Fine processing method of crude hexane
A technology for fine processing and crude hexane, applied in separation methods, hydrotreating processes, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of increased load of processing equipment, inability to meet production requirements, and increased processing costs, and achieve improved fractionation accuracy. , good stability and regeneration performance, and the effect of reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
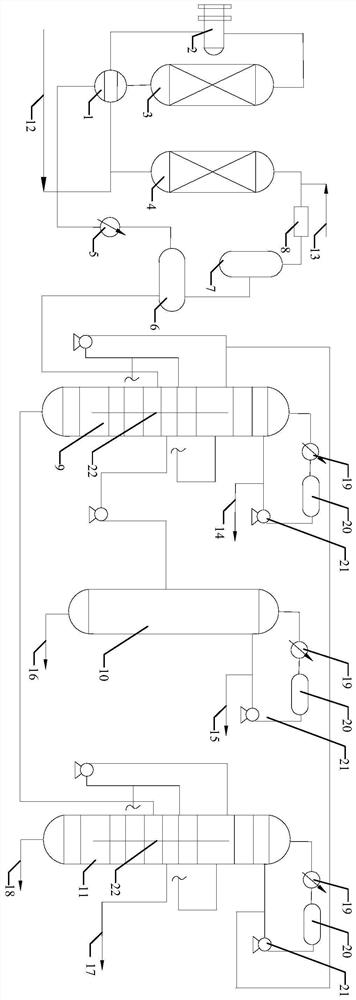
[0025] A fine processing method of crude hexane, which comprises the following steps:
[0026] Step 1. The raw material crude hexane is mixed with hydrogen, and after exchanging heat with the reaction product, the temperature is 73°C, heated to 144°C by a heater, enters the reactor to contact with the catalyst, and carries out the hydrofining reaction under the action of the hydrofining catalyst , Catalyst I is a Ni-based catalyst with a spherical appearance and a specific surface area of 50-90m 2 / g, pore volume: 0.15~0.3ml / g, bulk specific gravity: 0.6±0.02g / ml, radial compressive strength: 24~38N / grain.
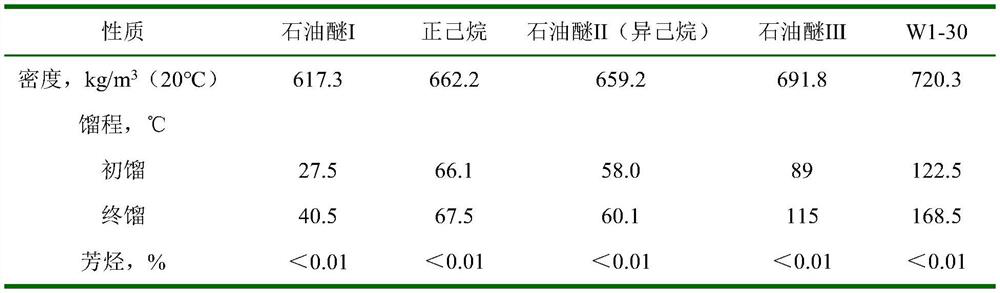
[0027] Step 2. After the gas-liquid separation of the reaction product in the low-pressure separator, it enters the first partition tower for fractionation, and the petroleum ether I product comes out from the top of the tower; the mixed carbon six comes out of the side line, and the mixed carbon six enters the de-hexanizer for de-hexanization Separation, petroleum ethe...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A fine processing method of crude hexane, which comprises the following steps:
[0037] Step 1. The raw material crude hexane is mixed with hydrogen, and after heat exchange with the reaction product, the temperature is 72°C, heated to 147°C by a heater, entering the reactor to contact with the catalyst, and the hydrofining reaction is carried out under the action of the hydrofining catalyst , Catalyst I is a Ni-based catalyst with a spherical appearance and a specific surface area of 60-85m 2 / g, pore volume: 0.18~0.35ml / g, bulk specific gravity: 0.6±0.02g / ml, radial compressive strength: 32~40N / grain.
[0038] Step 2. After the gas-liquid separation of the reaction product in the low-pressure separator, it enters the first partition tower for fractionation, and the petroleum ether I product comes out of the top of the tower; the mixed carbon six comes out of the side line, and enters the de-n-hexane tower for separation; The heavy component oil comes out from the b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com