A circulating tumor dna detection system and its application for screening minimal residual lesions after colorectal cancer surgery and predicting recurrence risk
A detection system and colorectal cancer technology, applied in the field of circulating tumor DNA detection, can solve the problems of inability to accurately guide adjuvant chemotherapy, poor risk stratification tool evaluation, difficulty in finding colorectal cancer minimal residual lesions, etc., and achieve recurrence prediction Risk, guiding postoperative adjuvant therapy, and the effect of convenient detection process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: Circulating tumor DNA detection
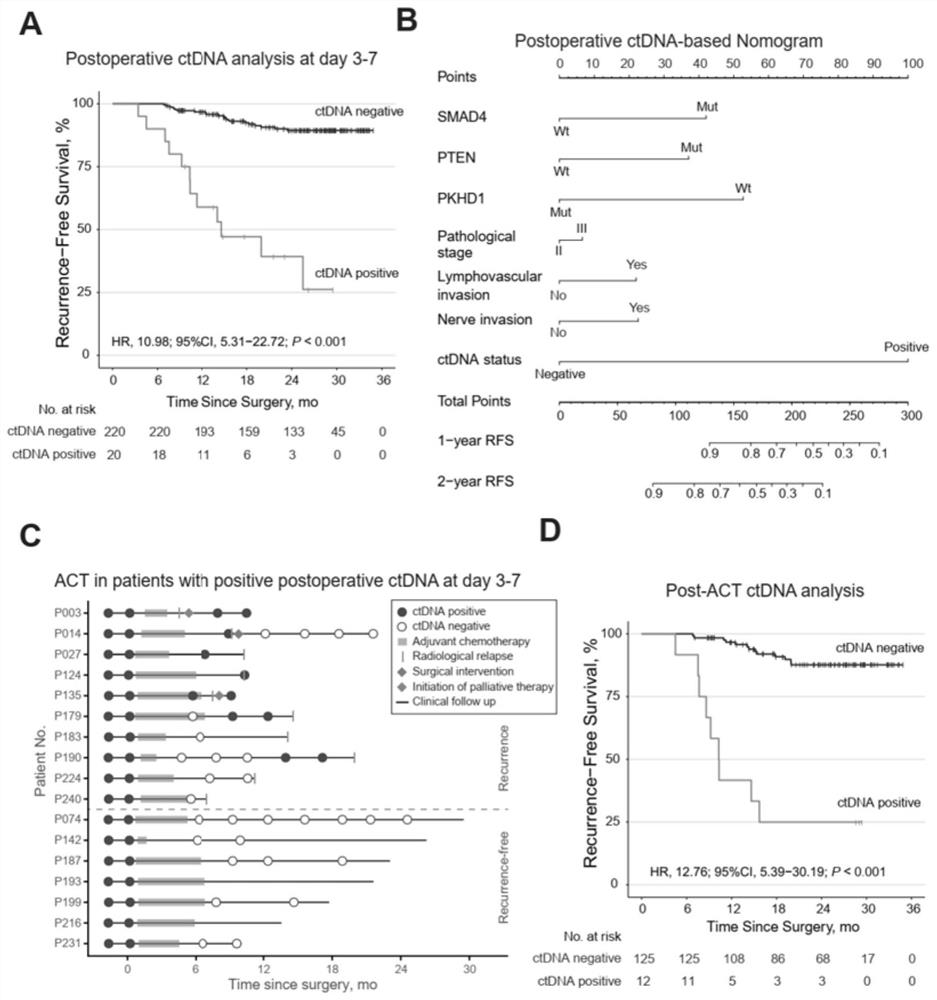
[0042] 1. Sample source: 240 colorectal cancer patients who received radical surgery were treated according to current guidelines and followed up regularly.
[0043] 2. Sample collection: collect tumor tissue samples and peripheral blood leukocyte samples from patients after surgery, 3-7 days after surgery, 6 months after surgery, 9 months after surgery, 12 months after surgery, and 15 months after surgery. Plasma samples were taken consecutively from the patients after 18 months, 21 months after surgery, and 24 months after surgery.
