A Salvia miltiorrhiza p450 mutant used for preparing tanshinone compounds
A technology of hypotanshinone diene and point mutation, which is applied in the direction of introducing foreign genetic material, application, fungi, etc. by using a carrier, can solve the problems of production limitation, reduction of amorphadiene production, and reduction of catalytic activity, and achieve an increase in production , Improving substrate utilization efficiency and optimizing catalytic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of mutant
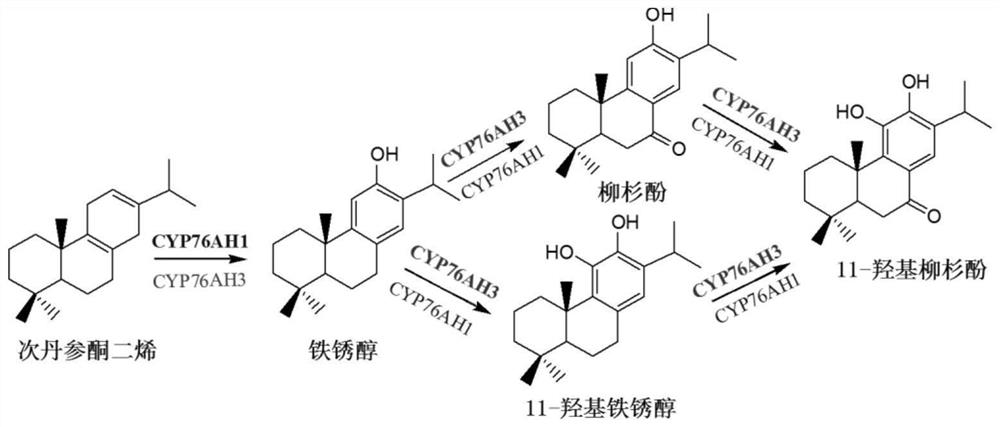
[0094] CYP76AH1 and CYP76AH3 proteins are P450 proteins involved in tanshinone biosynthesis. catalytic pathway see figure 1 . figure 1 In , each protein can catalyze the substrate before the arrow, but with different efficiencies.
[0095] The amino acid sequence of CYP76AH1 is shown in sequence 2 of the sequence listing, and its coding gene (CYP76AH1) is shown in sequence 1 of the sequence listing.
[0096] The amino acid sequence of CYP76AH3 is shown in sequence 4 of the sequence listing, and its coding gene (CYP76AH3) is shown in sequence 3 of the sequence listing.
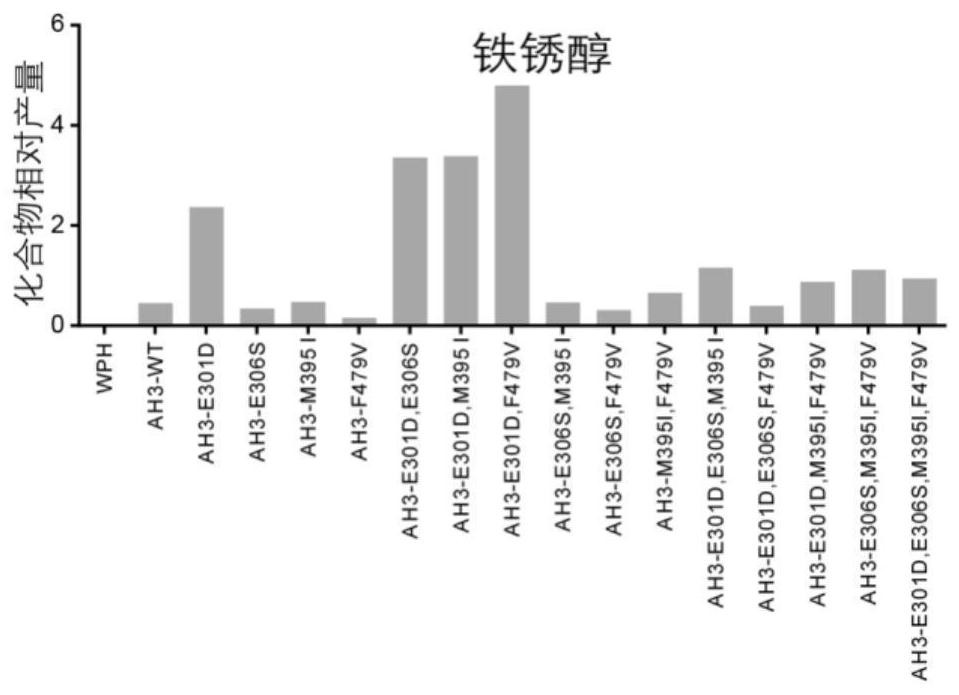
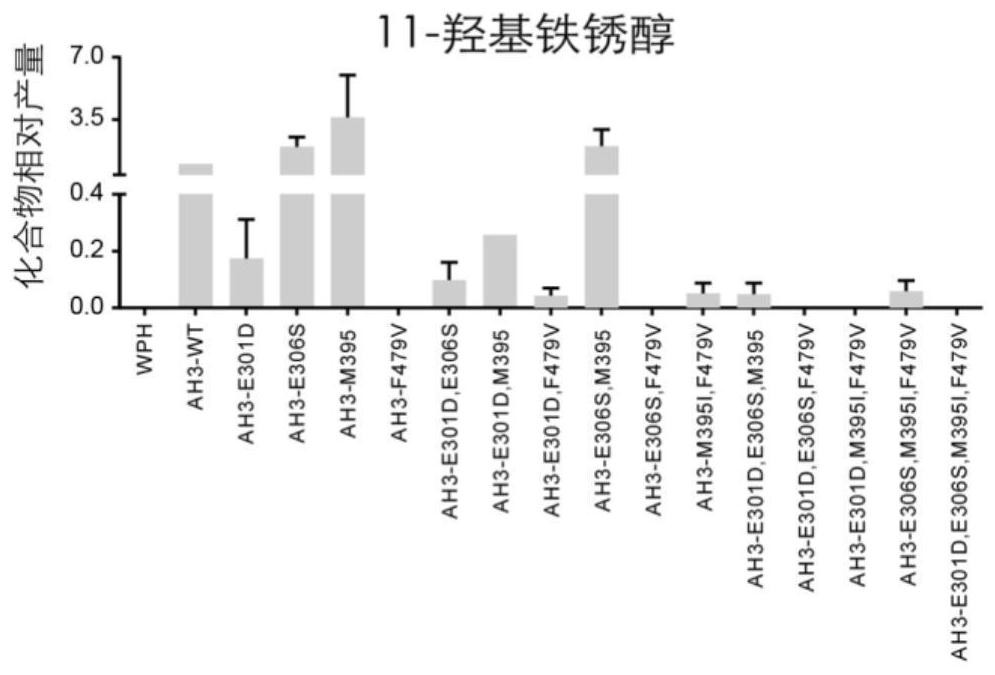
[0097] Sequence analysis, mutation and functional verification of CYP76AH3 revealed four active sites related to the catalytic efficiency of CYP76AH1, which were amino acid residues 301, 306, 395, and 479, respectively. These 4 amino acid sites were mutated in different forms (Table 1), and a total of 15 CYP76AH1 protein mutants were obtained (Table 2).
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Embodiment 2, preparation of recombinant expression vector
[0105] 1. Construction of wild-type recombinant expression vector
