A method for recovering arsenic and valuable metals from arsenic-containing soot
A technology for recovering valuable metals and arsenic, applied in chemical instruments and methods, arsenic oxide/arsenic hydroxide/oxyacid arsenic, arsenic compounds, etc. Secondary pollution and other problems can be achieved to improve the reduction efficiency and recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
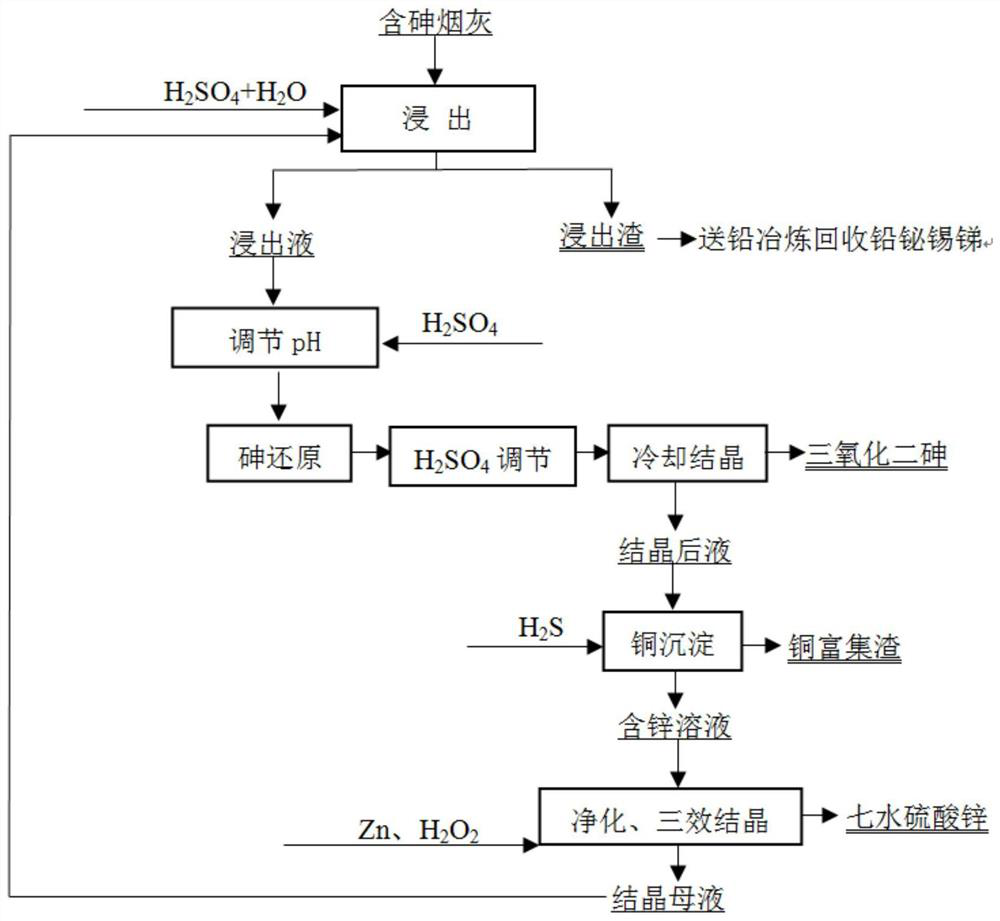
[0040] (1) Take 100 g of arsenic-containing copper soot, including 15.32% arsenic, 5.12% copper, 10.62% zinc, 14.86% lead, 3.21% bismuth, 1.26% antimony, and 1.53% tin.
[0041] (2) Add 10 mL of sulfuric acid, 30 mL of hydrogen peroxide, and 260 mL of water to the soot, and leaching for 3 hours at a leaching temperature of 85 °C. After the leaching is complete, the leaching residue and leaching solution are obtained by filtration. Lead, bismuth, antimony, and tin are all left in the leaching residue. , the recovery rates of lead, bismuth, antimony, and tin are 99.32%, 96.13%, 90.16%, and 95.32%, respectively.
[0042] (2) Add 20 mL of sulfuric acid to the leaching solution and then feed 30 g of sulfur dioxide (SO 2 The feeding speed is 50 mL / min), after the addition of sulfur dioxide, the stirring reaction is continued for 0.5 h, then 28 mL of sulfuric acid is added, and the solution is placed in a cooling chamber for stirring and cooling at 5 °C. After cooling for 1 hour, th...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) Take 100 g of arsenic-containing lead soot, including 20.53% arsenic, 0.53% copper, 12.33% zinc, 18.06% lead, 2.19% bismuth, 2.56% antimony, and 2.01% tin.
[0047] (2) Add 9 mL of sulfuric acid, 35 mL of hydrogen peroxide, and 256 mL of water to the soot, and leaching for 3 hours at a leaching temperature of 85°C. After the leaching is complete, filter the leaching residue and leaching solution. Lead, bismuth, antimony, and tin are all left in the leaching residue. , the recoveries of lead, bismuth, antimony and tin were 99.01%, 95.32%, 89.33% and 92.21%, respectively.
[0048] (2) After adding 22 mL of sulfuric acid to the leaching solution, feed 45 g of sulfur dioxide (SO 2 The feeding speed is 50mL / min), after the addition of sulfur dioxide, the reaction is continued to be stirred for 0.5h, then 30mL of sulfuric acid is added, and the solution is placed in a cooling chamber for stirring and cooling at 3°C. After cooling for 1 hour, filter to obtain arsenic trio...
Embodiment 3
[0052] (1) Take 100g of arsenic-containing tin soot, including 9.26% arsenic, 6.11% copper, 8.16% zinc, 15.33% lead, 7.83% bismuth, 3.62% antimony, and 9.13% tin.
[0053] (2) Add 12 mL of sulfuric acid, 35 mL of hydrogen peroxide, and 253 mL of water to the soot, and leaching for 3 hours at a leaching temperature of 80°C. After the leaching is complete, the leaching residue and leaching solution are obtained by filtration. Lead, bismuth, antimony, and tin are all left in the leaching residue. , the recovery rates of lead, bismuth, antimony, and tin are 99.52%, 96.13%, 92.16%, and 93.16%, respectively.
[0054] (2) Add 20 mL of sulfuric acid to the leaching solution and feed 25 g of sulfur dioxide (SO 2 The feeding speed is 50mL / min), after the addition of sulfur dioxide, the reaction is continued to be stirred for 0.5h, then 30mL of sulfuric acid is added, and the solution is placed in a cooling chamber for stirring and cooling at 3°C. After cooling for 1 hour, filter to obt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com