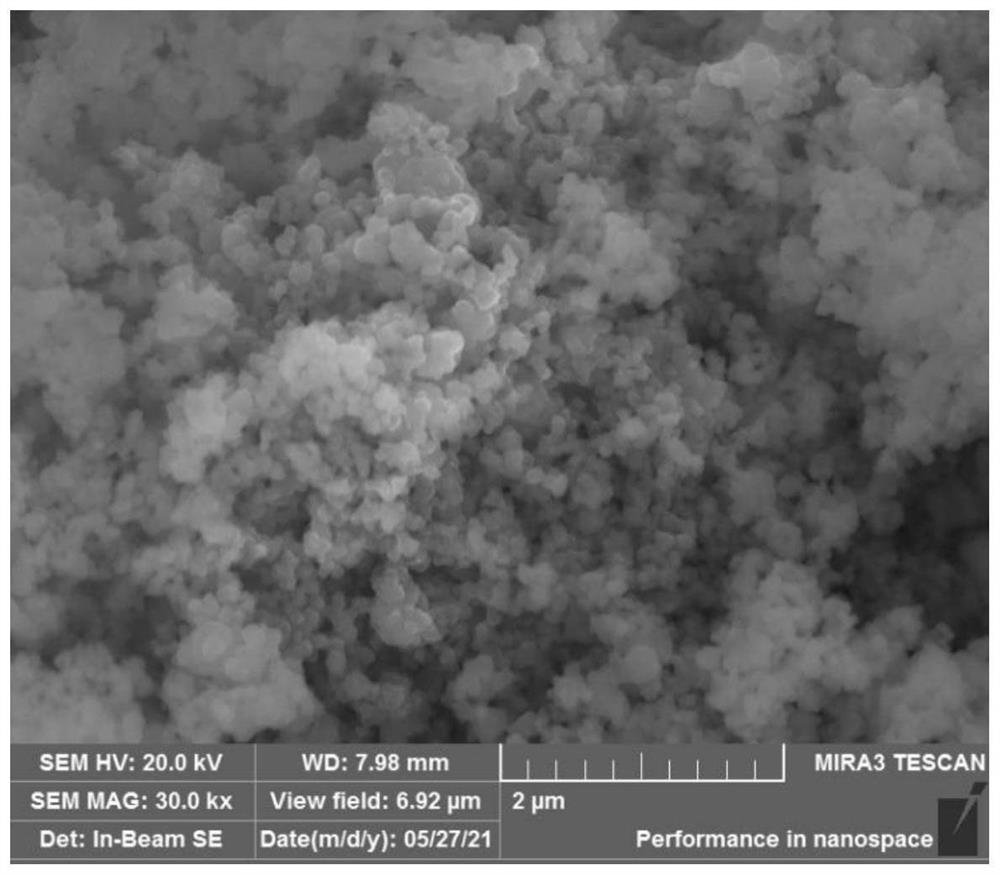
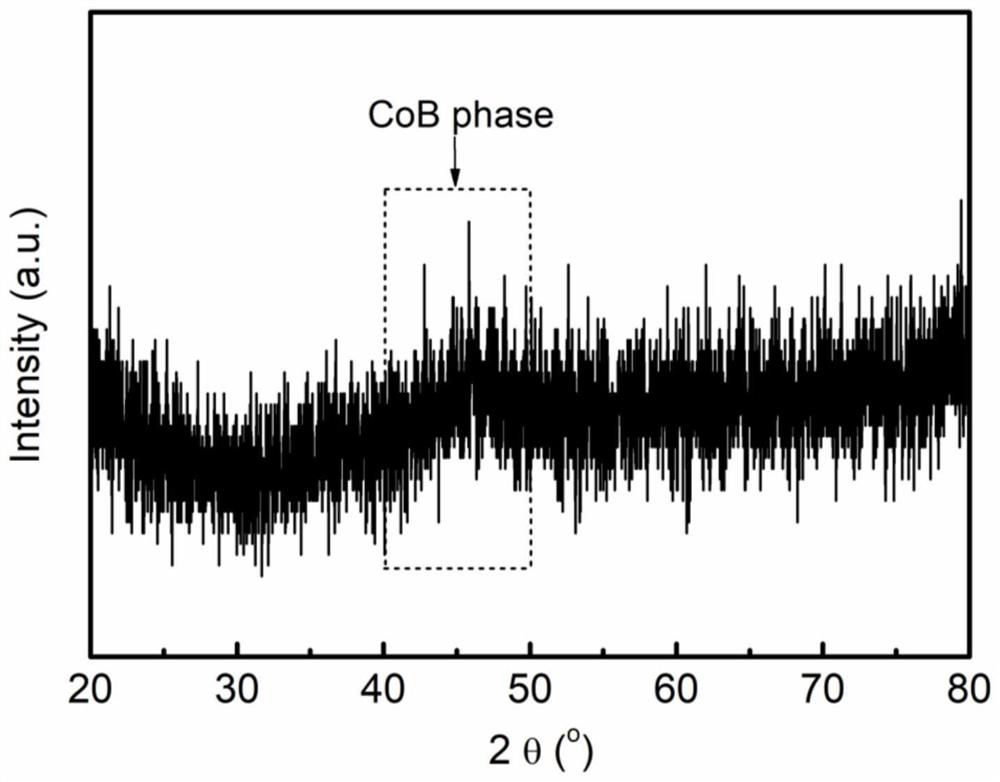
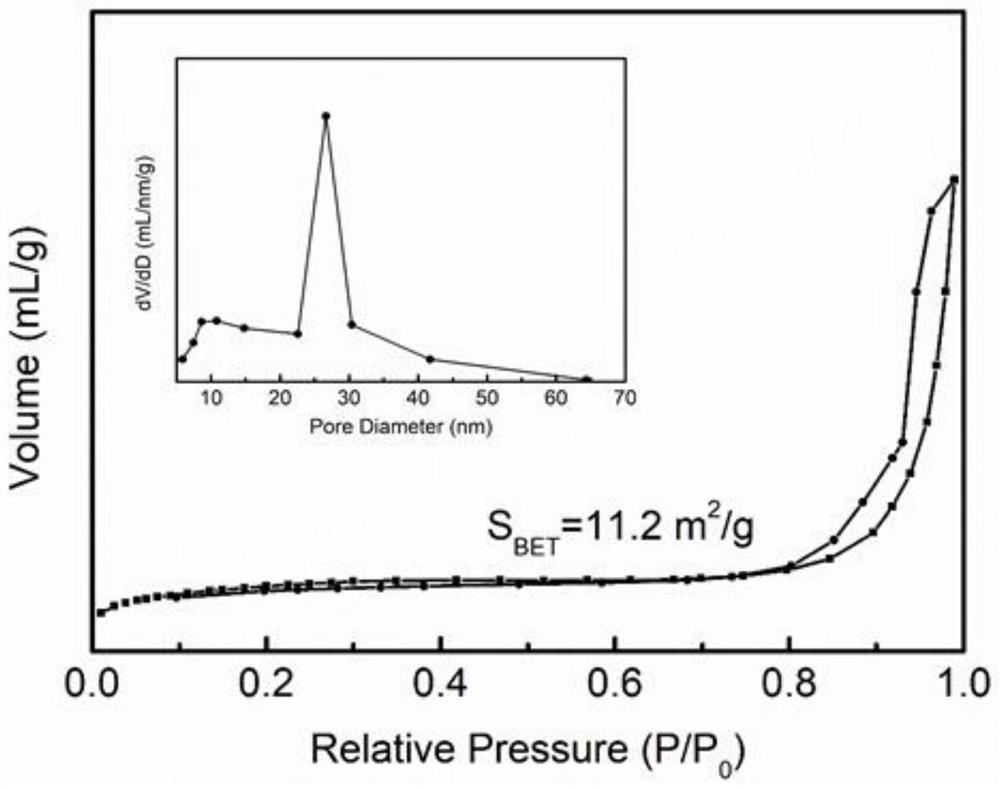
Preparation method of high-activity CoB catalyst
A catalyst and high-activity technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of slow hydrogen production rate in hydrolysis reaction, easy agglomeration of catalyst particles, Unsatisfactory catalyst performance and other problems, to achieve the effect of fast reaction speed, excellent catalytic hydrogen production performance, and complete recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1 A kind of preparation method of highly active CoB catalyst
[0038] This embodiment is a highly active CoB catalyst, which is carried out in sequence according to the following steps:
[0039] A kind of preparation method of highly active CoB catalyst is characterized in that, carries out successively according to following step order:
[0040] (1) Weigh cobalt chloride hexahydrate, place it in a mortar, and mechanically grind it at a speed of 4rad / s for 20min to obtain A1;
[0041] (2) Slowly add urea to A1, the molar ratio of urea to cobalt chloride hexahydrate is 56:1, and fully grind together in a mortar to a particle size of 80-100 mesh, the grinding speed is 4rad / s, to two After they are mixed evenly, B1 is obtained;
[0042] (3) Sodium borohydride is evenly dispersed on the surface of B1 at 1.2g / min, the molar ratio of sodium borohydride to cobalt chloride hexahydrate is 5:1, and it is fully ground while adding, and the grinding speed is 6rad / s, un...
Embodiment 2-4
[0049] The preparation method of the highly active CoB catalyst of embodiment 2-4
[0050] This example is a preparation method of a highly active CoB catalyst. The preparation process and detection process are similar to those of Example 1. The only difference is that the corresponding technical parameters in the preparation process are different, as follows:
[0051]
[0052]
Embodiment 5
[0053] Embodiment 5 comparative example
[0054] In order to explore the influence of different conditions on the preparation of CoB catalysts, the following comparative experiments were carried out in this example, specifically as follows:
[0055] Group A: The preparation process of the CoB catalyst is similar to that of Example 1, except that no urea is added in the process. The XPS analysis of this sample (such as Figure 7 ) shows that the content of metal Co on the surface of the catalyst is only 45.8%, compared with the CoB catalyst prepared in Example 1, the active Co sites that exist are significantly reduced, and correspondingly, the performance of catalytic hydrolysis for hydrogen production is significantly reduced.
[0056] Group B: The preparation process of the CoB catalyst is similar to that of Example 1, except that the molar ratio of urea to cobalt chloride hexahydrate is 39:1.
[0057] Group C: The preparation process of the CoB catalyst is similar to that...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com