Transparent conductive film and composition for forming same
A conductive film, transparent technology, used in conductive materials dispersed in non-conductive inorganic materials, conductive coatings, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve problems such as inappropriate use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
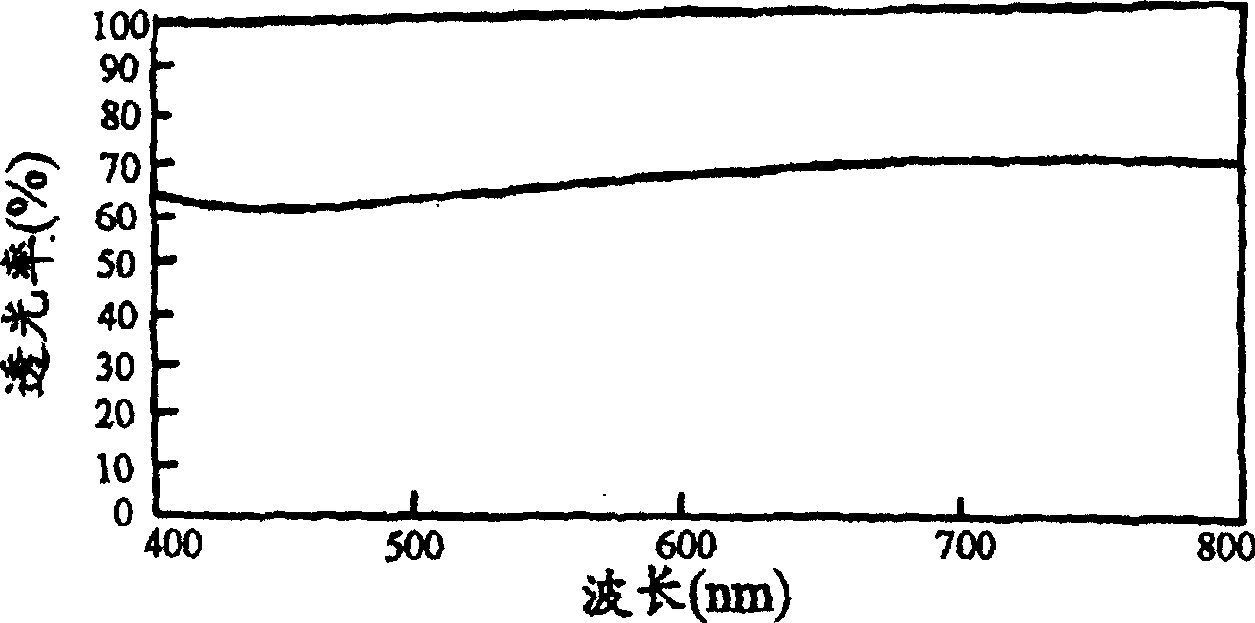
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0085] The preparation method of transparent conductive film of the present invention
[0086] There is no particular limitation on the preparation method of the transparent conductive film of the double-layer structure of the present invention, for example, the method described below can be used.
