Fluorescence detection method of acetylcholin esterase based on carbon dots
A technology of acetylcholinesterase and carbon dots, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, chemical instruments and methods, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity, complicated operation methods, long reaction time, etc., and achieve high sensitivity, fast response, The effect of low detection limit
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
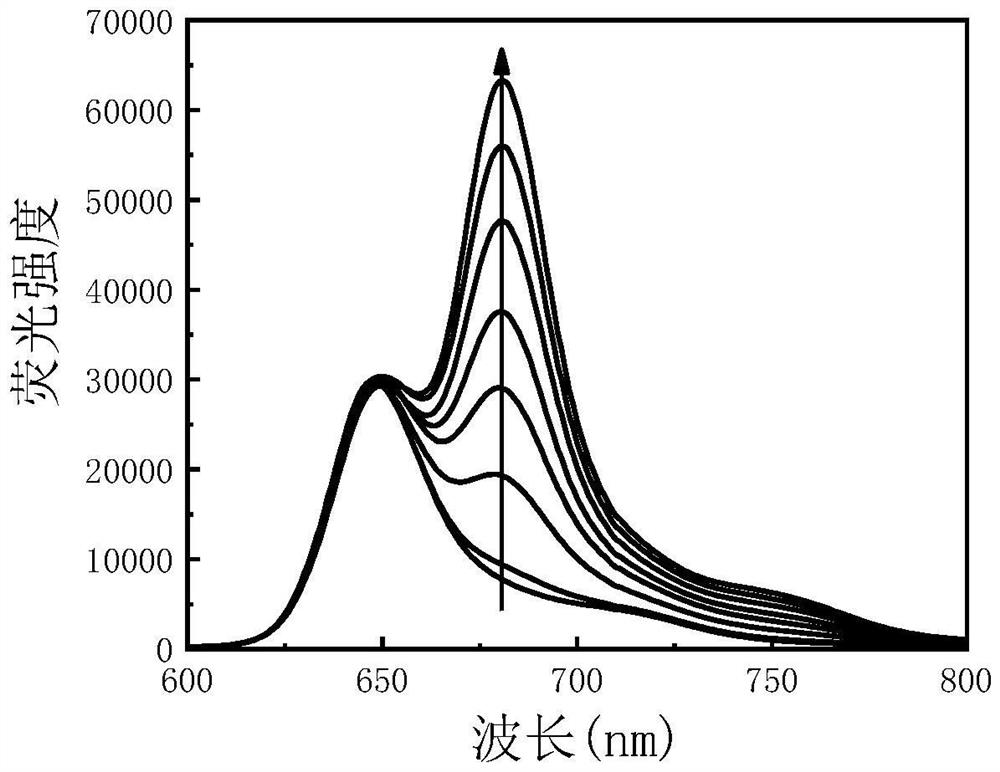
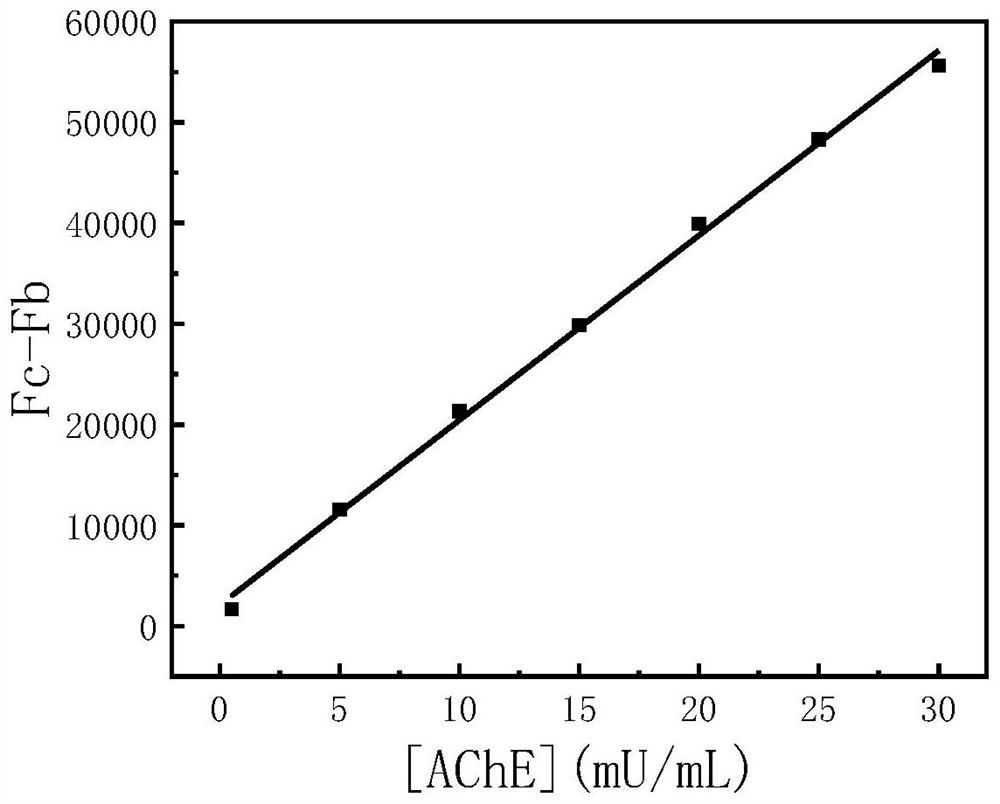
[0030] A method for detecting the concentration of acetylcholinesterase, specifically comprising the steps of:
[0031] 1. Preparation of near-infrared emitting carbon dot nanoparticles CDs:
[0032] Weigh 0.6g of glutathione and 19.4g of formamide solution, mix them ultrasonically for 30min, put them into a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene autoclave, and react at 160°C for 10h. Porous membrane filtration, after filtration, dialyze with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight of 1000 for two days, and finally freeze the product and put it in a freeze dryer for two days to freeze-dry to obtain near-infrared emitting carbon dots.
