Adoptive t-cell therapy for cmv infection and cmv-associated diseases
A cell and cell proliferation technology, applied in animal cells, vertebrate cells, preparation methods of peptides, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the risk of transplant rejection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] Example 1: Patient Characteristics
[0127] To assess the safety of autologous T cell therapy in solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients with CMV-related complications, patients were selected and considered eligible once they met one of the following four criteria:
[0128] (A) CMV reactivation or disease (as defined by histology) following successful initial therapy, e.g., ganciclovir-resistant CMV reactivation;
[0129] (B) Persistent CMV disease, i.e. unresponsive to 2 weeks of salvage foscarnet or other second-line antiviral agents, e.g., recurrent CMV relapse due to refractory to second-line drug therapy;
[0130] (C) Persistence of CMV replication (over 6 weeks by PCR) despite appropriate antiviral therapy; or
[0131] (D) Any CMV reactivation or disease when antiviral therapy is contraindicated based on intolerance or end-organ limitation (eg, renal insufficiency, bone marrow insufficiency), such as end-organ CMV disease or intolerance to antiviral therapy by...
Embodiment 2
[0156] Example 2: Preparation for T cell therapy
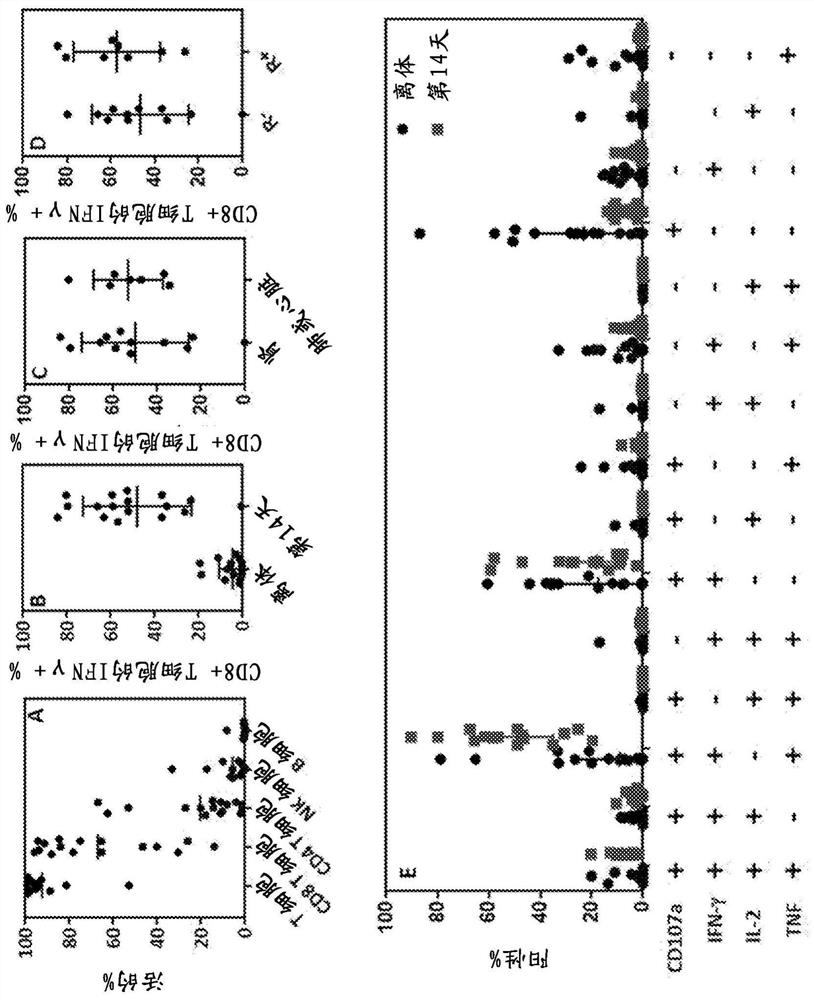
[0157]To generate CMV-specific T-cell therapy, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) obtained from each patient were separately stimulated with a clinical-grade CMV peptide pool in the presence of IL-21 (day 0, 40 ng / mL) Predefined HLA class I and II restricted peptide epitopes including pp65, pp50, IE-1, gH and gB (Table 1). Stimulated samples were then plated in Grex-10 flasks (WilsonWolf Corporation, Saint Paul, MN) at 2-5 x 10 6 cells / cm 2 cultured at the starting cell density. These cultures were supplemented with IL-2 (120 IU / mL) on day 2 and every three days thereafter. On day 14, expanded T cells were harvested and frozen in 1 mL single-dose aliquots in Alpexex 4 (CSLBehring, Broadmeadows, Australia) containing 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (WAK-Chemie Medical GmbH, Steinbach, Germany) in the sample. T cells were tested for microbial contamination prior to infusion and characterized for phenotype and function usin...
