A high-stable friction-resistant train brake disc and its preparation method
A technology of friction resistance and brake discs, which is applied in the direction of friction linings, manufacturing tools, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of friction stability and low-temperature strength and toughness matching, so as to improve friction instability and improve low-temperature strength. Tough matching, the effect of improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
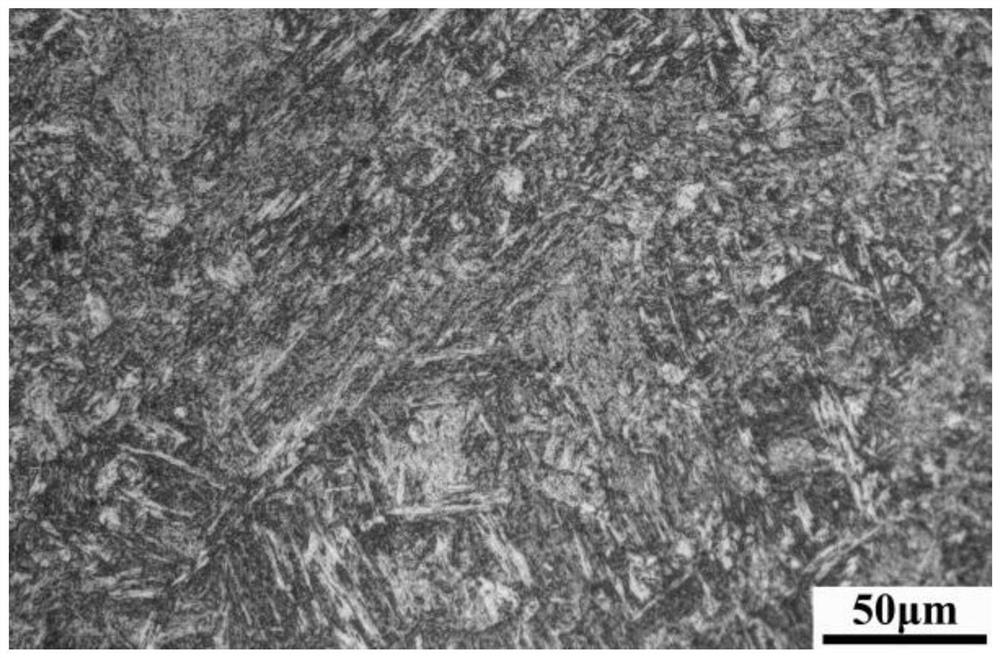
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
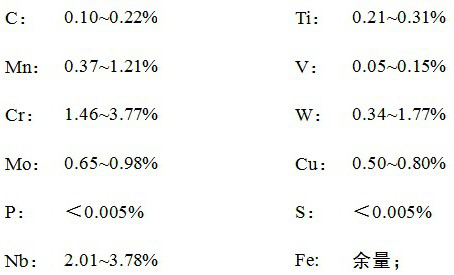
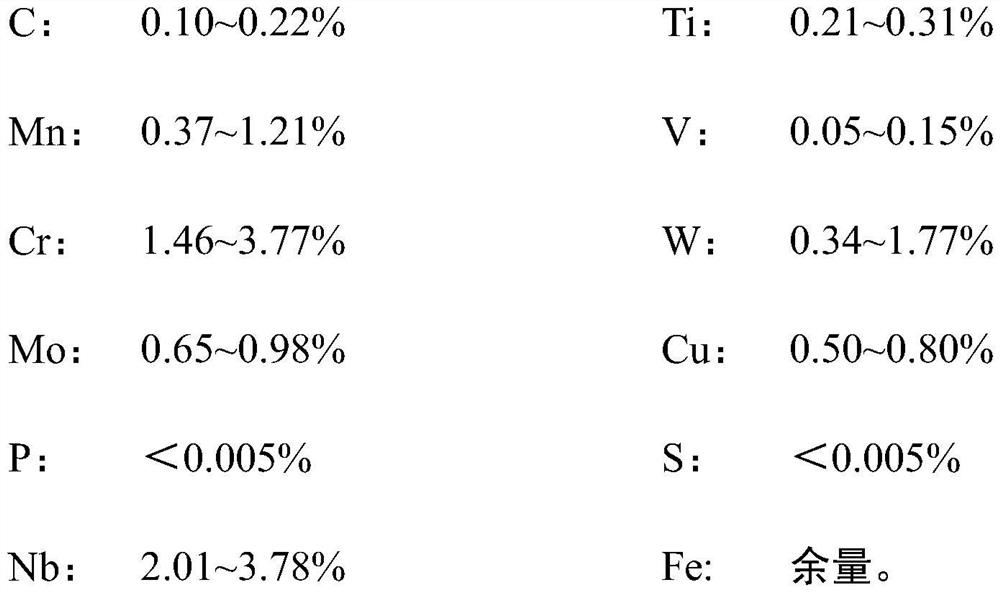
[0033] A high-stable friction-resistant train brake disc, in terms of mass percentage, its raw materials and proportioning are as follows:
[0034]
[0035]
[0036] A method for preparing a high-stable friction-resistant train brake disc, comprising the following steps:
[0037] S1. Alloy smelting: using an electric furnace for segmental smelting. First, heat the molten iron to 1650°C to fully melt it to obtain molten steel; The Ti, Mn, V, Cr, W, Mo, Cu, P, S and Nb elements prepared in mass percentage are added to the refining furnace for refining to obtain refined molten steel;
[0038] S2. Alloy casting: adding a crystal forming agent to the refined molten steel, and then casting it into an ingot;
[0039] S3. Alloy composite forging: use free forging to forge the billet; then use the hot-warm intermittent multi-step ring rolling forging process to make the billet to obtain the forged billet;
[0040] S4. Performance heat treatment: The obtained forged billet is su...
Embodiment 2
[0060] A high-stable friction-resistant train brake disc, in terms of mass percentage, its raw materials and proportioning are as follows:
[0061]
[0062] A method for preparing a high-stable friction-resistant train brake disc, comprising the following steps:
[0063] S1. Alloy smelting: using an electric furnace for segmental smelting, firstly heat the molten iron to 1720°C to make it fully melted to obtain molten steel; The Ti, Mn, V, Cr, W, Mo, Cu, P, S and Nb elements prepared in mass percentage are added to the refining furnace for refining to obtain refined molten steel;
[0064] S2. Alloy casting: adding a crystal forming agent to the refined molten steel, and then casting it into an ingot;
[0065] S3. Alloy composite forging: use free forging to forge the billet; then use the hot-warm intermittent multi-step ring rolling forging process to make the billet to obtain the forged billet;
[0066] S4. Performance heat treatment: The obtained forged billet is subjec...
Embodiment 3
[0084] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is only:
[0085] A highly stable and friction-resistant train brake disc, the raw materials and proportions are as follows in terms of mass percentage: C: 0.15%; Ti: 0.25%; Mn: 0.85%; V: 0.10%; Cr: 2.55%; W: 1.00%; Mo: 0.80%; Cu: 0.70%; P: 0.002%; S: 0.001%; Nb: 3.05%;
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com