Method for producing carbonate derivative
A technology of derivatives and carbonates, applied in the field of preparation of carbonate derivatives, can solve the problems of expensive, by-products, and limited polycarbonate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0038] In the production method of the carbonate derivative of the present invention, high-energy light is irradiated to a composition containing a methyl halide and a hydroxyl-containing compound in the presence of oxygen.
[0039] 1. Methyl halides
[0040] In the reaction of the present invention, it is considered that methyl halide may be decomposed by high-energy light and oxygen, converted into carbonyl halides or compounds similar to carbonyl halides, and reacted with hydroxyl-containing compounds to generate carbonate derivatives. Even if harmful carbonyl halides are generated, the carbonyl halides react immediately with the hydroxyl group-containing compound due to their high reactivity, and do not leak out of the reaction solution, or even if they leak, the amount of leakage is small. In particular, in the present invention, since the amount of the hydroxyl-containing compound used is relatively high relative to the methyl halide, it is considered that the generated ...
Embodiment 1-4
[0175] Embodiment 1-4: the reaction of fatty alcohol
[0176] [chemical formula 16]
[0177]
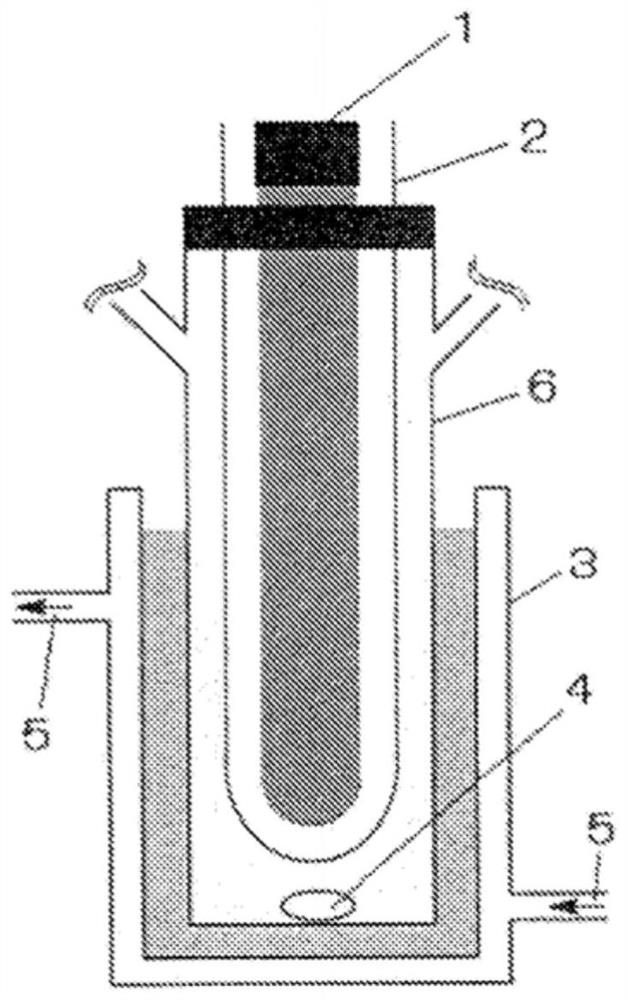
[0178] A quartz glass sleeve with a diameter of 30 mm is placed in a cylindrical reaction vessel with a diameter of 42 mm and a capacity of 100 mL, and then a low-pressure mercury lamp (“UVL20PH-6” produced by SEN Light Company, 20 W, Build a reactive system. figure 1 A schematic diagram of the reaction system is shown. In addition, the irradiation light from this low-pressure mercury lamp contains UV-C with a wavelength of 254 nm, and the illuminance of the light with a wavelength of 254 nm at a position 5 mm from the tube wall is 6.23 to 9.07 mW / cm 2 . Purified chloroform (20 mL, 250 mmol) and aliphatic alcohol (250 mmol) shown in Table 1 were added to the reaction vessel, and stirred and mixed. While stirring the reaction solution, 0.5 L / min of oxygen gas was blown in by bubbling at 50° C., and irradiated with high-energy light including UV-C. Then, the reaction liquid wa...
Embodiment 5-7
[0182] Embodiment 5-7: the synthesis of ethylene carbonate
[0183] In the reaction vessel of the reaction system used in Example 1, add refined chloroform (16mL, 200mmol) and ethylene glycol (5.6mL, 100mmol), and blow into it by bubbling while stirring at the temperature shown in Table 2. Oxygen at 0.5L / min is irradiated with high-energy light containing UV-C.
[0184] Eight hours later, water and dichloromethane were added to the reaction liquid for liquid separation, and the organic phase was concentrated under reduced pressure at 80°C to obtain ethylene carbonate as a white solid. The yields are shown in Table 2.
[0185] [Table 2]
[0186] Example temperature reflex yield 5 0℃ 40% 6 20℃ 87% 7 25℃ 70%
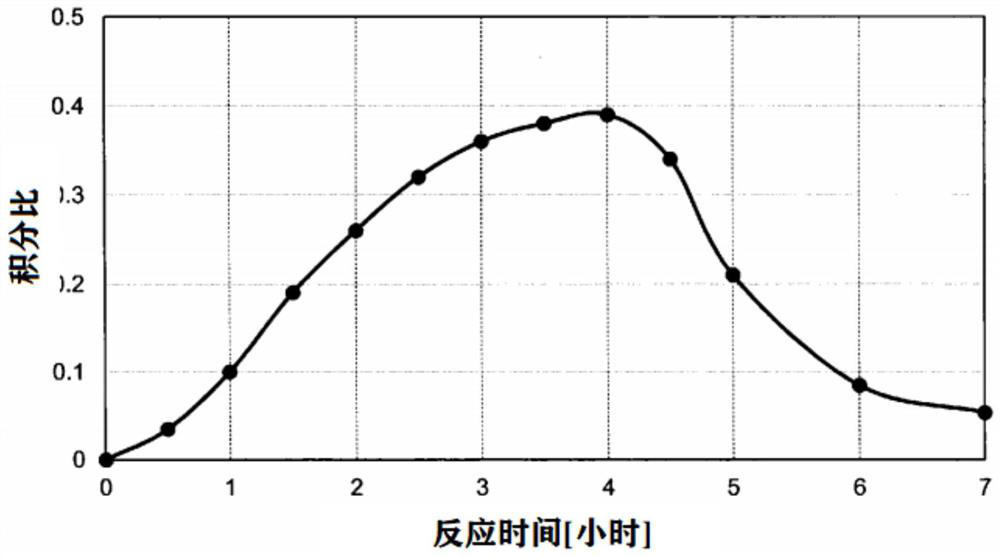
[0187] In addition, the reaction temperature was changed to 50°C, samples were taken from the reaction solution every 30 minutes up to 6 hours, and analyzed by 1HNMR to obtain the peak area of the methylene proton of ethylene carbona...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com