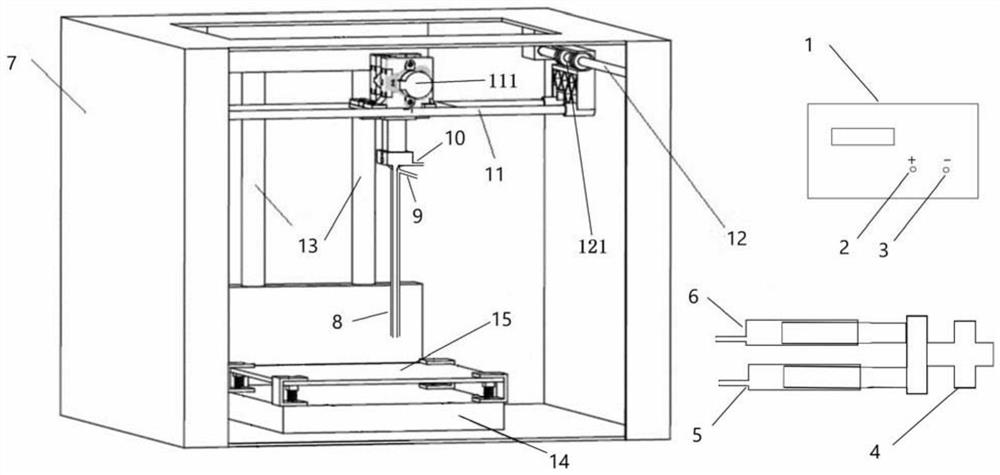
3D printed artificial periosteum, artificial bone, artificial skeleton and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing and artificial bone technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of increased infection risk, application restrictions, surrounding fibrosis, etc., and achieve improved mechanical strength and biocompatibility, good tissue compatibility and degradability , promote the effect of degradation and bone remodeling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] 1. Preparation of 3D printed artificial bone
[0071] 2g of nanoscale porcine cross-linked collagen fibers, 4g of nanoscale hydroxyapatite, and 94g of PLA (Sigma, USA) were used for ultrasonic dispersion, and 120mL of chloroform was added and mixed by mechanical stirring. After mixing evenly, vacuum freezing Dryer for drying. Then use a crushing machine to crush to form small particles with a particle size of ≤2mm. Finally, use a single / twin-screw extruder to set the temperature in the three zones to 160°C, 190°C, and 160°C (extrusion die) for wire production. Made and extruded into a uniform 3D printable linear material with a diameter of 2mm. The performance of the produced wire was tested, the tensile strength was 29.7MPa, the elongation at break was 6.7%, and the tensile modulus was 984MPa.
[0072] In the implementation of bone repair surgery, according to the actual size and shape of the patient's bone defect, the artificial bone linear material is used as a raw...
Embodiment 2
[0081] 1. Preparation of 3D printed artificial bone
[0082] 3g of nanoscale porcine cross-linked collagen fibers, 7g of nanoscale hydroxyapatite, and 90g of PLA (Sigma, the United States) were used for ultrasonic dispersion, and 110mL of chloroform was added and mixed by mechanical stirring. After mixing evenly, vacuum freezing Dryer for drying. Then use a crushing machine to crush to form small particles with a particle size of ≤2mm. Finally, use a single / twin-screw extruder to set the temperature in the three zones to 150°C, 200°C, and 160°C (extrusion die) for wire production. Made and extruded into a uniform 3D printable linear material with a diameter of 2.0mm. The produced wire rod was tested for performance, and the tensile strength was 35.2 MPa, the elongation at break was 6.9%, and the tensile modulus was 1228 MPa.
[0083] In the implementation of bone repair surgery, according to the actual size and shape of the patient's bone defect, the artificial bone linear m...
Embodiment 3
[0091] 1. Preparation of 3D printed artificial bone
[0092] 1g of nanoscale porcine cross-linked collagen fibers, 2g of nanoscale hydroxyapatite, and 95g PLA (Sigma, USA) were used for ultrasonic dispersion, and 110mL of chloroform was added and mixed by mechanical stirring. After mixing evenly, vacuum freezing Dryer for drying. Then use a crushing machine to crush to form small particles with a particle size of ≤2mm. Finally, use a single / twin-screw extruder to set the temperature in the three zones to 150°C, 180°C, and 150°C (extrusion die) for wire production. Made and extruded into a uniform 3D printable linear material with a diameter of 2mm. The performance of the produced wire was tested, and the tensile strength was 26.3MPa, the elongation at break was 6.6%, and the tensile modulus was 870MPa.
[0093] In the implementation of bone repair surgery, according to the actual size and shape of the patient's bone defect, the artificial bone linear material is used as the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com