A method for determining the glycemic index of carbohydrate foods in vitro
A glycemic index and carbohydrate technology, which is applied in the field of in vitro determination of the glycemic index of carbohydrate foods, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, data analysis dependence, and low accuracy, and achieves high prediction accuracy and reduces data analysis time. , the effect of simple operation
Active Publication Date: 2022-06-07
JINAN UNIVERSITY
View PDF13 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0006] 1). Unreasonable or unnecessary steps lead to cumbersome operations
This method requires the use of liquid nitrogen auxiliary equipment to grind solid or semi-solid food materials, which is very different from the real human oral chewing and intestinal peristalsis environment; this method also requires the use of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or equivalent quantitative methods Determination of the amount of a series of sugars or sugar alcohols (fructose, galactose, lactose, sucrose and maltitol), but in the real digestive environment, starch molecules are hydrolyzed by various digestive enzymes into reducing sugars (maltose, malt three Sugar, monomolecular glucose) are the main components of blood sugar. This method does not specifically characterize and measure the rate of starch digestion and hydrolysis to form reducing sugar, so the accuracy is not high.
[0007] 2). The isolated point test cannot reflect the overall digestion situation
This method - immediately after the fixed time, the digested sample is treated as a whole to stop the enzymatic reaction, so that only a single time point of food digestion products can be obtained for testing, and it is impossible to evaluate the reducing sugar content of the food in the whole time period Release rate, for diabetic and obese patients, the release rate of reducing sugar has a more important impact on the blood glucose level in the body after eating
[0008] 3). Data analysis relies too much on professional statistical software
[0011] In summary, in the field of in vitro assays to measure GI, many existing analytical methods have significant deficiencies
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
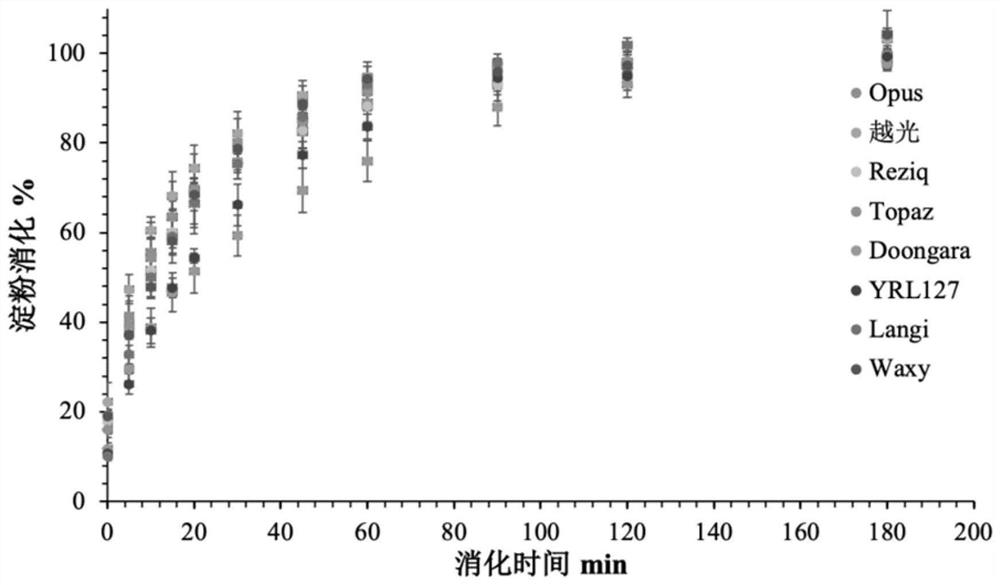
[0082] Seven kinds of commercial rice with known GI values (Opus rice, Reziq rice, Doongara rice, Langi rice, Topaz rice, Waxy rice, YRL127 rice) were selected as the standard carbohydrate food, and Koshihikari rice was the tested rice variety.