[0033] 2. Preparation of oxidized near-infrared emitting carbon dot nanoparticles CDs-HNO 3 :
[0034] Weigh 10 mg of the near-infrared emitting carbon dot nanoparticles CDs prepared in step 1, and measure 17 μL of HNO with a concentration of 14.5 mol / L 3 , the HNO 3 Dilute with 20mL deionized water, and then dissolve the weighed near-infrared emitting...
Embodiment 2
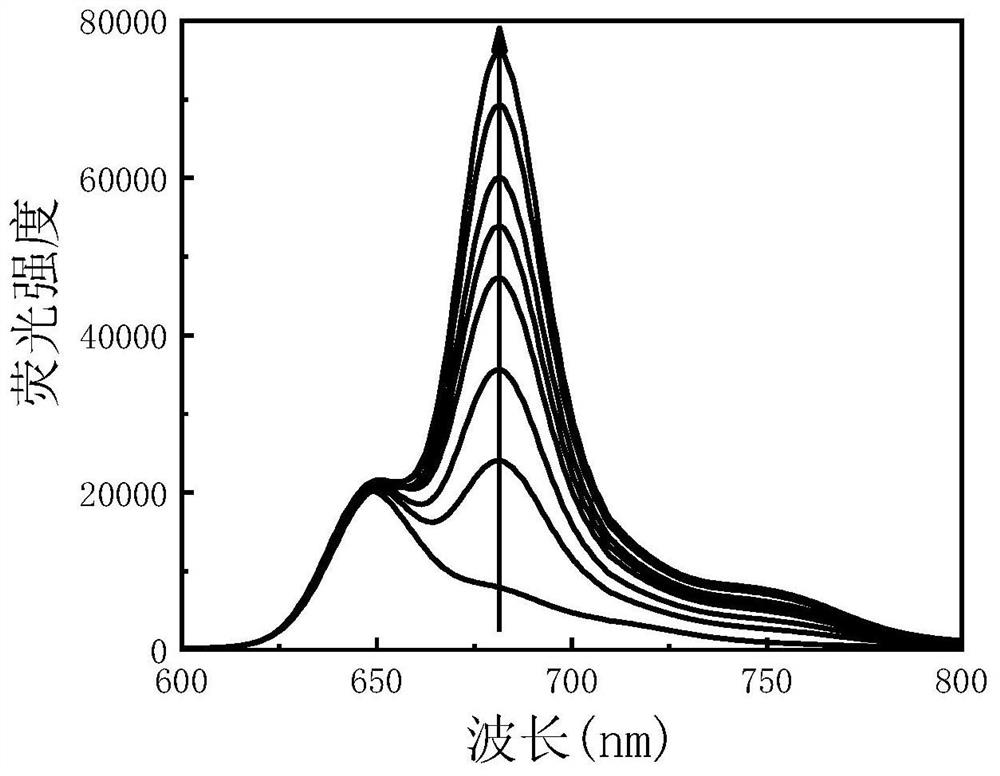
[0044] A method for detecting the concentration of acetylcholinesterase, specifically comprising the steps of:
[0045] 1. Preparation of near-infrared emitting carbon dot nanoparticles CDs: the same as in Example 1;
[0046] 2. Preparation of oxidized near-infrared emitting carbon dot nanoparticles CDs-HNO 3 :
[0047] Weigh 10 mg of the near-infrared emitting carbon dot nanoparticles CDs prepared in step 1, and measure 17 μL of HNO with a concentration of 14.5 mol / L 3 , the HNO 3 Dilute with 20mL deionized water, and then dissolve the weighed near-infrared emitting carbon dot nanoparticles CDs into the diluted HNO 3 solution, after mixing evenly, add the mixed solution into a 50mL round-bottomed flask, and reflux with magnetic stirring in an oil bath at 60°C for 24 hours. properties, and then filtered with a 0.22-micron microporous membrane, and then dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight of 1000 for 24 hours. Finally, the product was frozen and put into a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com