Stannide thermoelectric conversion element and stannide thermoelectric conversion module
A thermoelectric conversion and component technology, which is applied in the manufacture/processing of electrical components, thermoelectric device parts, and thermoelectric devices, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in generating electricity efficiently, and achieves the goal of suppressing the reduction of power generation performance and the increase of resistance value. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] [Example] 1. Manufacture of thermoelectric conversion module
[0074] (Example 1)
[0075] (1) Manufacture of thermoelectric conversion elements
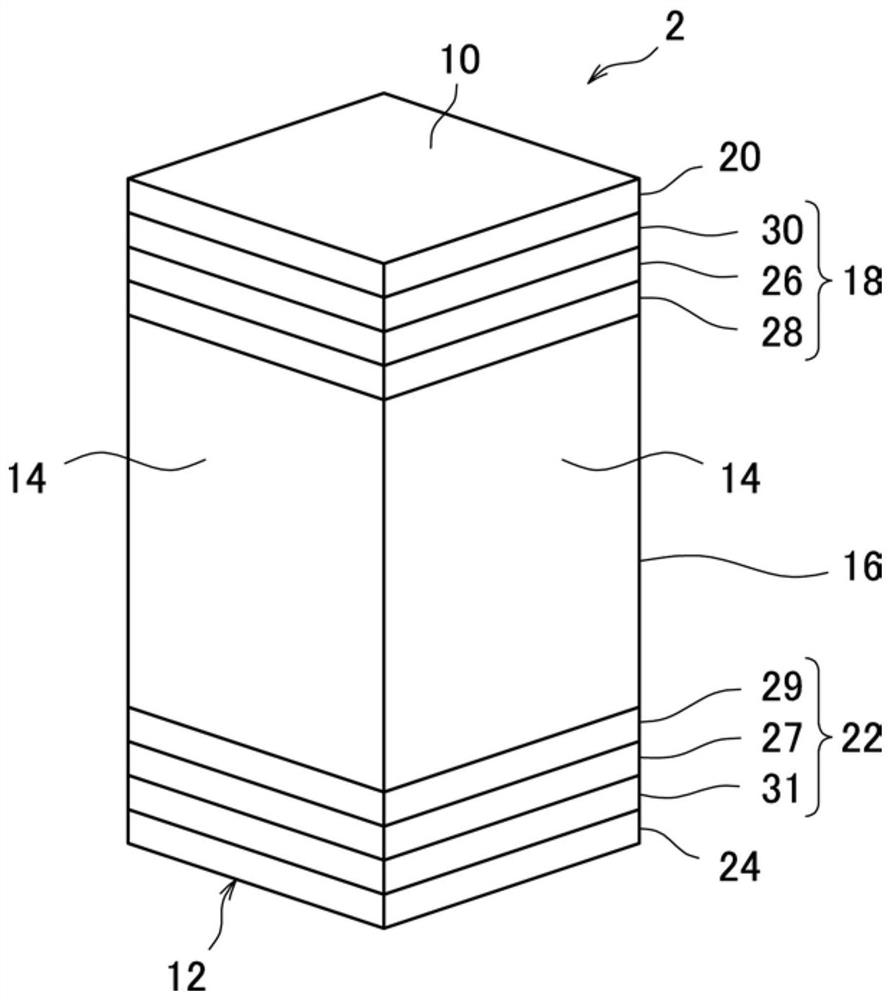
[0076] so that the composition becomes Mg 2 Si 0.3 sn 0.7 In this method, Mg, Si, and Sn were measured, and predetermined amounts of Mg, Si, and Sn were mixed to obtain a mixture. The obtained mixture was charged into an induction melting furnace, and then heated and melted under an argon atmosphere. Then, the obtained molten material was cooled to room temperature (about 25 degreeC), and the ingot was produced. The obtained ingot was mechanically pulverized to obtain Mg composed of particles with an average particle diameter of several tens of μm. 2 Si 0.3 sn 0.7 of powder.
[0077] The obtained powder was put into a jig for sintering made of graphite, at 5×10 -3 Sintering was carried out at a sintering pressure of 50 MPa and a sintering temperature of 680° C. under a reduced-pressure atmosphere below Pa. As a res...
