Special-shaped magnet processing technology
A processing technology and magnet technology, which is applied in the field of special-shaped magnet processing technology, can solve the problems of high temperature, low processing efficiency, and long production time, so as to reduce the sintering time, improve the production and processing effect, and reduce energy consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Each material is composed of the following components by weight percentage: 31% of neodymium, 64.1% of iron, 1.1% of boron, 1.5% of dysprosium, 0.4% of niobium, 0.4% of aluminum, and 1.5% of sintering agent.
[0036] The special-shaped magnet processing technology includes the following steps:
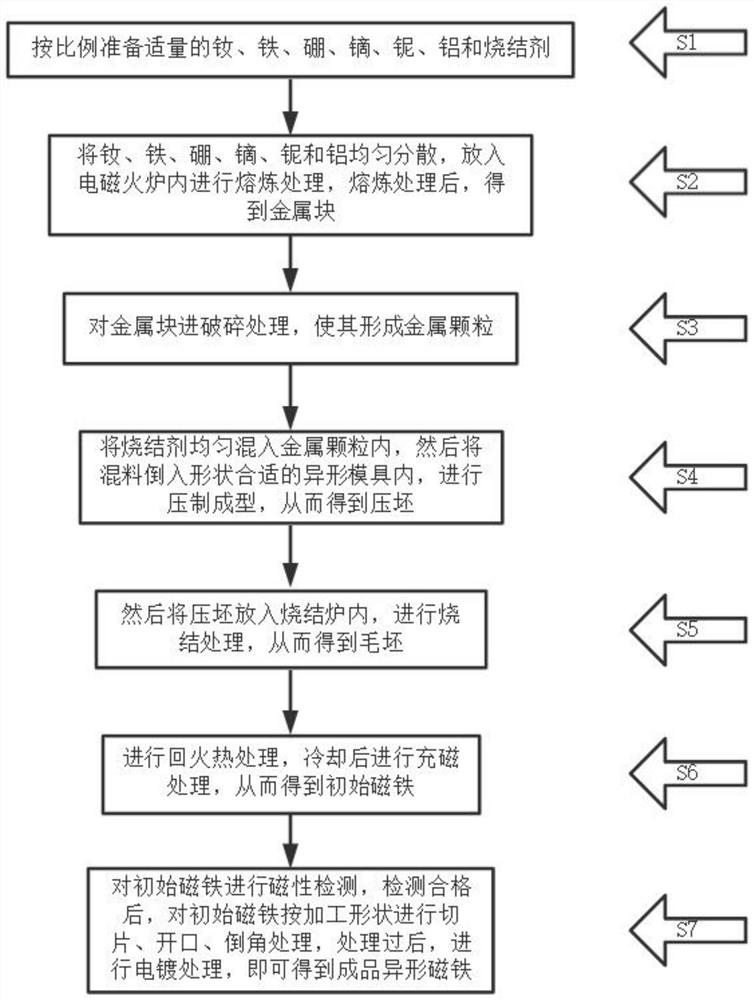
[0037] S1: Prepare appropriate amount of neodymium, iron, boron, dysprosium, niobium, aluminum and sintering agent in proportion;
[0038] S2: Evenly disperse the neodymium, iron, boron, dysprosium, niobium and aluminum prepared in S1, put them into an electromagnetic furnace for melting treatment, the melting temperature is 1620°C, and the melting time is 24 minutes. After the melting treatment, a metal block is obtained ;
[0039] S3: Use a secondary crusher to crush the obtained metal block to form metal particles;
[0040] S4: Evenly mix the sintering agent into the metal particles, then pour the mixture into a special-shaped mold with a suitable shape, and perform compres...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Each material is composed of the following components by weight percentage: 30% of neodymium, 63.8% of iron, 1.2% of boron, 2% of dysprosium, 0.5% of niobium, 0.5% of aluminum, and 2% of sintering agent.
[0046] The special-shaped magnet processing technology includes the following steps:
[0047] S1: Prepare appropriate amount of neodymium, iron, boron, dysprosium, niobium, aluminum and sintering agent in proportion;
[0048] S2: Evenly disperse the neodymium, iron, boron, dysprosium, niobium and aluminum prepared in S1, put them into an electromagnetic furnace for melting treatment, the melting temperature is 1630°C, and the melting time is 24 minutes. After the melting treatment, a metal block is obtained ;
[0049] S3: Use a secondary crusher to crush the obtained metal block to form metal particles;
[0050] S4: Evenly mix the sintering agent into the metal particles, then pour the mixture into a special-shaped mold with a suitable shape, and perform compression...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Each material is composed of the following components by weight percentage: 29% of neodymium, 62.6% of iron, 1.3% of boron, 4% of dysprosium, 0.5% of niobium, 0.3% of aluminum, and 2.3% of sintering agent.
[0056] The special-shaped magnet processing technology includes the following steps:
[0057] S1: Prepare appropriate amount of neodymium, iron, boron, dysprosium, niobium, aluminum and sintering agent in proportion;
[0058] S2: Evenly disperse the neodymium, iron, boron, dysprosium, niobium and aluminum prepared in S1, put them into an electromagnetic furnace for melting treatment, the melting temperature is 1680°C, and the melting time is 22 minutes. After the melting treatment, a metal block is obtained ;
[0059] S3: Use a secondary crusher to crush the obtained metal block to form metal particles;
[0060] S4: Evenly mix the sintering agent into the metal particles, then pour the mixture into a special-shaped mold with a suitable shape, and perform compressi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com