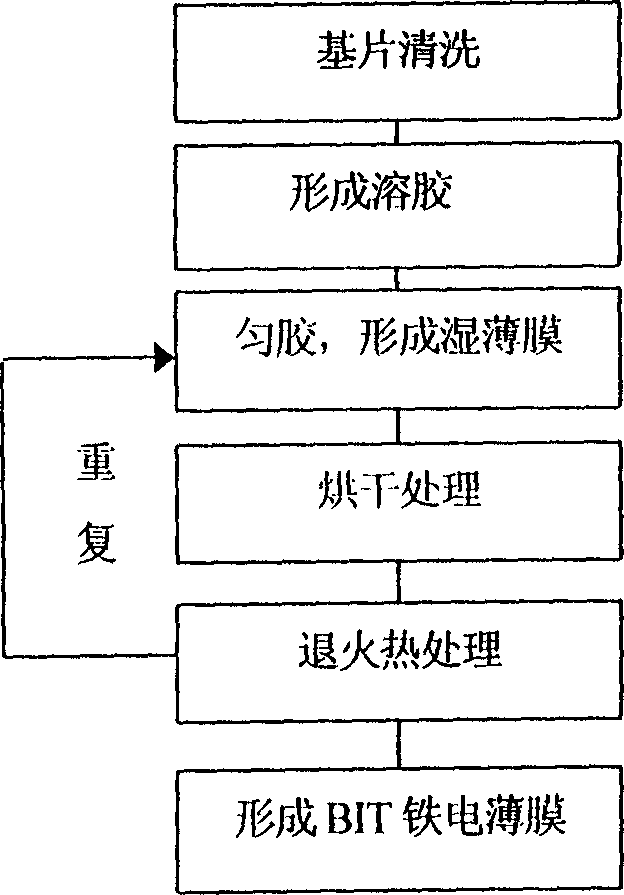
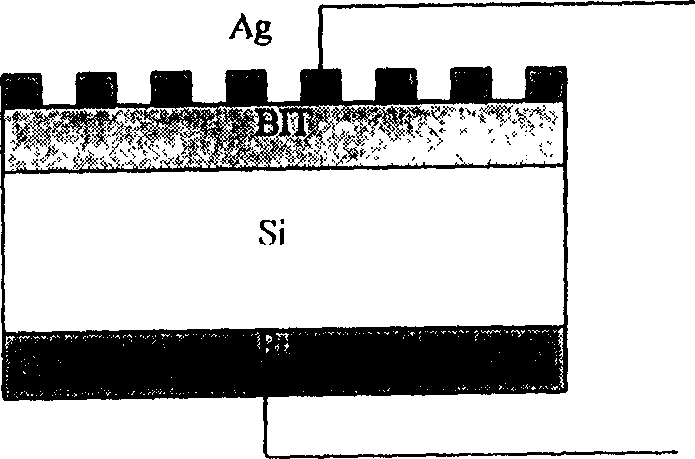
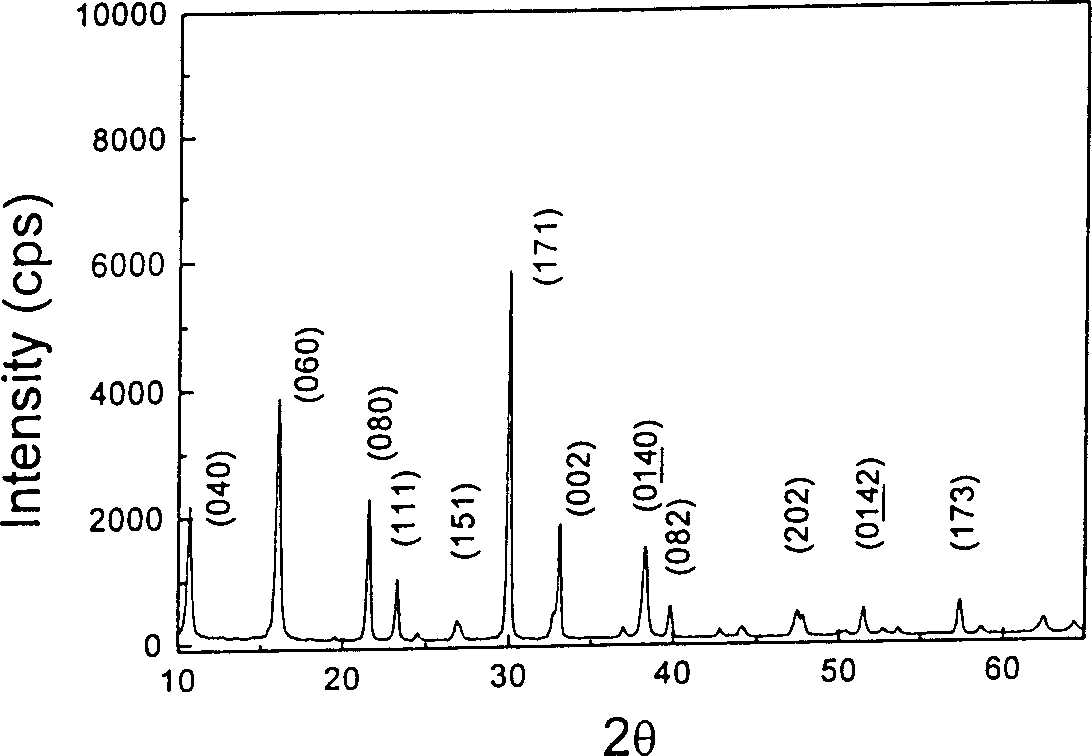
Process for preparing Si base Bi4 Ti3 O12 ferroelectric film
A ferroelectric thin film, thin film technology, applied in the manufacture/assembly of piezoelectric/electrostrictive devices, circuits, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] (1) Select a p-type single crystal Si substrate with a resistivity of 3Ω cm and a (100) crystal orientation as the substrate, and perform surface treatment and cleaning according to the requirements of the semiconductor plane process;
[0042] (2) adopt the following raw materials (its purity is analytically pure 99.9%) to prepare Bi 4 Ti 3 o 12 Sol:
[0043] Butyl titanate (C 16 h 36 o 4 Ti) 5.11ml
[0044] Glacial acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) 6.00ml
[0045] Bismuth nitrate (Bi(NO3) 3 ·5H 2 O) 10.67g
[0046] Acetylacetone (C 16 h 36 o 4 Ti) 38.00ml
[0047] The specific method is:
[0048] (2.1) Put the weighed bismuth nitrate into the beaker;
[0049] (2.2) adding glacial acetic acid;
[0050] (2.3) Stir with a magnetic stirrer to make it react evenly and fully until the bismuth nitrate is completely dissolved;
[0051] (2.4) Butyl titanate (C 16 h 36 o 4 Ti) put into another beaker;
[0052] (2.5) Add an appropriate amount of acetylacetone to make ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2: (the purity of each raw material is required to be more than 99.9% of analytical purity)
[0064] 1) Select a p-type single crystal Si substrate with a resistivity of 5Ω cm and (100) crystal orientation as the substrate, and perform surface treatment and cleaning according to the requirements of the semiconductor planar process;