Embodiment 2
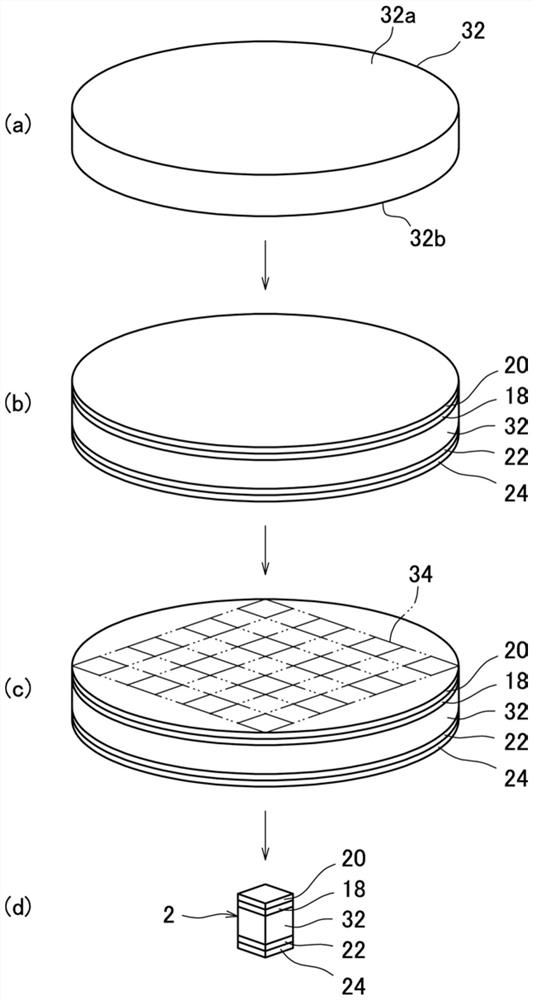
[0091] In addition to polishing the both end surfaces 32a, 32b of the sintered body 32 using diamond paste containing diamond particles with a particle size of 3 μm, the surface roughness (Rz) of the both end surfaces 32a, 32b is set to The thermoelectric conversion module 4 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the thickness was 4.0±0.2 μm.
Embodiment 3
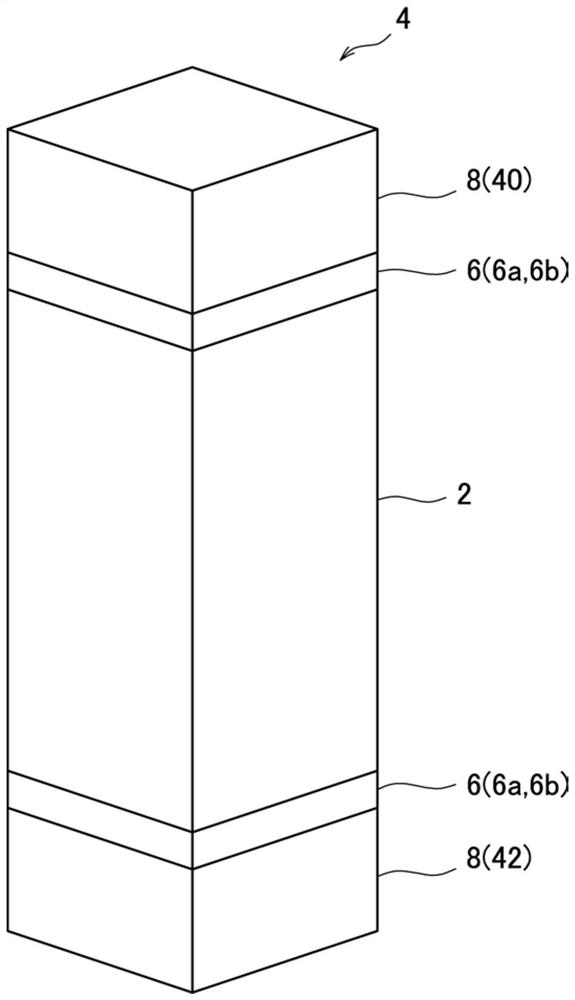
[0093] except as Image 6 As shown, when manufacturing the thermoelectric conversion module, a composite plating layer as a metal layer composed of a Ni plating layer and an Au plating layer is formed on the surface of the electrode material 8 (Cu member) in advance, and a composite plating layer is formed between one end surface of the thermoelectric conversion element 2 and the second end surface of the thermoelectric conversion element 2. Joining is performed with the metal layers (composite plating of Ni plating and Au plating) 48 and 50 present between the first Cu members 60 and between the other end surface of the thermoelectric conversion element 2 and the second Cu member 62. In addition, the thermoelectric conversion module 4 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0094] That is, Example 3 is a configuration using the non-fluid joint material 6a.
[0095] It should be noted that a Ni plating layer was formed on the surface of the electrode material 8 (me...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com