[0106] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in sequence 1 into the BamHI site of the expression vector pESC-His (circular plasmid shown in sequence 5 of the sequence listing) to obtain the recombinant expression vector pESC-His-H1WT (sequencing verified correctly). The DNA molecule shown in sequence 1 encodes the protein shown in sequence 2.
[0107] 2. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule shown in Sequence 3 between the BamHI sites of the expression vector pESC-His to obtain the recombinant expression vector pESC-His-H3WT (sequence verification is correct). The DNA molecule shown in sequence 3 encodes the protein shown in sequence 4.
[0108] 2. Construction of mutant recombinant expression vector
[0109] 1. Insert the double-stranded DNA molecule 1 between the BamHI sites of the expression vector pESC-His to obtain the re...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Example 3, preparation of recombinant bacteria and extraction of microsomal protein
[0125] 1. The wild-type recombinant expression vector, mutant recombinant expression vector and expression vector pESC-His prepared in Example 2 were respectively introduced into the yeast expression strain BY4741 integrating the Arabidopsis P450 reductase ATR1 to obtain wild-type recombinant bacteria, 15 species Mutant recombinant bacteria and empty vector recombinant bacteria.
[0126] 2. The wild-type recombinant bacteria obtained in step 1 and 15 kinds of mutant recombinant bacteria were inoculated respectively in the defective SD-His liquid medium for yeast transformation (Ubiquino, SD-His liquid medium formula: 8g / LSD-His powder , 20g / L glucose, sterilized for 15min), cultured at 30°C and 200 rpm for 48 hours, centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5min to collect the bacteria, and used an equal volume of YPL liquid medium (10g / L yeast extract, 20g / L peptone, 20g / L galactose) after resusp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com