[0044] 3. Detection method:
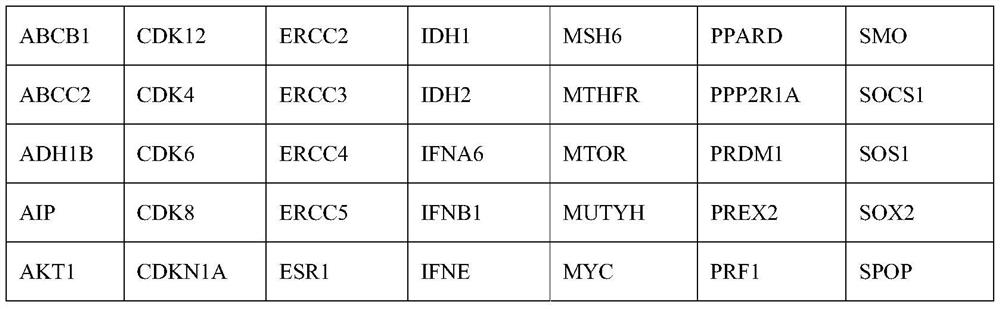
[0045] 1. High-throughput sequencing: Obtain surgically resected tumor tissue specimens and peripheral blood leukocyte samples from colorectal cancer patients, extract cellular genomic DNA, construct a sequencing library, and then use a next-generation sequencing gene panel panel containing 425 cancer-related genes ( panel) for targeted capture, and the specific ...
Embodiment 2
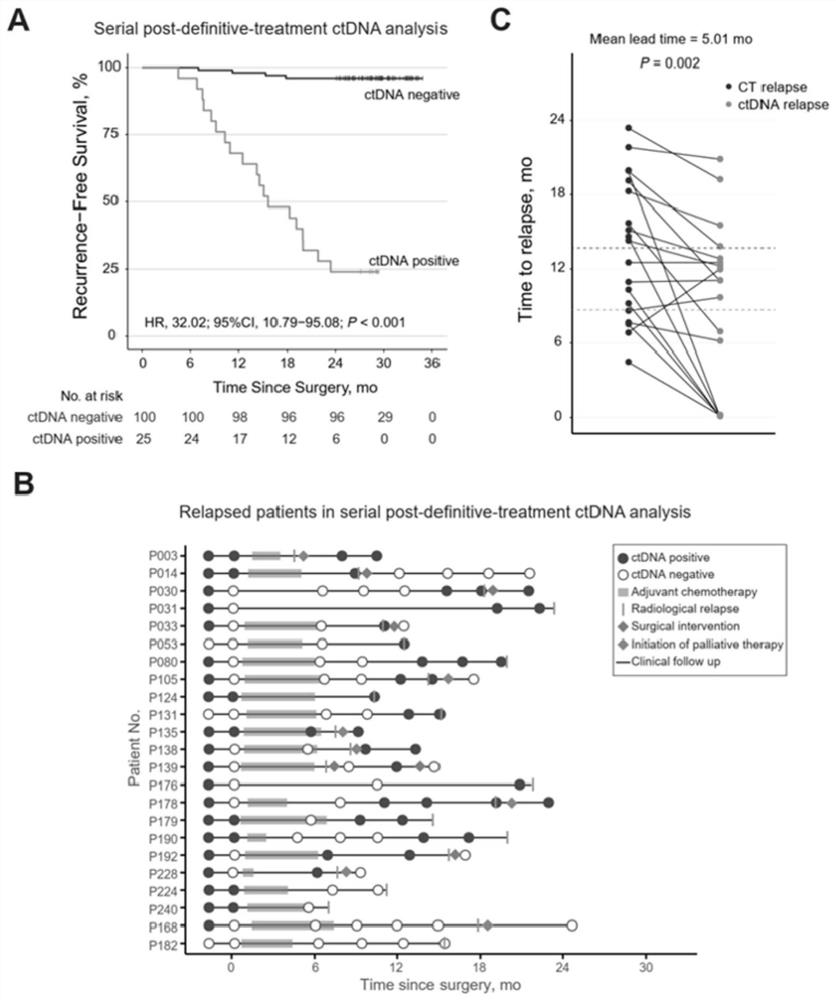
[0065] Example 2: Continuous blood collection to detect circulating tumor DNA to identify tumor recurrence
[0066] Based on Example 1, colorectal cancer patients with serial postoperative plasma samples (≥3) and sufficient follow-up time (≥24 months or tumor recurrence) were included to analyze whether serial blood sampling to detect circulating tumor DNA can early identify tumor recurrence.
[0067] Follow up to observe whether the ctDNA-positive patients determined by the detection system of the present invention eventually have tumor recurrence, and calculate the time from the first positive ctDNA detection to tumor recurrence, which is the advance of ctDNA detection compared with conventional imaging methods in predicting tumor recurrence. time.
[0068] like figure 2 As shown in A, the parameters of the COX proportional hazards model calculated based on the patient's follow-up survival data are: hazard ratio ln[h(t,X) / h 0 (t)]=32.02*ctDNA, patients with positive circu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com