Forming method for electric arc fuse wire additive manufacturing
An additive manufacturing and fuse technology, applied in the field of additive manufacturing, can solve problems such as the relationship and research of magnetic and magnetron-assisted arc fuses that are not involved, and improve the forming morphology and internal structure, and the surface of the weld bead is flat. Smooth, Manufacturing Efficiency Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This embodiment provides a forming method for arc fuse additive manufacturing, which is used to form arc fuse additive manufacturing for 316L stainless steel, including the following steps:
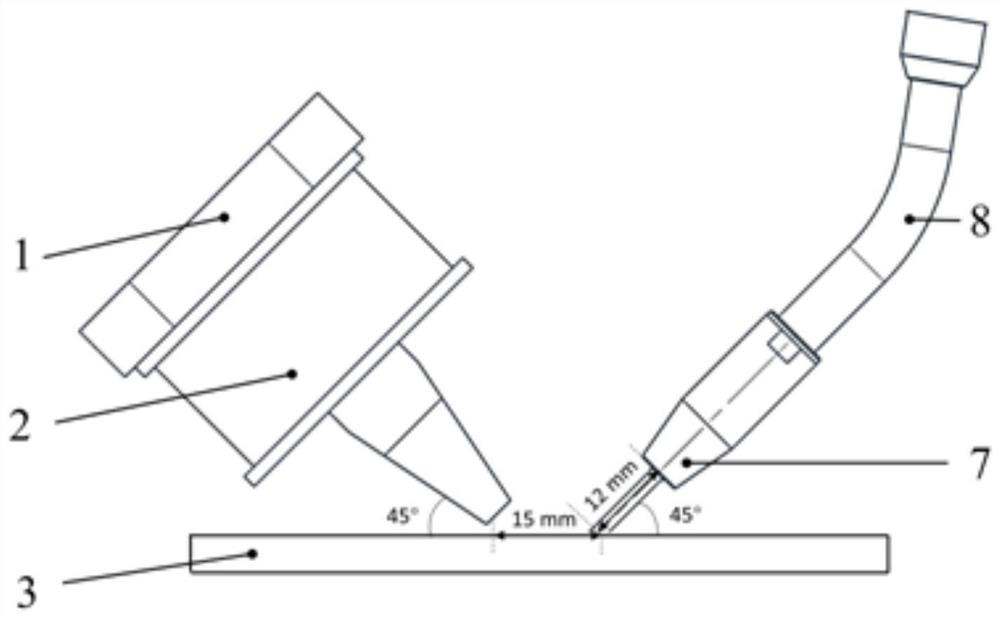
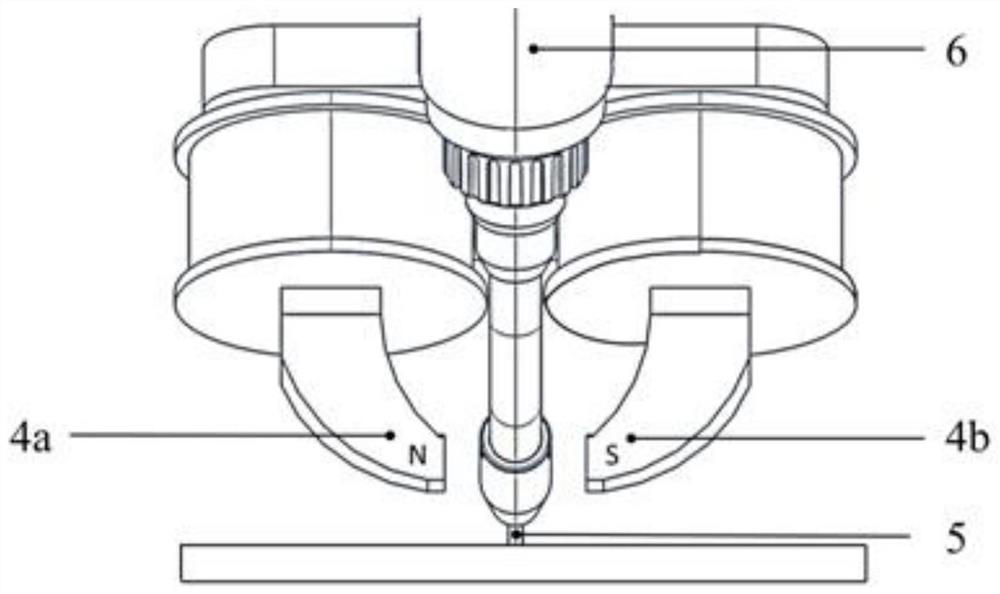
[0041] S1 Clamp the 316L stainless steel substrate 3 on the working platform, fix the clamp type electromagnet device and the arc welding torch device through the tooling fixture, set the dry elongation 5 of the welding wire to 1.2cm, and control the horizontal distance between the end point of the welding wire and the center of the magnetic pole 4 to 20mm , The inclination angle of the arc torch is 45°, and the inclination angle of the magnetic pole is 135°.
