Drug-loaded cell network-type growth-induced decellularized heart valve scaffold and preparation method thereof
A heart valve and inducing cell technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve problems such as weak adhesion, and achieve the effects of solving the phenomenon of sudden release, unstable drug release speed, and weak adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035]The present invention also provides a preparation method of drug-loaded induced cell network growth decellularized heart valve stent, comprising the following steps:
[0036] S1. Dissolve polylactic acid in a solvent to prepare a polylactic acid solution with a predetermined concentration; add a predetermined amount of silk fibroin to the polylactic acid solution to obtain a polylactic acid / silk fibroin spinning solution, which is wet-spun through a skin core Silk obtained polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber;
[0037] S2. Cut the polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber obtained in step S1 into several sections, and seal one end of each polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber; The hollow interior of the polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber is injected with a drug solution, and then the open end is sealed to obtain several sections of drug-loaded polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber;
[0038] S3. Arrange the several pieces of drug-loaded polylactic aci...
Embodiment 1
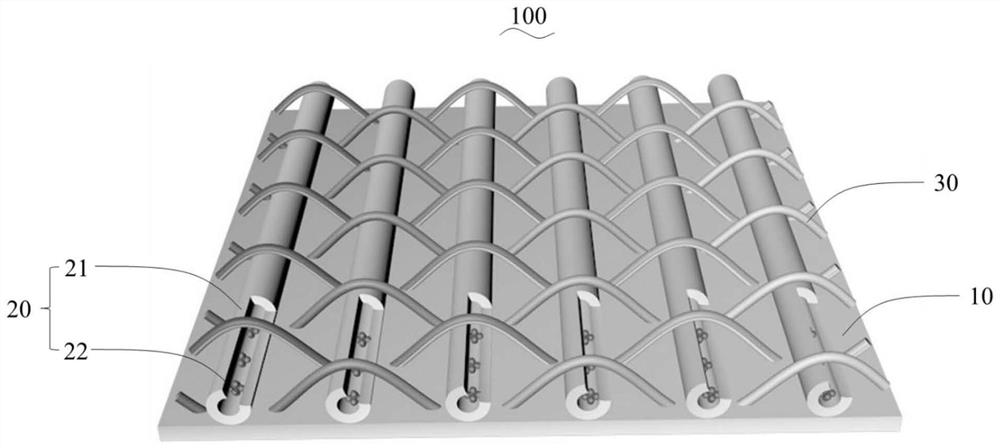
[0043] This embodiment provides a drug-loaded acellular heart valve stent 100 induced by cell network growth, the schematic diagram of which is shown in figure 1 As shown, it includes a decellularized heart valve 10 and several sections of drug-loaded polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fibers 20 arranged in parallel on one side of the decellularized heart valve; the drug-loaded polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fibers 20 pass through The polylactic acid yarn 30 is sutured on the decellularized heart valve 10 , including the polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber 21 and the drug 22 encapsulated inside the polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber 21 .
[0044] This embodiment also provides a preparation method of the above drug-loaded acellular heart valve stent 100 induced by cell network growth, including the following steps:
[0045] S1. Preparation of polylactic acid / silk fibroin hollow fiber 21
[0046] Dissolving polylactic acid in the solvent 1,4-dioxane to prepar...
