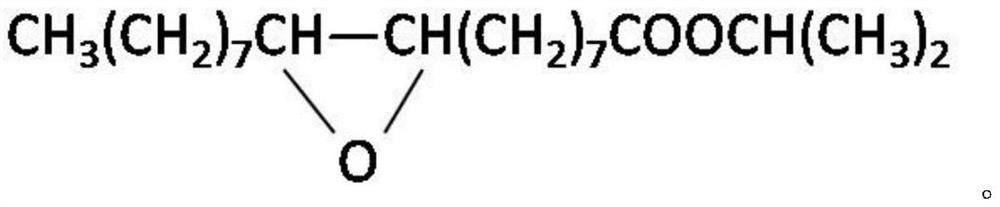Preparation method of chemically modified lipase, lipase and application of lipase in synthesis of L-lactide
A technology for chemically modifying and immobilizing lipase, which is applied in the field of lipase catalysts and can solve problems such as limitations, catalytic activity, stability, and resistance to organic solvents that cannot be effectively improved at the same time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This example provides a chemically modified immobilized lipase. The preparation method comprises: weighing 1 g of lipase (Candida antarctica lipase B, product of Sigma Company), adding 50 mL of sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH7.5) , then add petroleum ether 500mL (which contains 1mL epoxy isopropyl oleate), stir and mix thoroughly for 24h;
[0039] Then add 50 g of solid-phase carrier macroporous resin ECR1030M (Purolite company product), shake the water-bath shaking table for 8 hours (30 ° C, 120 r / min) after adsorption, separate the solid and supernatant by suction filtration, and wash and immobilize with sodium phosphate buffer The enzyme was then vacuum-dried at 35°C for 3 hours to obtain chemically modified and immobilized lipase CALB-M1, which was stored in a refrigerator at 4°C until use.
Embodiment 2
[0044] The lipases prepared in Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were tested for activity respectively. The determination method is as follows:
[0045] Weigh immobilized lipase (CALB1 and CALB-M1 each 20mg), then add sodium phosphate buffer (50mM, pH7.5) 5mL in a 50mL Erlenmeyer flask, preheat in a constant temperature water bath shaker at 37°C for 15min, then add 5 mL of tributyrin was shaken at 200 rpm for 20 min, and 15 mL of 95% ethanol was added to stop the reaction. Blank is to use buffer instead of enzyme solution. After the reaction was terminated, the fatty acid produced by the reaction was titrated with 0.05 mol / L sodium hydroxide standard solution, using phenolphthalein as indicator.
[0046] Enzyme activity is defined as: under the above conditions, the amount of enzyme required to generate 1 μmol of fatty acid per minute is 1 activity unit, expressed in LU / mg. Calculated as follows:
[0047]
[0048] Among them: V1—the volume of NaOH used for titration, ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Using chemically modified lipase to catalyze the synthesis of L-lactide, the steps include: the reaction system is carried out in a 1000mL conical flask with a stopper, and the chemically modified immobilized lipase CALB-M1 10.0 prepared in Example 1 is added to the reaction flask g, L-lactic acid 180.0g (2.0mol), 5A molecular sieve 20.0g, petroleum ether 450mL; at 25°C, 400rpm, react for 48h.
[0059] After the reaction, filter and remove 5A molecular sieves, solid-phase enzyme catalysts, etc., and collect the reaction solution; the collected reaction solution is concentrated at 60±2°C in vacuo to remove the solvent petroleum ether, and a light yellow viscous liquid is obtained; the viscous liquid Distill under -0.09MPa vacuum condition, discard the fraction before the low temperature, collect the fraction with a temperature of 130±5°C, cool and crystallize, and obtain 109.4g of L-lactide white crystals, the yield is 76% (109.4 / 180), and the content is 99.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com