Method for detecting residual titer of erythromycin A in erythromycin fungi residues
A technology of erythromycin bacterial residue and determination method, which is applied in the directions of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex bacteria residues, inability to accurately detect the content of erythromycin A, and many interfering substances.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
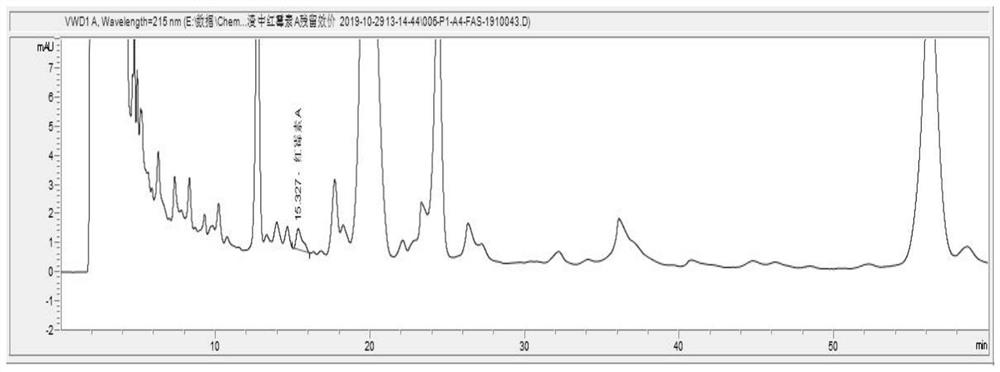
[0048] Determination of residual potency of erythromycin A in solid spray-dried inactivated erythromycin residue
[0049] 1) Preparation of mobile phase
[0050] Mobile phase A is 0.025mol / L phosphate buffer solution; mobile phase B is acetonitrile; mobile phase A: mobile phase B is 55:45.
[0051] 2) Extraction and separation of solid erythromycin residue
[0052] Take the spray-dried and inactivated solid erythromycin slag sample, grind it with a grinding bowl for more than 300 laps with medium force, and grind it to a fine and uniform powder, so that the powder particle size is D97=218.01μm; weigh the spray-inactivated erythromycin Put 5 g of the ground sample of the bacterial residue (accurate to 0.1 mg), into a 50 ml volumetric flask, add an appropriate amount of methanol, vortex for 1 min, ultrasonically assisted extraction for 10 min, centrifuge at 4500 rpm for 10 min, and take the supernatant.
[0053] 3) Detection of erythromycin residue titer
[0054] a. Chromatog...
Embodiment 2
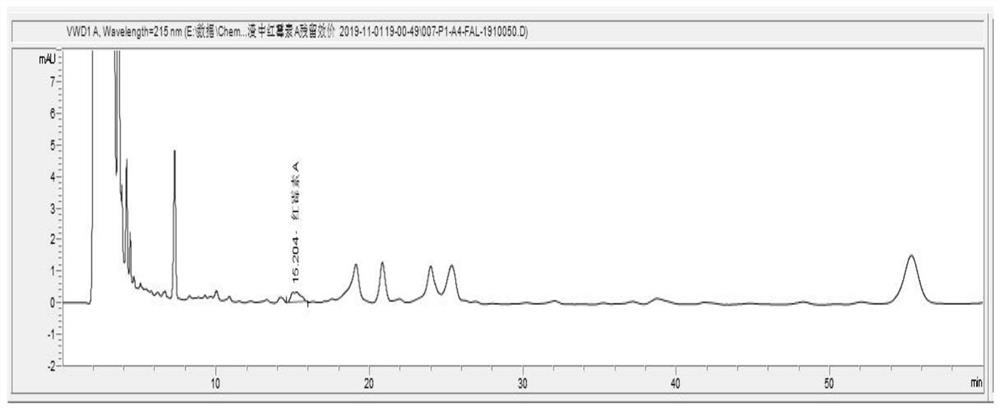
[0075] Determination of residual potency of erythromycin A in liquid inactivated erythromycin residue
[0076] 1) Preparation of mobile phase
[0077] With step 1) among the embodiment 1.
[0078] 2) Extraction and separation of a batch of liquid erythromycin residue
[0079] Take the liquid inactivated erythromycin residue sample, weigh 5g of the liquid inactivated erythromycin residue sample (accurate to 0.1mg), add an appropriate amount of methanol to a 50ml volumetric flask, vortex for 1min, and ultrasonically assist extraction for 30min. Add methanol to dilute to the mark, centrifuge at 4500rpm for 10min, and take the supernatant.
[0080] 3) Detection of erythromycin residue titer
[0081] With step 3) in embodiment 1.
[0082] 4) Determination result data of erythromycin A residue in a batch of liquid inactivated erythromycin residue
[0083] For the results of the system suitability test and the determination of erythromycin residue A in a batch of liquid inactiva...
experiment example 3
[0088] Experimental Example 3 Repeatability Experiment
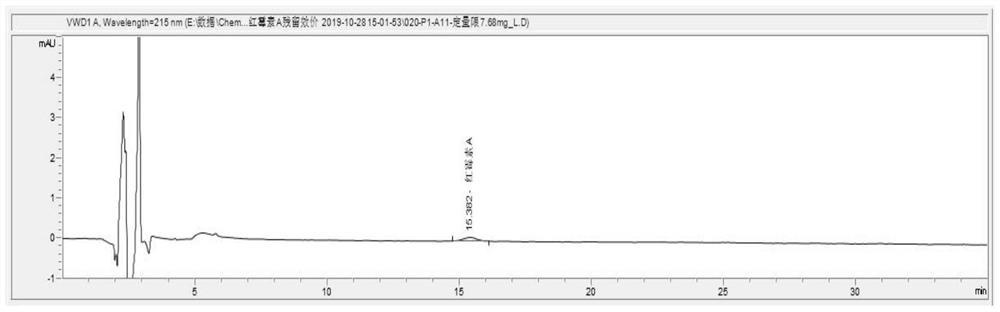
[0089] Accurately weigh two parts of about 40 mg of erythromycin reference substance, accurately weigh them, place them in two 10ml volumetric flasks respectively, dissolve them with methanol and dilute to the scale, shake well and repeat the measurement 6 times according to the chromatographic conditions of the analysis method, the results See Table 3.
[0090] Table 3 Repeatability experiment
[0091] serial number Erythromycin retention time (min) Erythromycin peak area (mAU*s) 1 15.469 1804.61218 2 15.459 1806.45020 3 15.443 1801.22144 4 15.430 1796.55554 5 15.417 1799.17029 6 15.408 1809.18335 RSD 0.036% 0.33%
[0092] Conclusion: After 6 consecutive injections, the RSD of retention time was 0.036%, and the RSD of peak area was 0.33%, indicating good repeatability.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com