Aqueous zinc ion battery electrolyte additive
An electrolyte additive, zinc-ion battery technology, applied in water-based electrolytes, secondary batteries, acidic electrolytes, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient site coverage, weak inhibition of hydrogen evolution reaction, weak molecular adsorption and binding force, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] This embodiment provides a method for using an amino acid electrolyte additive:
[0028] The additive used in this embodiment is:
[0029]
[0030] Wherein m is 0, n is 1, wherein K2 (basic amino acid residue) is selected from arginine, that is, the additive is arginine of amino acids.
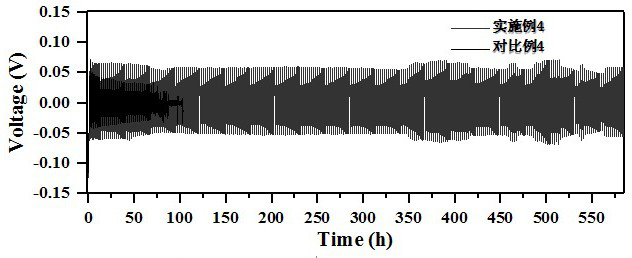
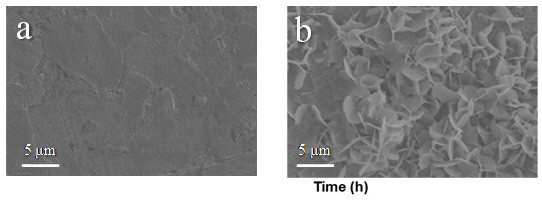
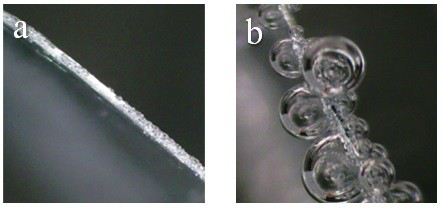
[0031] Dissolve 0.01 mol of arginine and 0.3 mol of zinc sulfate in deionized water to prepare 100 ml of electrolyte solution containing 3 mol / L zinc sulfate and 0.1 mol / L arginine. One of the Ti flakes / Zn flakes / Cu mesh was placed in the electrolyte as a current collector for the electrodeposition of zinc. The deposition morphology of zinc was as follows: figure 1 a, Zinc deposition without obvious dendrites. The zinc deposition was then observed in situ with an optical microscope, as shown in figure 2 a, It can be seen from the figure that there are no obvious bubbles during the deposition process, reflecting that the hydrogen evolution reaction is not obvious during the zinc d...
Embodiment 2
[0036] This example provides a method of using a lipopeptide electrolyte additive:
[0037] The additive used in this embodiment is:
[0038]
[0039] Where m is 1, and K1 is a saturated carbon chain in the fatty acid acyl chain, which corresponds to a fatty acid with a carbon number of 12, that is, a lauric acid acyl chain.
[0040] n is 4, wherein K2 (basic amino acid residue) is selected from lysine.
[0041] That is, the additive is a lipopeptide composed of lauric acid (containing 12 carbons) and 4 lysine polycondensed, which is abbreviated as C12K4 in this example (C12 refers to the acyl chain of lauric acid, and K refers to the residue of lysine).
[0042]Dissolve 0.001 mol of additive C12K4 and 0.1 mol of zinc sulfate in deionized water to prepare 100 ml of electrolyte solution containing 1 mol / L zinc sulfate and 0.01 mol / L lipopeptide. One of the Ti flakes / Zn flakes / Cu mesh was placed in the electrolyte as a current collector for the electrodeposition of zinc. Th...
Embodiment 3
[0044] This example provides a method of using a lipopeptide electrolyte additive:
[0045] The additive used in this embodiment is:
[0046]
[0047] Wherein m is 1, K1 is the saturated carbon chain in the fatty acid acyl chain, and its corresponding fatty acid carbon number is 24, namely the acyl chain of lignoceric acid.
[0048] n is 1, wherein K2 (basic amino acid residue) is selected from lysine.
[0049] That is, the additive is a lipopeptide formed by polycondensation of lignoceric acid (containing 24 carbons) and 1 lysine, which is abbreviated as C24K1 in this example (C24 refers to the acyl chain of lignoceric acid, and K1 refers to a lysine residue).
[0050] Dissolve 0.01 mol of additive C24K1 and 0.2 mol of zinc chloride in deionized water to prepare 100 ml of electrolyte solution containing 2 mol / L zinc chloride and 0.1 mol / L lipopeptide. One of the Ti sheet / Zn sheet / Cu mesh is placed in the electrolyte as a current collector for zinc electrodeposition, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com