A method for secondary aluminum ash reduction of hazardous solid waste heavy metals and slag utilization
A technology of heavy metals and aluminum ash, applied in the field of solid waste recycling, can solve the problems of secondary aluminum ash and hazardous solid waste pollution, achieve low cost, realize harmless disposal and high-value utilization, and solve the problem of heavy metals Effects of Pollution Problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
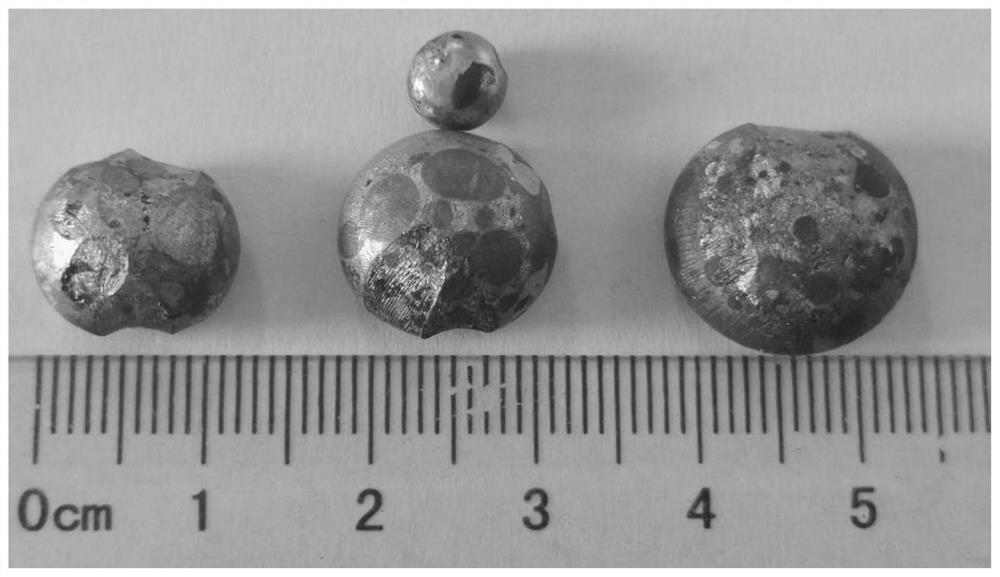
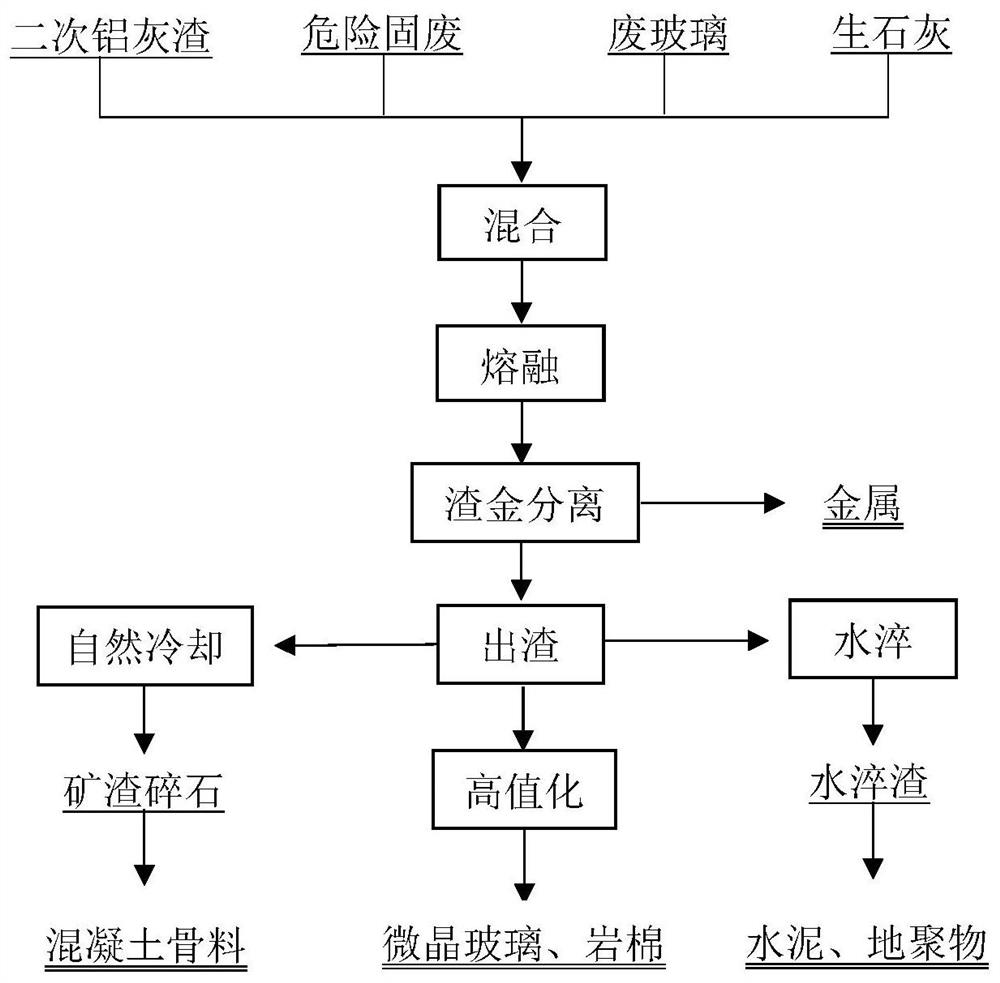
[0047] Mix 20wt.% of secondary aluminum ash, 20wt.% of hazardous solid waste (all stainless steel slag), 30wt.% of waste glass and 30wt.% of quicklime to obtain a mixture. The mixture is heated to 1200° C. for melting and kept for 3.0 hours, and the heavy metal ions in the stainless steel slag are reduced to liquid metal by using the aluminum nitride in the secondary aluminum ash slag. The liquid metal has a high density and is located at the bottom of the melt; the slag phase has a low density and is located at the upper part of the melt. The liquid metal is casted through the taphole to obtain metal; the slag phase flows out through the slag taphole, and the slag crushed stone is obtained after natural cooling, which is used as a resource for the production of concrete aggregate.
Embodiment 2
