A hybrid magnetic circuit permanent magnet synchronous motor for electric vehicles and its driving method
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and hybrid magnetic circuit technology, applied in electric vehicles, motor generator control, AC motor control, etc. The effect of compact structure and high effective magnetic density of air gap
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
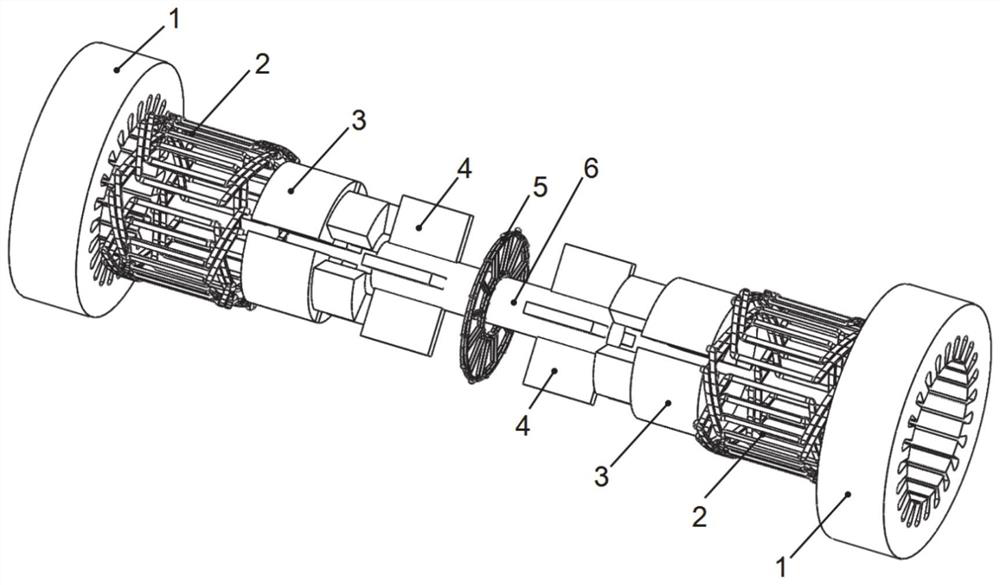
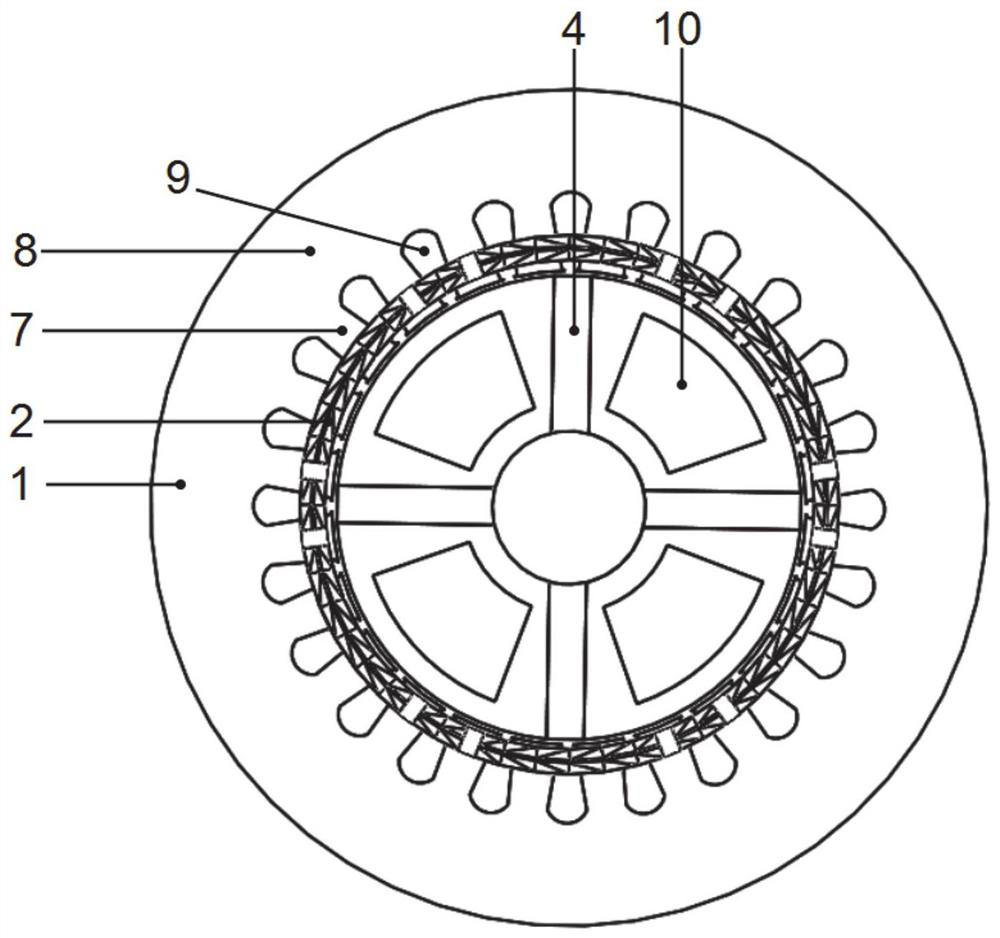
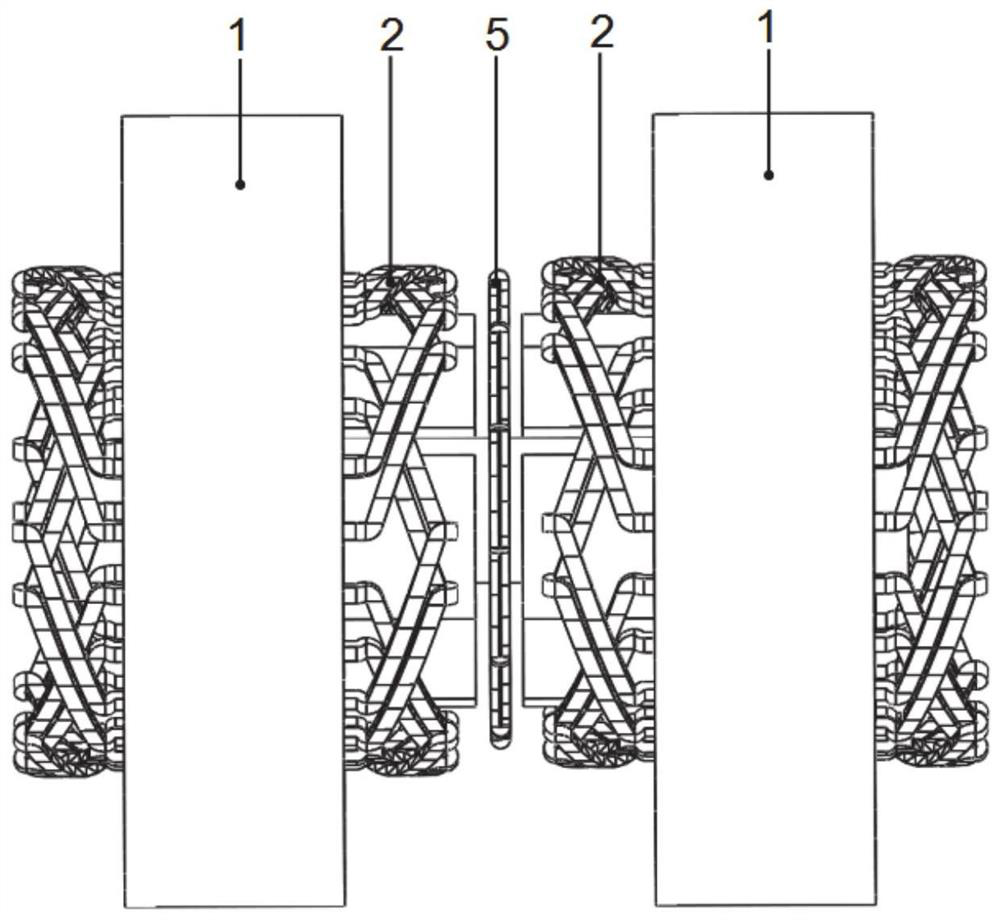
[0068] Such as figure 1 As shown, the overall three-dimensional schematic diagram of the motor, the number of phases of the motor in this embodiment is 3, the number of radial stator teeth is 24, the number of rotor slots is 8, the number of permanent magnet blocks is 8, the number of radial magnetic poles is 4, and the number of axial magnetic poles is 4. This embodiment includes a radial stator, an axial winding and a rotor. The radial stator is made of laminated silicon steel sheets, such as figure 2 As shown, the radial stator includes radial stator teeth 7, radial stator yoke 8 and radial stator slots 9, radial armature windings 2 are placed in the radial stator slots 9, and the radial armature windings 2 can be distributed windings , concentrated winding or stacked winding, the number of poles of the radial armature winding is consistent with the number of radial magnetic poles of the rotor, the radial stator and the rotor are coaxial, and there is a radial air gap betw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com