A promoter from Fusarium venetianus and a visual gene knockout screening method
A fusarium and promoter technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of laborious and laborious, low homologous recombination rate, etc., and achieve the effect of improving screening efficiency and efficient screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Construction of a high-efficiency Fusarium venetianus TB01 endogenous promoter regulated GFP gene expression vector
[0045] Through investigation and analysis, referring to the situation of promoters in other species, the endogenous promoters PgpdA, Pgla and Ptef of Fusarium venezia TB01 were studied and explored to screen out the strong endogenous promoters. The specific process is as follows:
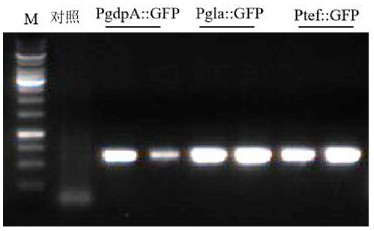
[0046] The sequences of the endogenous promoters PgpdA (FVRRES_09878), Pgla (FVRRES_01380) and Ptef (FVRRES_13282) were amplified from the DNA genome of Fusarium venezia TB01 with primer pairs PgpdA1 / 2, Pgla1 / 2 and Ptef1 / 2, respectively. Pgfp-T1 / 2 amplified the GFP-Ttrpc sequence from the vector pK2-Ptrpc-GFP-Ttrpc. Subsequently, it was connected to the resistance backbone vector pK2-neo by homologous recombinase to obtain the corresponding endogenous promoter-regulated GFP gene expression vector. After transforming it into E. coli DH5α, a single colony was selecte...
Embodiment 2
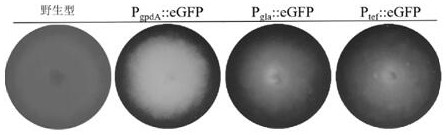
[0053] Example 2 Protoplast transformation of Fusarium venezia TB01 with different promoters regulating GFP gene expression cassette
[0054] 1. Culture medium
[0055] YEPD: yeast powder 3g, peptone 10g, glucose 20g, make up to 1L; buffer for dissolving enzyme: 0.7 M sodium chloride; STC: 0.8 M sorbitol; 50 mM CaCl 2 , 50 mM Tris-HCl (Ph 8.0); SPTC: STC containing 40% PEG6000; regeneration medium: yeast extract 1g, tryptone 1g, sucrose 274g, agarose 10g, constant volume 1L; screening medium: glucose 30g , Yeast powder 6g, agar powder 15g, dilute to 1L.
[0056] 2. Primers
[0057] PpKLB1:GGTGGCAGGATATATTGTGG (SEQ ID NO. 8);
[0058] PpKLB2: TTGGTTGGTCAAGTCCTGGT (SEQ ID NO. 9).
[0059] 3. Fragment Amplification Procedure
[0060] 98℃ 10s, 55℃ 15s, 72℃ 3mins; 35 cycles (primestar, TaKaRa)
[0061] 4. Experimental method
[0062] 1) Amplification of transformed fragments
[0063] The fragment PgpdA::GFP-neo was amplified from pK2-Promoter::GFP-neo by designing the prime...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3 Construction of a visual gene knockout transformant screening vector
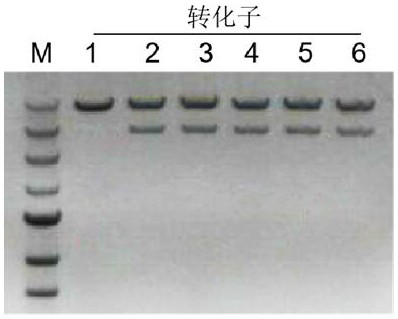
[0078] The left and right arm sequences of the chitin synthase gene knockout region were amplified from the DNA genome of Fusarium venezia TB01 with primer pairs a few left arm 1 / 2 and a few right arm 1 / 2, respectively, and sequenced by seamless cloning Linked to both sides of the resistance gene expression cassette of the vector pK2-neo; then knocked out 1 / 2 of the cassette from the constructed pK2-Chs with primer pairs upstream -neo-Chs downstream Chs amplified in the vector upstream -neo-Chs downstream fragment, and ligated it into the backbone vector pK2-PgpdA::GFP by homologous recombinase (US Everbright) to obtain pK2-PgpdA::GFP-Chs upstream -neo-Chs downstream , after transformation of E. coli DH5α, a single colony was selected for Pme I and Xba I double-enzyme digestion verification, select the correct transformants.
[0079] Table 3 Construction of visual gene knockout tran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com