Natural strain for producing pullulan and application of natural strain
A technology of pullulan polysaccharides and bacterial strains, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of small cells, large glucose repression, and ineffective control of bacterial contamination.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
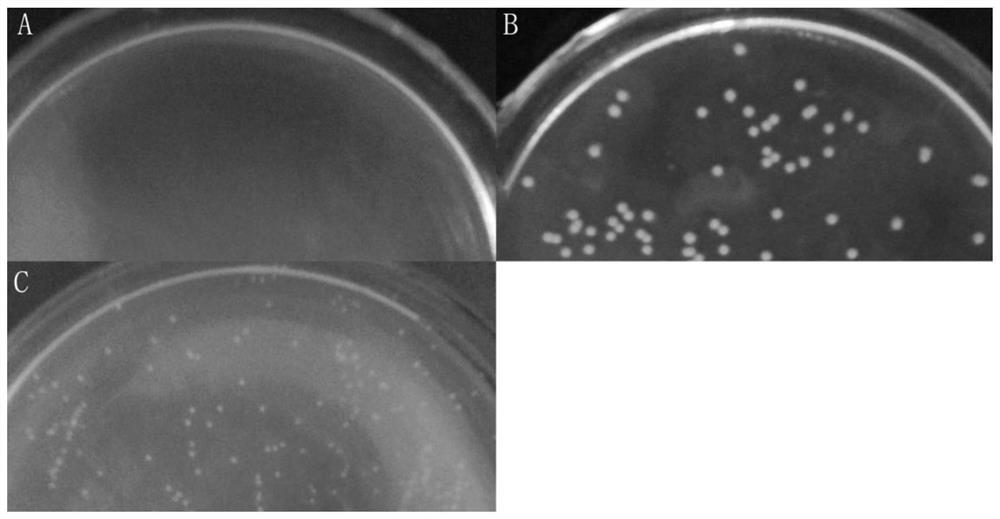
[0031] Embodiment 1: strain screening
[0032] 1. Collection of samples and separation of yeast cells
[0033] When Sophora japonica blooms in May every year in the north, collect 100 grams of honeycombs from all over the country, and quickly put them into sterile centrifuge tubes through aseptic operation. Take it back to the microbiology laboratory quickly, inoculate 1-2 grams of honey into 50.0 mL of liquid medium containing 140.0 g / L glucose and 0.5 g / L chloramphenicol, and culture it at a constant temperature of 28 ° C for 5 days. Dilute the bacterial suspension obtained with sterile physiological saline, and carry out a series of dilutions, and the diluted solution is evenly spread on the solid medium containing 140.0g / L glucose and 0.5g / L chloramphenicol by aseptic operation, at 28 Cultivate at constant temperature for 5 days to obtain various colonies. According to the unique colony morphological characteristics of different strains of Aureobasidium spp., different c...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Morphological observation and taxonomic identification of XCC bacterial strains
[0037] The XCC strains were cultured on the above-mentioned YPD medium plate and potato juice+10.0g / L glucose+20.0g / L agar (PDA) plate (28°C) for 4 days. Use an ordinary camera to take pictures of the colony morphology, observe the cultured yeast cells with a 100× oil lens of a fluorescent microscope, and take pictures. It is found that most of the cells of the XCC strain cultured on the YPD plate are typical yeast budding cells, that is, there are transparent arthrospores . Most of the cells cultured on the PDA plate were chryspores with and without melanin, and the chryspores without melanin could divide by forming diaphragms.
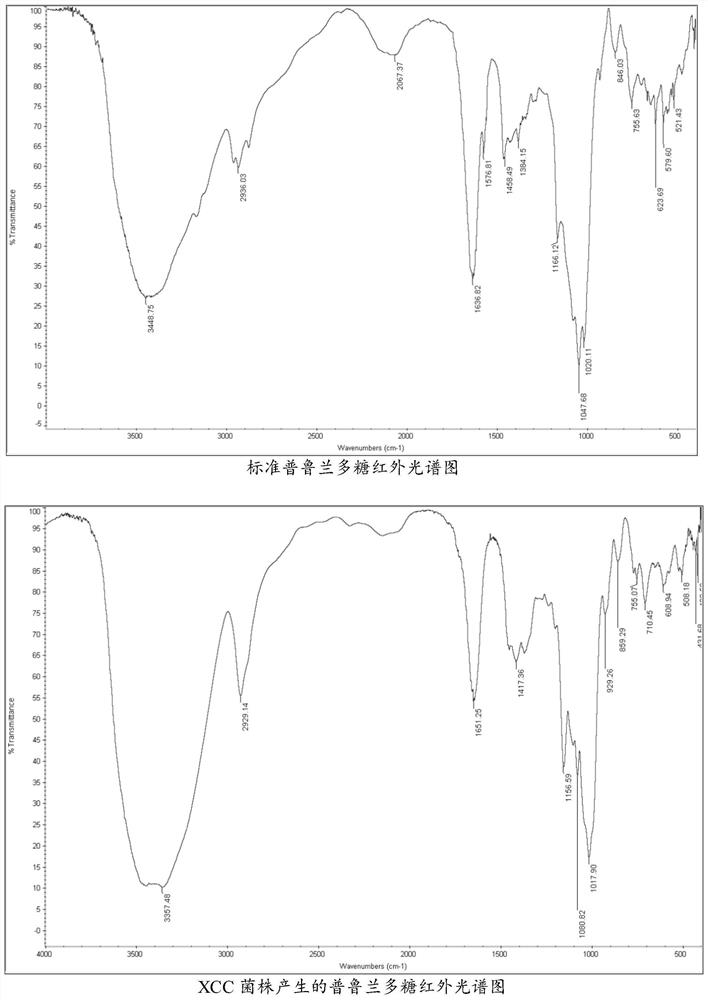
[0038] When cultured in the medium for producing pullulan, most of the cells of the XCC strain are thick-walled spores that do not contain melanin, and the production of pullulan is very high at this time, so it is the thick-walled spores that do not ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Preparation of XCC strain cell ultrathin sections and transmission electron microscope observation
[0040] In order to compare with the currently widely used pullulan-producing Aureobasidium melanogenum P16 strain (hereinafter referred to as P16 strain) cells, the above-mentioned pullulan-producing fermentation medium was used to cultivate XCC strain and P16 strain at the same time. The cultured cells were prefixed with 3.0% glutaraldehyde (prepared with 0.1M phosphate buffer) for 3 hours, and then fixed with 1.0% osmic acid for 2 hours. The fixed cells were dehydrated with ethanol, and the dehydrated cells were embedded in Epon-812 resin. Ultrathin sections of embedded yeast cells were prepared with an ultramicrotome (LKB-NOVA, Japan) and stained with lead acetate and uranyl acetate. The prepared ultrathin sections of yeast were observed and photographed with a transmission electron microscope (H-7000, Hitachi, Japan). It was found that most of the cells ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com