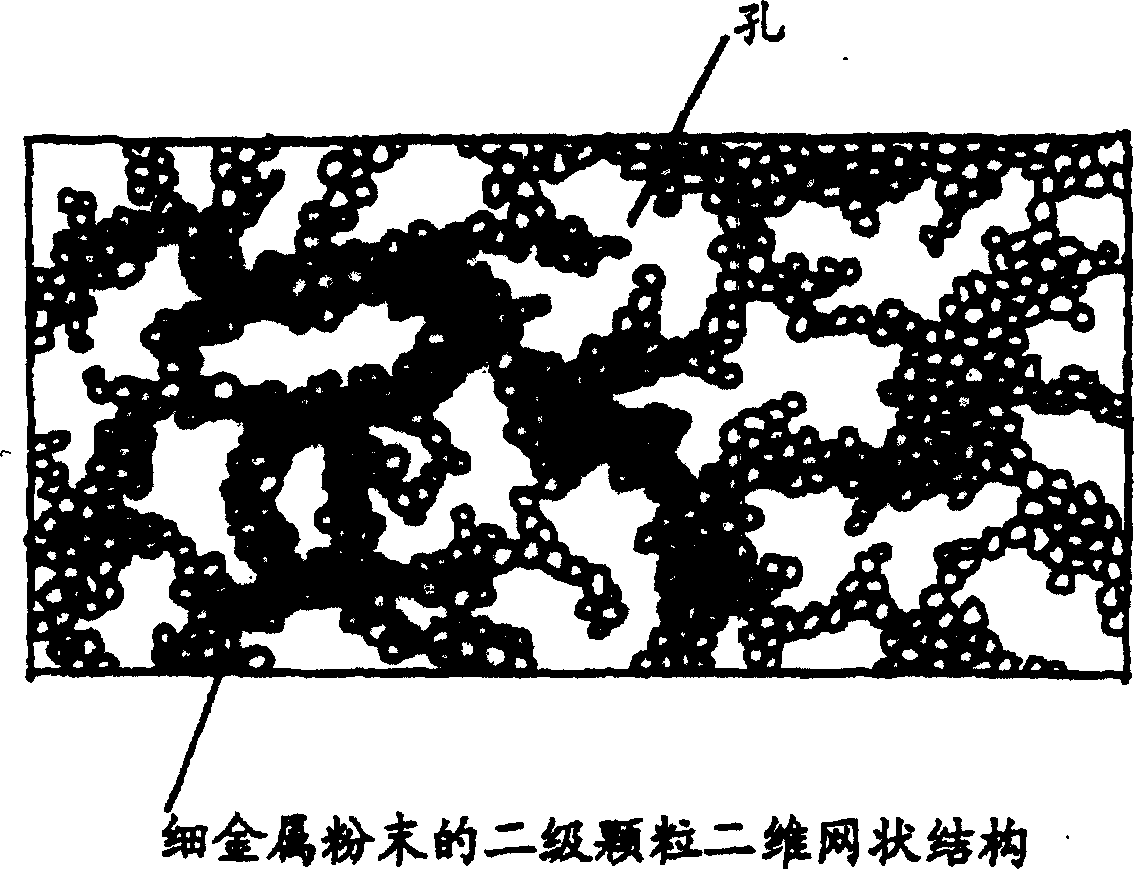
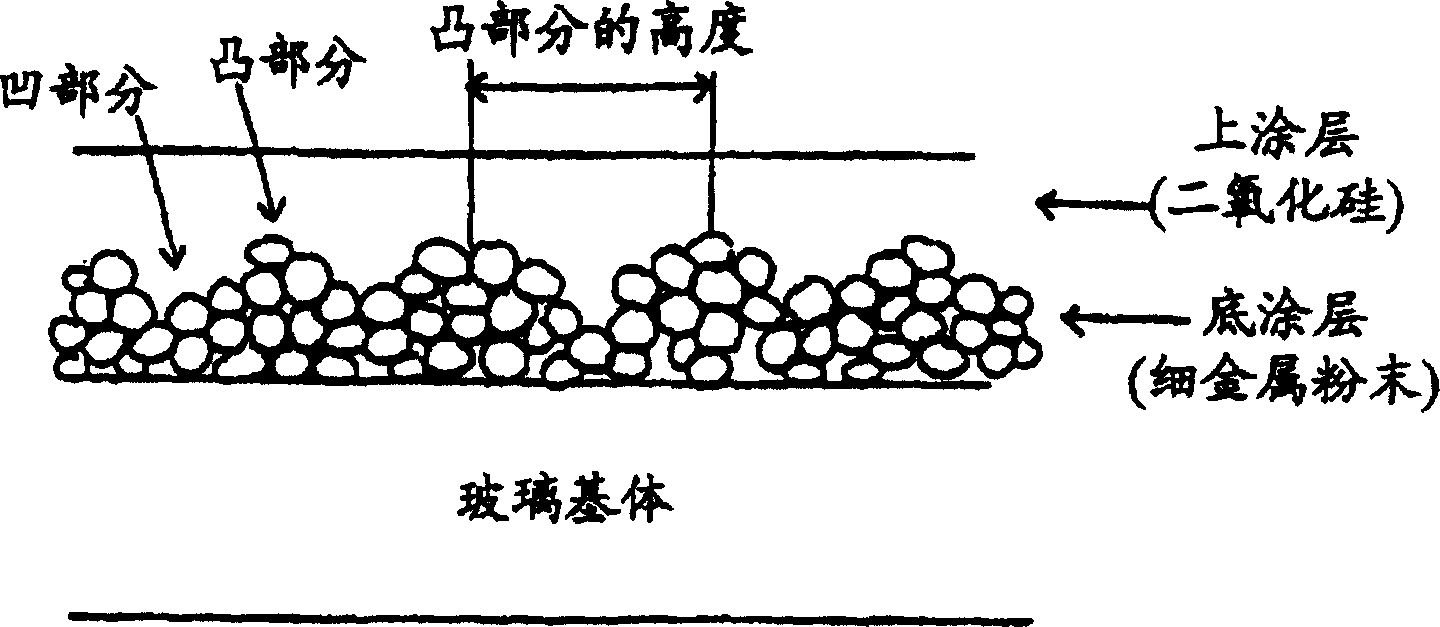
[0087] First, a coating material containing fine metal powder and other desired powders (ATO, ITO or black powder) (film-forming composition) for forming an underlayer is coated on a transparent substrate to form a film containing fine metal powder. Coating materials are prepared by dispersing fine metal powders and other optional powders in suitable solvents. Dispersion can be accomplished by conventional equipment used in the preparation of coating materials.
[0088] The coating material forming the base layer may or may not contain a binder consisting of an alkoxysilane which is at least partially pre-hydrolyzed, which after baking can form a binder with a silica matrix. In g...
Embodiment 1
[0208] Example 1 relates to a bilayer film containing black powder prepared using a binder-free coating material forming an undercoat layer.
[0209] Coating materials that form the base coat
[0210] Preparation of silicone-free basecoat-forming coating material: Add fine metal powder and black powder, if desired, to a solvent mixture of isopropanol / 2-isopropoxyethanol in a weight ratio of 80 / 20 , and titanium compound, the types and ratios of the black powder and the titanium compound are listed in Table 1, and the resulting mixture was mixed in a paint mixer with zirconia pellets (0.3 mm in diameter) to disperse the two powders in the solvent . Both the fine metal powder and the black powder have an average primary particle size of up to 0.1 micron in the coating material. The total content of the two powders in the coating material is 0.7-3.2%, and the viscosity of the coating material is 1.0-1.6 cps.
[0211] The symbols for titanium compounds used in Table 1 have the ...
Embodiment 2
[0234] Example 2 relates to the preparation of a bilayer film using a binder-containing undercoat-forming coating material, wherein the undercoat layer contains black powder.
[0235] Coating materials that form the base coat
[0236] The details of this embodiment are the same as those in Example 1, except that tetraethoxysilane (ethyl silicate) is added as a binding agent in an amount of 10 parts by weight relative to 10 parts by weight of fine metal powder and black powder. Parts (converted to silica), and a small amount of hydrochloric acid can be added as a hydrolysis catalyst.
[0237] Coating material forming the top coat
[0238] Same as Example 1
[0239] Film forming method
[0240] The procedure is the same as in Example 1, except that, after the coating material forming the undercoat layer is applied on the substrate by means of a spin coater, the coated substrate is heated at 50° C. for 5 minutes in the open air to Baking of the undercoat layer is completed be...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com