A method of producing silicon carbide seed crystals by liquid phase epitaxy
A technology of liquid phase epitaxy and silicon carbide seeds, which is applied in the direction of liquid phase epitaxy layer growth, chemical instruments and methods, single crystal growth, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory transportation effect, reduce carbon solubility, and fill crystal joints, and achieve Avoid polycrystalline nucleation, graphite surface improvement, low production cost effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] This embodiment provides a method for producing silicon carbide seed crystals by liquid phase epitaxy, comprising the following steps:
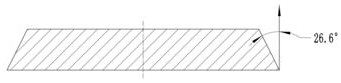
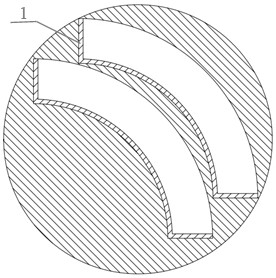
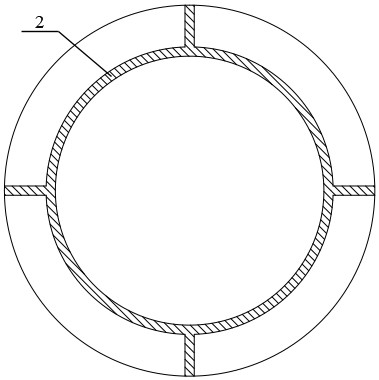
[0080] S1. Take a single crystal silicon carbide crystal with a thickness greater than 15 mm and a single crystal form of 4H, cut it into three sub-crystal plates with a thickness of 5 mm, and grind and polish the carbon and silicon surfaces of each sub-crystal plate to ensure consistency surface type, so that the surface type of the sub-crystal plate is BOW=15μm, Warp=50μm, TTV=25μm; wherein, the diameter of the single crystal region of each sub-crystal plate is not less than 150mm, refer to figure 1 As shown, the epitaxial edge of one of the sub-crystal plates is cut at 26.6° from the C-plane, and the other two sub-crystal plates, see figure 2 Shown are fan ring plates, the edge area 1 of the two fan ring plates is cut at 26.6° along the C plane, and the defect area is removed;
[0081] S2. Splice the sub-crystal plates according t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com