Method for rapidly extracting waste biomass lignin by microwave method and recycling waste biomass lignin
A waste biomass and lignin technology, applied in the fields of environmental protection and resource comprehensive utilization, can solve the problems of limiting depolymerization and transformation, achieve huge economic benefits, efficient wood separation and extraction methods, simple process and effective effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
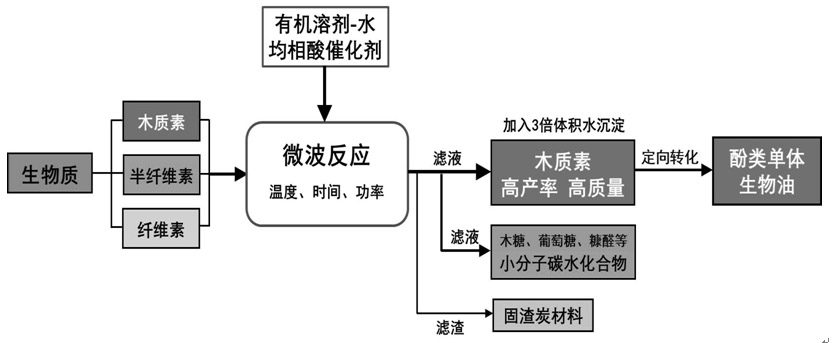
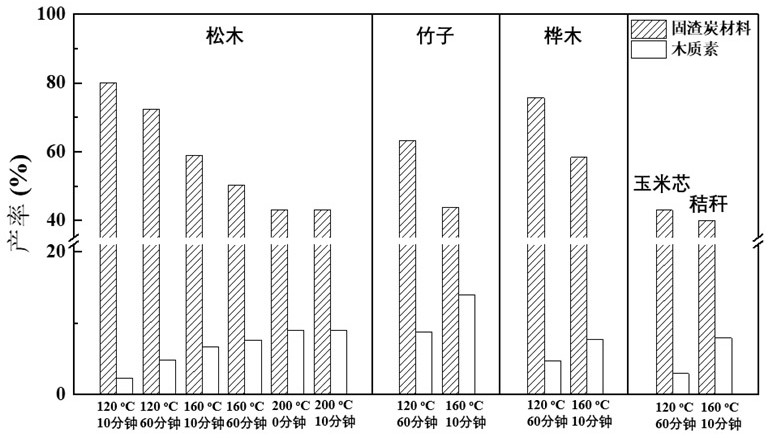
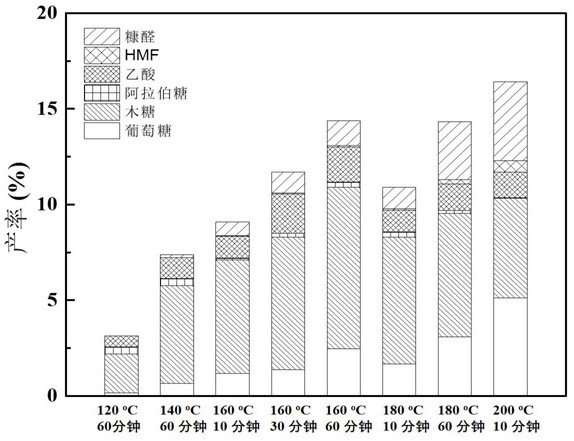
[0028] Put 5g of poplar biomass, 25g of water and 25g of ethanol in a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene microwave reactor, add 0.1% sulfuric acid catalyst, mix to obtain a mixture, and set the microwave heating power to 900W. The mixture was reacted at 160°C for 60 minutes. After the reaction was completed, it was cooled to room temperature, and the reaction solution was filtered. After filtering, 3 times the volume of water was added to the filtrate. The lignin was precipitated, collected by centrifugation, and dried in vacuum at 50°C to obtain lignin. The yield of lignin relative to poplar biomass was 10%. The filtrate contains small molecular carbohydrates, mainly including xylose and furfural, with a total yield of 15% relative to poplar biomass, and a residual solid carbon yield of 48%. The obtained lignin was subjected to microwave-assisted alkali-catalyzed conversion, and the qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenolic monomers was carried out by GC-MS and GC-FID. The...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Put 5g of corncob biomass, 25g of water and 25g of ethanol in a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene microwave reactor, add 0.1% sulfuric acid catalyst, mix to obtain a mixture, and set the microwave heating power to 900W. The mixture was reacted at 120°C for 60 minutes. After the reaction was completed, it was cooled to room temperature, and the reaction solution was filtered. After filtering, 3 times the volume of water was added to the filtrate. The lignin was precipitated, collected by centrifugation, and dried in vacuum at 50°C to obtain lignin. The yield of lignin relative to corn cob biomass was 5%. The filtrate contains small molecular carbohydrates, mainly including xylose, furfural and glucose, with a total yield of 23% relative to the biomass and a 43% yield of residual solid charcoal. The obtained lignin was subjected to microwave-assisted alkali-catalyzed conversion, and the qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenolic monomers was carried out by GC-MS and GC...
Embodiment 3
[0032] 2g of bamboo biomass, 25g of water and 25g of ethanol were placed in a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, and 0.1wt% sulfuric acid catalyst was added. Mix to obtain a mixture, and set the microwave heating power to 1200W. The mixture was reacted at 160°C for 10 minutes. After the reaction was completed, it was cooled to room temperature, and the reaction solution was filtered. After filtering, 3 times the volume of water was added to the filtrate. The lignin was precipitated, collected by centrifugation, and dried in vacuum at 50°C to obtain lignin. The yield of lignin relative to corncob biomass was 13%. The filtrate contains small molecular carbohydrates, mainly including xylose and furfural, with a total yield of 14% relative to the biomass and a 50% yield of the remaining solid residue charcoal. The obtained lignin was subjected to microwave-assisted base-catalyzed conversion, and the qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenolic monomers was carried out by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com