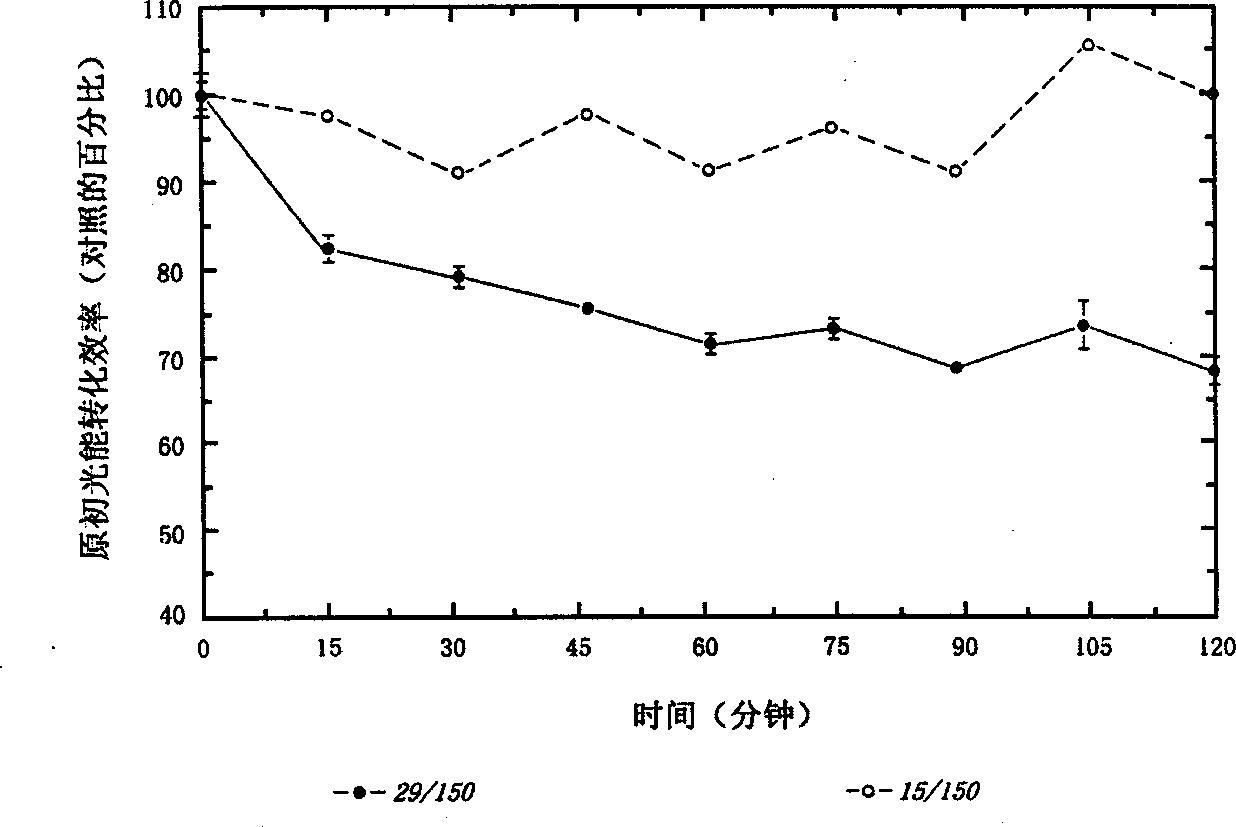
[0070] We have pointed out that when cyanobacteria and Plectonema boryanum are exposed to too much light radiation (and thus the photosynthetic system is exposed to too much light radiation), the culture will increase the production of the following three important sun-shielding factors: carotenoids (cyanobacteria lutein) , Bifidobacterium and Bacterosporine amino acids. When these cyanobacteria are exposed to excessive radiation, ( figure 1 .15 / 150), and the control group ( figure 1 .29 / 150), the body produces 5 times or more cyanobacteria lutein. This response is specific to cyanobacteria lutein, because the other major carotenoids, β-carotene and zeaxanthin show only minimal increases. In addition, when these cultures are reduced from radiation ( figure 1 .15 / 6), cyanobacteria lutein was reduced to a level equivalent to that of the control group ( figure 1 , Compare 15 / 6 and 29 / 150). In addit...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2 Modification of Cyanobacteria Sunshine Shielding Factors and Related Sunshine Shielding Factors
[0081] Compounds similar to carotenoids, polyphenol compounds and mycosporine amino acids as well as light-absorbing amino acids such as tyrosine (Tyr) and tryptophan (Trp) described in the present invention can be applied to the composition. The derivative can be prepared by the following methods, steps, or other steps. For example, the carbonyl groups of bifidin and mycosporin can be reduced or reductive amination can be achieved by administration of alcohol and amine compounds. These alcohols and amine-based compounds can optionally be further derivatized by reaction. For example, acid halides, acyl acyl, formate and isocyanate can provide esters, amides, ureas or the like. Amino compounds can also be reductively alkylated from subunit amine groups with aldehydes and ketones. The derivatization reactions of these alcohols and amines are qu...
Embodiment 4
[0085] Example 4 Preparation of Sunshine Shielding Components
[0086] In the past two decades, a large number of effective methods for formulating solar radiation protection products have emerged (Flick, 1984, Cosmetic and Toiletry Formulations, pp513, Noyes Pub., New Jersey; Casparro et al., 1998, Photochem.Photobiol.68 : 243). Sunshine shielding products can contain a wide range of ingredients. These ingredients do not absorb solar radiation, but they can help control the characteristics of the product. These characteristics include film hardness, transparency, anti-friction, water resistance, and uniformity. The sun-shielding factor of the present invention, carotenoids, such as cyanobacteria lutein, polyphenolic compounds such as bifidophytes and mycosporine amino acids or derivatives of these compounds, are formulated together with known compounds to obtain the best Performance of sun shielding function (Sun Care Products Formulary, 1998, Cosmetics...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com