[0065] (3) adopt the following raw materials (its purity is analytically pure 99.9%) to prepare Bi 4 Ti 3 o 12 Sol:
[0066] Butyl titanate (C 16 h 36 o 4 Ti) 5.11ml
[0067] Glacial acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) 15.00ml
[0068] Bismuth nitrate (Bi(NO3) 3 ·5H 2 O) 10.40g
[0069] Acetylacetone (C 16 h 36 o 4 Ti) 32.00ml
[0070] The specific method is:
[0071] (2.1) Put the weighed bismuth nitrate into the beaker;
[0072] (2.2) adding glacial acetic acid;
[0073] (2.3) Stir with a magnetic stirrer to make it react evenly and fully until the bismuth nitrate is completely dissolved;
[0074] (2.4) Butyl titanate (C...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Embodiment 3: (the purity of each raw material is required to be more than 99.9% of analytical purity)
[0085] 1) Select a p-type single crystal Si substrate with a resistivity of 10Ω cm and (100) crystal orientation as the substrate, and perform surface treatment and cleaning according to the requirements of the semiconductor planar process;
[0086] (4) adopt the following raw materials (its purity is analytically pure 99.9%) to prepare Bi 4 Ti 3 o 12 Sol:
[0087] Butyl titanate (C 16 h 36 o 4 Ti) 5.11ml
[0088] Glacial acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) 30.00ml
[0089] Bismuth nitrate (Bi(NO3) 3 ·5H 2 O) 10.50g
[0090] Acetylacetone (C 16 h 36 o 4 Ti) 12.00ml
[0091] The specific method is:
[0092] (2.1) Put the weighed bismuth nitrate into the beaker;
[0093] (2.2) adding glacial acetic acid;
[0094] (2.3) Stir with a magnetic stirrer to make it react evenly and fully until the bismuth nitrate is completely dissolved;
[0095] (2.4) Butyl titanate (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com