[0049] Mix 20wt.% of secondary aluminum ash, 20wt.% of hazardous solid waste (including 15wt.% of stainless steel slag, 5wt.% of pickling sludge), 30wt.% of waste glass and 30wt.% of quicklime to obtain a mixture. The mixture is heated to 1200°C for melting and kept for 2.5 hours, and the heavy metal ions in the stainless steel slag and pickling sludge are reduced to liquid metal by using the aluminum nitride in the secondary aluminum ash slag. The liquid metal has a high density and is located at the bottom of the melt; the slag phase has a low density and is located at the upper part of the melt. The liquid metal is casted through the tap hole to obtain metal; the slag phase flows out through the slag tap, and the high-temperature slag is obtained after heat preservation, which is used as a resource for the production of glass-ceramics.
Embodiment 3
[0051] Mix 20wt.% of secondary aluminum ash, 20wt.% of hazardous solid waste (10wt.% of stainless steel slag, 10wt.% of pickling sludge), 30wt.% of waste glass and 30wt.% of quicklime to obtain a mixture. The mixture is heated to 1200° C. for melting and kept for 2.0 hours, and the heavy metal ions in the stainless steel slag and pickling sludge are reduced to liquid metal by using the aluminum nitride in the secondary aluminum ash slag. The liquid metal has a high density and is located at the bottom of the melt; the slag phase has a low density and is located at the upper part of the melt. The liquid metal is casted through the tap hole to obtain metal; the slag phase flows out through the slag tap, and is water-quenched to obtain water-quenched slag, which is used as a resource for cement production.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com