Embodiment 2~5
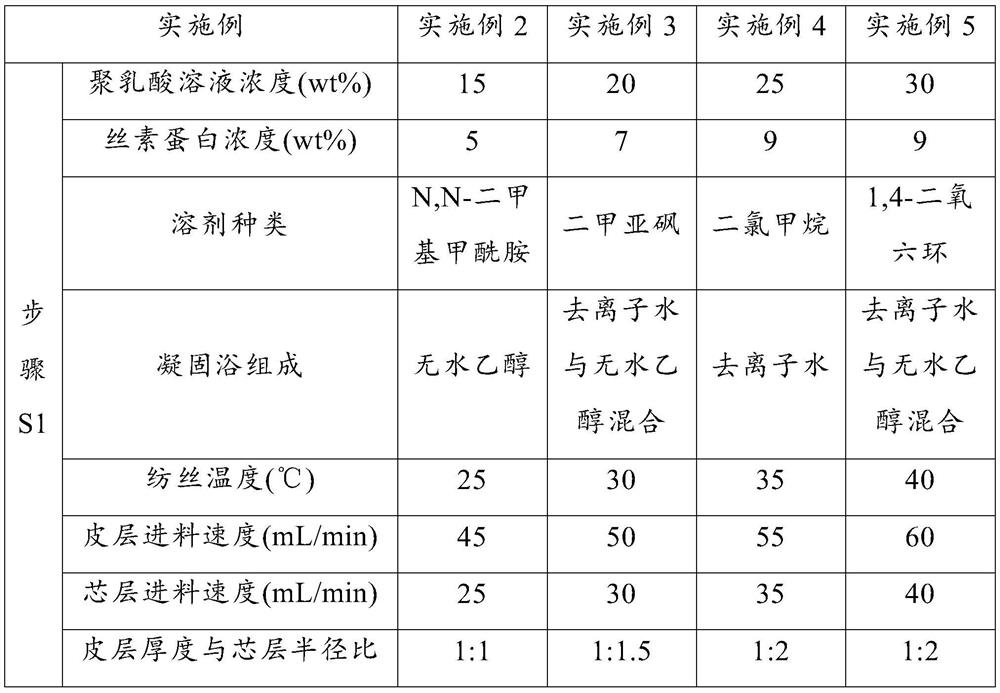
[0055] Examples 2 to 5 respectively provide a preparation method for drug-loaded cell-network-type growth decellularized heart valve stents. Compared with Example 1, the difference is that the process parameters in each step are changed. Each example The corresponding parameter values are shown in Table 1, and the rest of the steps are consistent with those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0056] The technological parameter value of table 1 embodiment 2~5
[0057]
[0058]
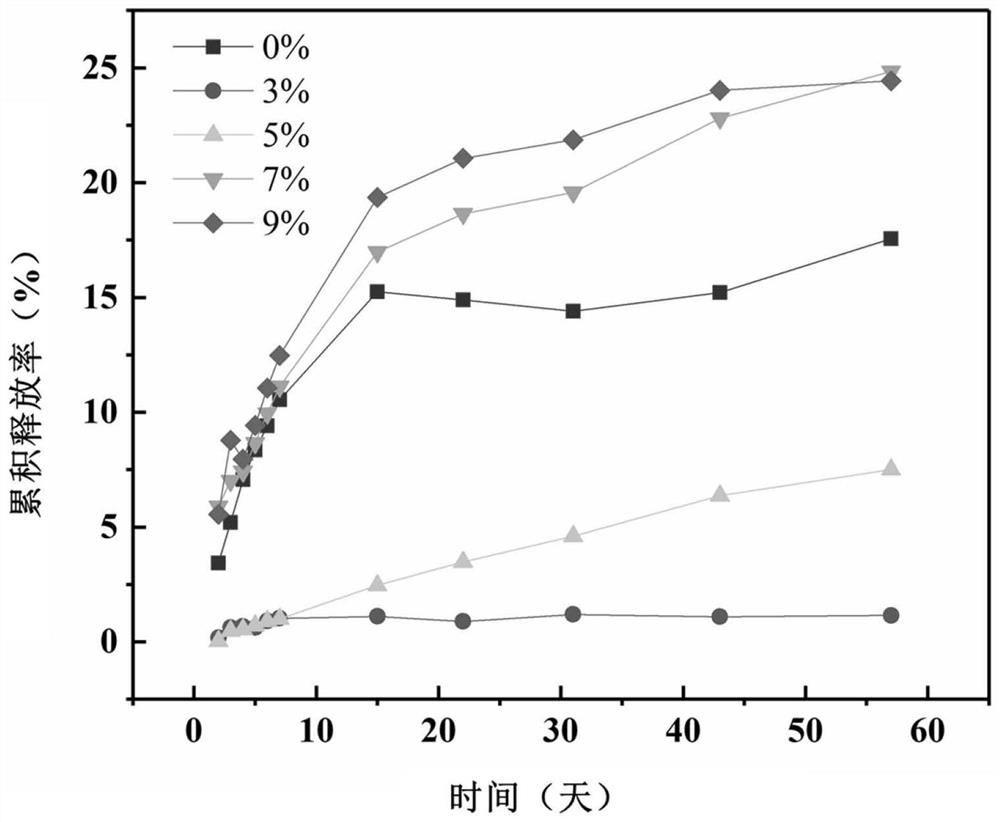
[0059] After testing, the drug-loaded cell-network-type growth decellularized heart valve stents prepared according to the above-mentioned process parameters respectively in Examples 2-5 have different drug release rates and cell growth rates, indicating that polylactic acid / silk fibroin can be adjusted Process parameters such as the content of silk fibroin in the hollow fiber and its preparation process, drug concentration, polylactic acid yarn fineness, and suture spacing can reg...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com