Kit and a detection method for high-throughput detection of intestinal protozoa based on honeycomb chip
A high-throughput, kit-based technology, applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, and resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing the incidence of false positives, good specificity, and improving detection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
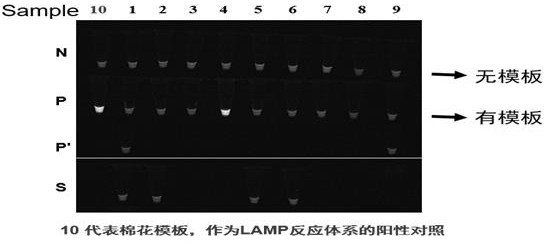
[0172] Example 1 DNA extraction of different strains.
[0173] (1) Positive samples of Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Amoeba histolytica, and Microsporidium were isolated from the laboratory and stored in potassium dichromate at 4°C.
[0174] (2) On-site samples were collected from diarrhea patients and animal feces samples in hospitals in Shanghai, Jiangsu and other places.
[0175] I: Fecal DNA extraction kit was purchased from Qiagen, USA, and PCR mix was purchased from Bio-Serve.
[0176] II: The nucleic acid of the sample was carried out in accordance with the "Technical Plan for Diarrheal Syndrome Detection" for molecular detection of related pathogens, and the species of the sample was confirmed by sequencing and comparison.
Embodiment 2
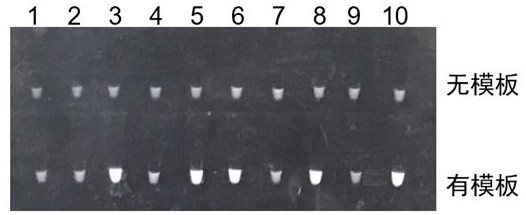
[0177] Example 2 Independent design and screening of detection primers for 5 kinds of intestinal protozoa
[0178] (1) Based on bioinformatics analysis, different target genes were used for target design.
[0179] (2) Primer design.
[0180] (3) Primer screening
[0181] Screening strategy: perform literature search for each strain first, and select literature-reported primers for verification. If the primers are valid, they will be used as spare primers for the chip; The possible primers were verified one by one to obtain effective specific amplification primers.
[0182] Among them, the sequences of Cryptosporidium human, Cryptosporidium turkey, Giardia, and amoeba were independently designed and synthesized; the general primers for Cryptosporidium (associated with 2 loop primers), Cryptosporidium parvum, and Cryptosporidium ansei Literature primers were used; one primer from Microsporidia was designed as a degenerate primer. See below for primers:
[0183] Group 1, Cry...
Embodiment 3
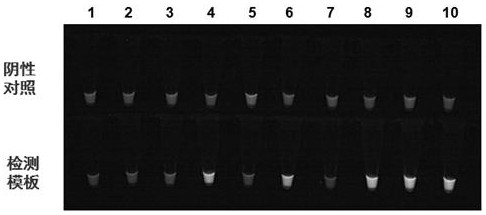
[0232]Example 3 Plasmid construction
[0233] Download the sequence of each strain according to the NCBI database. After comparing the sequences of different isolates of the same strain, select the appropriate region for template synthesis; construct a plasmid, which is consistent with the target sequence after sequencing;
[0234] A total of 8 template plasmids:
[0235] (1) CRY-403bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.39;
[0236] (2) Ch-244bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.40;
[0237] (3) Cp-221bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.41;
[0238] (4) Cm-408bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.42;
[0239] (5) Ca-230bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.43;
[0240] (6) GD-810bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.44;
[0241] (7) E.his-266bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.45;
[0242] (8) EnW-310bp, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.46.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com