Embodiment 3
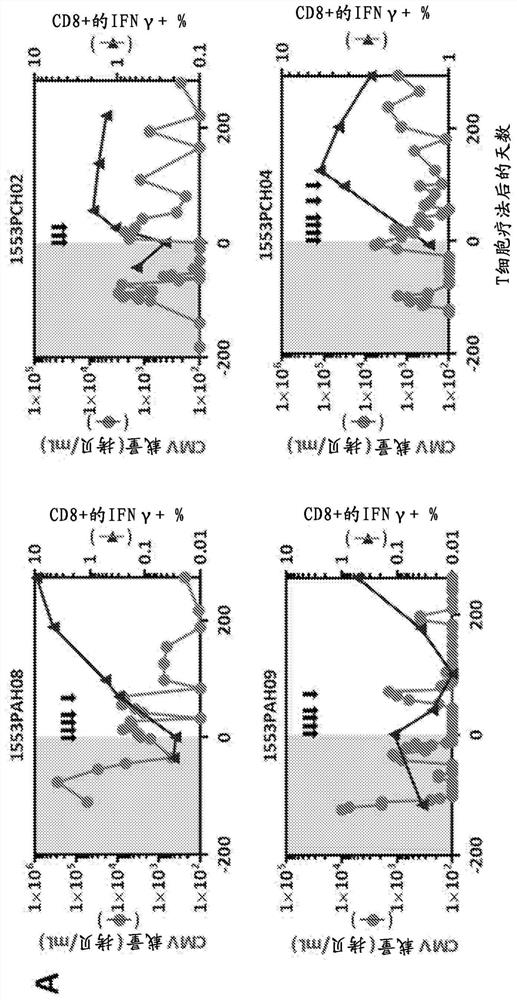
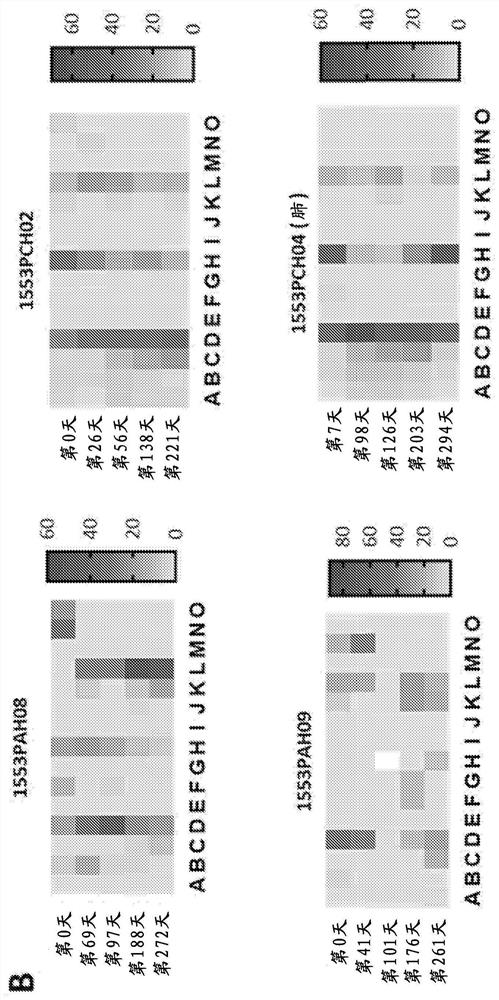
[0167] Example 3: Clinical Outcomes After Adoptive Immunotherapy
[0168] None of the patients who received adoptive CMV-specific T-cell therapy exhibited treatment-related grade 3, 4, or 5 adverse events (Table 4). All adverse events considered at least possibly attributable to T-cell infusion were grade 1 and 2, including fatigue and malaise. Importantly, no adverse events related to changes in graft status were detected. Clinical follow-up of patients designated for T-cell therapy intervention showed that 11 of 13 patients showed objective symptom improvement. These improvements include reducing or resolving CMV reactivation and / or disease, as well as improving response to antiviral drug therapy. Among the 11 patients who demonstrated clinical response, the median peak viral load prior to adoptive T-cell therapy was 3.2 × 10 4 CMV copies / mL blood (range 1.4 × 10 3 –3.44×10 5 copy). Median viral load decreased to 1.2 × 10 after adoptive immunotherapy 3 CMV copies / mL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com