[0042] S2 Set the excitation current to 1.5A and the voltage to 7.45V on the panel of the DC excitation power supply, corresponding to the magnetic field strength at the end point of the welding wire at 20.7mT, and check the magnetic field strength at the end point of the welding wire and the direction of the magnetic inducti...
Embodiment 2
[0048] This embodiment provides a forming method for arc fuse additive manufacturing, which is used to form arc fuse additive manufacturing for 30CrMnSiNi2A high-strength steel (30Cr), including the following steps:
[0049] S1 Preheat the 30CrMnSiNi2A substrate to 300°C, then clamp it on the working platform, fix the clamp-type electromagnet device and the arc welding torch device through the tooling fixture, set the dry elongation of the welding wire to 1.2cm, and control the end point of the welding wire and the magnetic pole The horizontal distance between the 4 centers is 15mm, the inclination angle of the arc torch is 30°, and the inclination angle of the magnetic pole is 120°.
[0050] S2 Set the excitation current on the DC excitation power panel to 4A, the voltage to 18.18V, corresponding to the magnetic field strength at the end point of the welding wire at 59.6mT, and check the magnetic field strength at the end point of the welding wire and the direction of the magn...
Embodiment 3、 comparative example 1
[0055] Embodiment 3, comparative example 1, comparative example 2
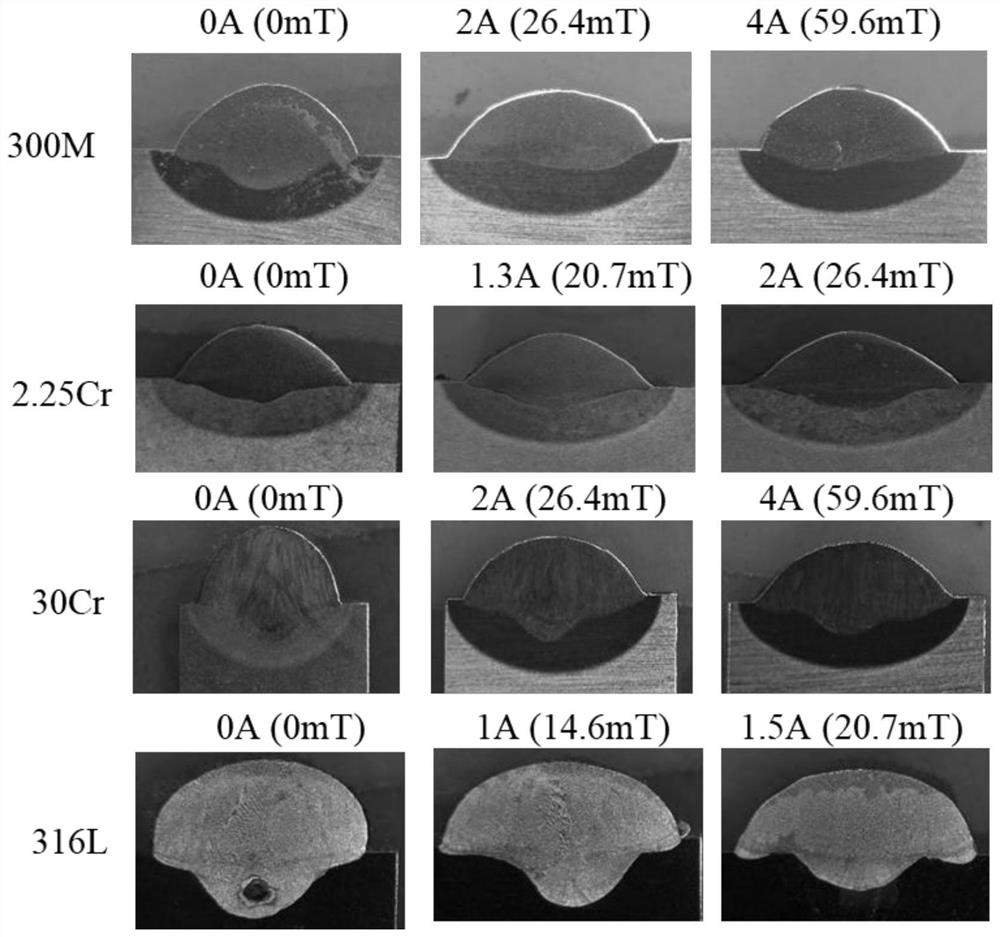
[0056] These comparative examples and examples adopt the same method as Example 1, the difference is that the applied transverse magnetic field has different magnetic field strengths at the end of the welding wire, specifically see Table 1 below:
[0057] Table 1-316L stainless steel arc fuse additive manufacturing magnetic field strength table
[0058]
[0059] It should be noted that the weld bead corresponding to the excitation current of 2A in Comparative Example 2 has poor morphology and high surface roughness, which is mainly due to the increase in arc instability observed during the additive process. As the excitation current continues to increase, the forward deflection angle of the arc column increases, causing an increase in the amount of spatter.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetic flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| magnetic flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com