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
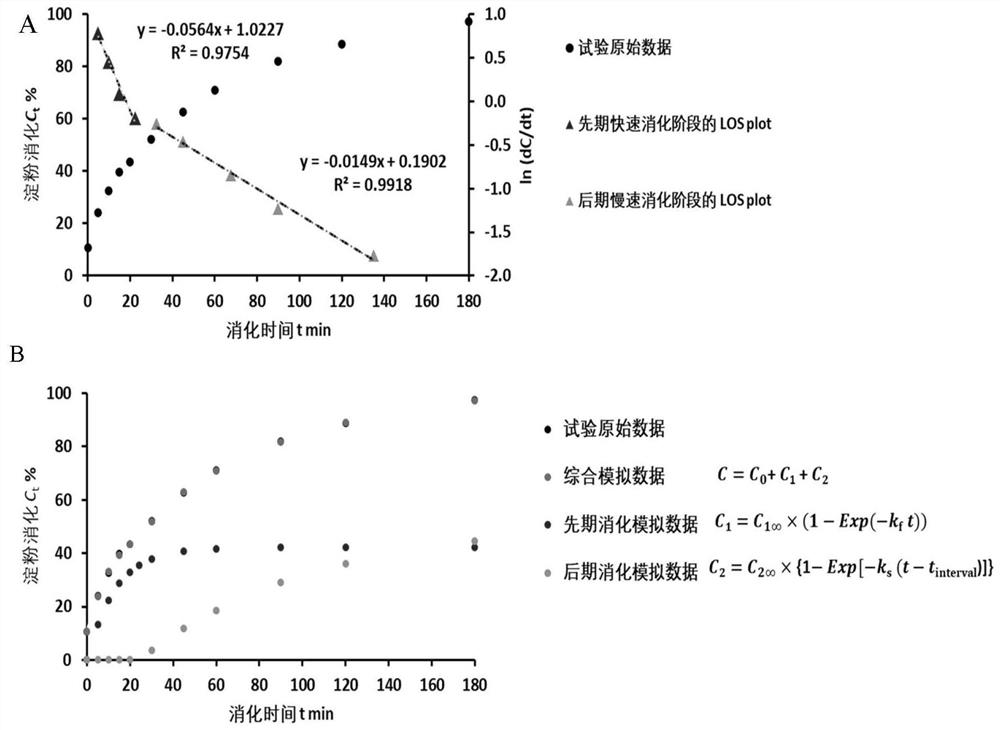
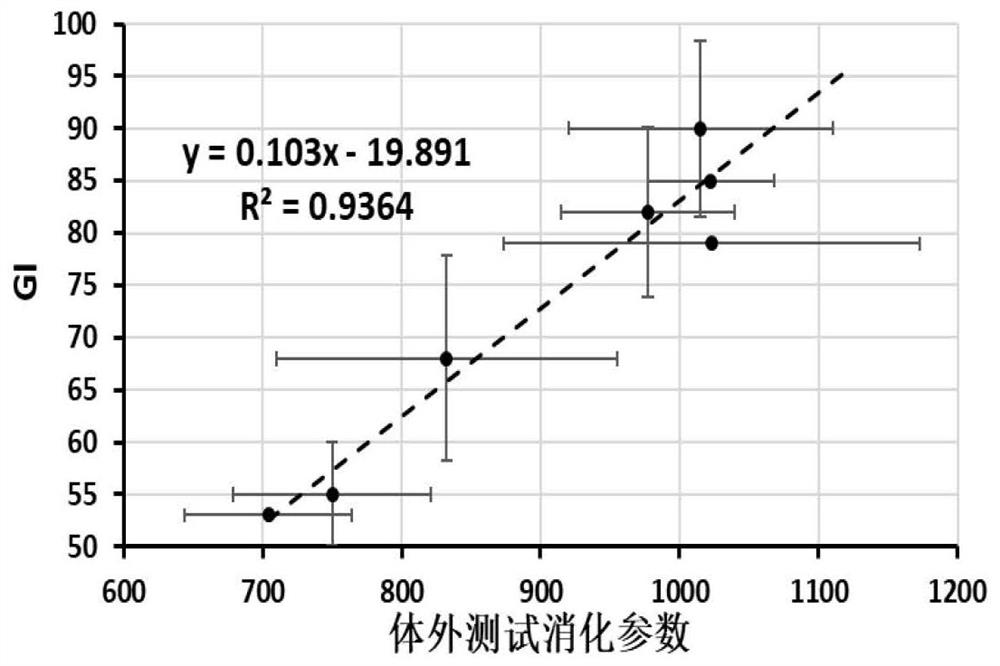
The invention discloses a method for measuring the glycemic index of carbohydrate food in vitro, which belongs to the technical field of food detection. The method for measuring the glycemic index of carbohydrate food in vitro comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining the rate and digestibility thereof of releasing reducing sugar from the carbohydrate food to be tested; (2) obtaining relevant in vitro digestion test parameters; (3) ) Establish a database for standard carbohydrate foods with known GI values, and define and establish the functional relationship between the standard sample glycemic index GI and the in vitro digestion test parameters; (4) Carry out in vitro digestion tests for the carbohydrate foods to be tested, and obtain a variety of The relevant parameters of the external digestion test are compared with the standard database to predict the glycemic index, that is, the GI value. The relationship between the in vitro digestion parameter and the GI value obtained by the method of the present invention has a linear correlation above 0.9, and the prediction accuracy is higher.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of food detection, in particular to a method for measuring the glycemic index of carbohydrate food in vitro. Background technique [0002] With the development of social economy and the improvement of residents' living standards, the public's awareness of health care is increasing, consumers' demand for dietary nutrition quality is gradually increasing, and the potential health food consumption market is expanding. Carbohydrate is one of the most important food nutrients. It enters the human body in the form of glucose molecules through the metabolism and absorption of the human digestive system, and provides the main energy source for various metabolic activities. In order to study the changes in blood sugar in the human body, researchers such as Jenkins from the University of Toronto in Canada proposed the important concept of glycemic index (GI). The GI value of carbohydrate foods can be graded on a 0-10...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Patents(China)
IPC IPC(8): G01N33/10G01N21/31G01N1/38G01N1/42G01N1/44G06F17/15
CPCG01N33/10G01N21/31G01N1/38G01N1/42G01N1/44G06F17/15
Inventor 余稳稳邹伟李成
Owner JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com