Method for decomposition treatment and resource utilization of ardealite by using sintering machine
A sintering machine, a technology for disposing of phosphorus, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, phosphorus compounds, etc., can solve the problems of large equipment loss, low decomposition rate of phosphogypsum, large dust removal load, etc. The effect of avoiding fluidization power consumption and reducing pressure drop loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
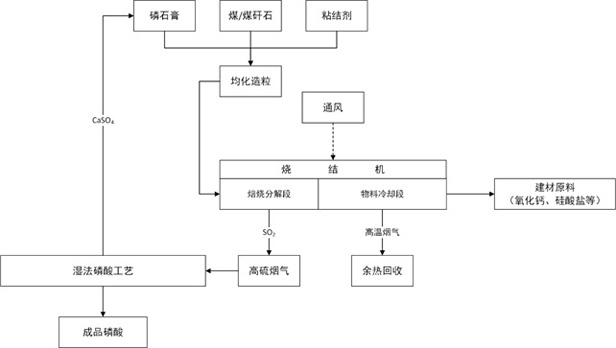
[0029] S1. After mixing phosphogypsum, bituminous coal and bentonite according to the mass percentage of 65%, 30% and 5%, after granulation and drying, pellets with a particle size of 1-10 mm are obtained, and the pellets are divided into two different particle size intervals;
[0030] S2. The pellets are layered into the sintering machine according to different particle size intervals to form a granular layered cloth structure in which the lower layer is the pellets in the smaller particle size range and the upper layer is the pellets in the larger particle size range; The wind decomposes the pellets vertically and layer by layer. The temperature of the material layer of the sintering machine is controlled at 800~1000℃, the residence time is 15~100s, and the air-fuel ratio is 9:1. The sulfur-containing flue gas generated is sent to the wet-process phosphoric acid process. The filter residue produced by solid-liquid separation in the process is phosphogypsum, and the phosphogyp...
Embodiment 2
[0032] S1. After mixing phosphogypsum, anthracite and bentonite according to the mass percentage of 76%, 20% and 4%, after granulation and drying, pellets with a particle size of 8-15mm are obtained, and the pellets are divided into 3 different particle size intervals;
[0033] S2. Put the pellets into the sintering machine in layers according to different particle size intervals to form a granular layered cloth structure in which the lowest layer is the pellets in the smallest particle size interval, and the particle size intervals become smaller from bottom to top; roasting During the process, the pellets are thermally decomposed layer by layer longitudinally by means of air induction. The material layer temperature of the sintering machine is controlled at 900~1100℃, the residence time is 100~300s, and the air-fuel ratio is 10:1. The sulfur-containing flue gas generated is sent to the wet process phosphoric acid process , The filter residue produced by the solid-liquid separ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] S1. After mixing phosphogypsum, lignite and bentonite according to the mass percentage of 85%, 13% and 2%, after granulation and drying, pellets with a particle size of 8-15mm are obtained, and the pellets are divided into 4 different particle size intervals;
[0036] S2. Put the pellets into the sintering machine in layers according to different particle size intervals to form a granular layered cloth structure in which the lowest layer is the pellets in the smallest particle size interval, and the particle size intervals become smaller from bottom to top; roasting During the process, the pellets are thermally decomposed layer by layer longitudinally by induced air. The material layer temperature of the sintering machine is controlled at 1100~1250℃, the residence time is 300~500s, and the air-fuel ratio is 11:1. The sulfur-containing flue gas generated is sent to the wet process phosphoric acid process , The filter residue produced by the solid-liquid separation of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com