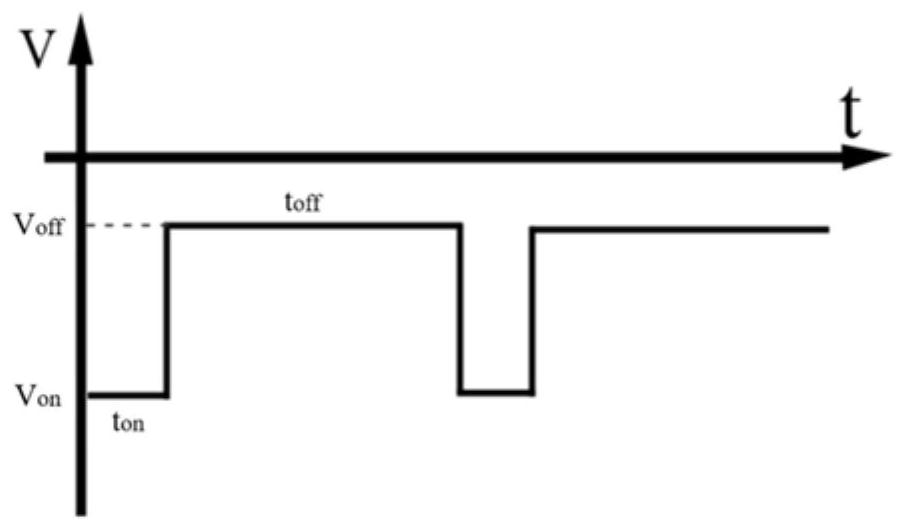
Method for covalently grafting dielectric film on surface of semiconductor
A surface covalent, dielectric film technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as low dielectric constant, and achieve the effects of preventing strong corrosion, controllable composition, and controllable film thickness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035]This embodiment relates to a method for covalently grafting a dielectric film on the surface of a semiconductor based on diazonium salt technology. The semiconductor substrate can be silicon, germanium, or gallium arsenide (specifically, silicon is selected as the substrate in this embodiment). Specific implementation steps as follows:
[0036]Step (1): Using acetone, alcohol and deionized water to ultrasonically clean the semiconductor substrate in sequence at a temperature of 20°C, each cleaning time is 5 minutes;
[0037]Step (2): Place the cleaned semiconductor substrate in a 3v% HF solution at a temperature of 20°C for a immersion time of 1 min;
[0038] Step (3): At a temperature of 20℃, directly immerse the corroded semiconductor surface in the configured chemical solution ① for surface passivation. The immersion time is 30s, so that the semiconductor surface is transformed into a passivation layer surface, thereby preventing the semiconductor The surface is oxidized in the nex...
Embodiment 2
[0044]This embodiment relates to a method for covalently grafting a dielectric film on the surface of a semiconductor based on diazonium salt technology. The semiconductor substrate is silicon. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0045]Step (1): Using acetone, alcohol and deionized water to ultrasonically clean the semiconductor substrate in sequence at a temperature of 20°C, each cleaning time is 5 minutes;
[0046]Step (2): Place the cleaned semiconductor substrate in a 0.5v% HF solution at a temperature of 20°C, and the immersion time is 10 minutes;
[0047]Step (3): Under the condition of temperature 20℃, directly immerse the corroded semiconductor surface in the configured chemical solution ① for surface passivation. The immersion time is 30s, so that the semiconductor surface is transformed into the surface of the passivation layer, thereby preventing the semiconductor The surface is oxidized in the next reaction;
[0048]The configuration process of the chemical solution ...
Embodiment 3
[0053]This embodiment relates to a method for covalently grafting a dielectric film on the surface of a semiconductor based on diazonium salt technology. The semiconductor substrate is silicon. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0054]Step (1): Using acetone, alcohol and deionized water to ultrasonically clean the semiconductor substrate in sequence at a temperature of 20°C, each cleaning time is 5 minutes;
[0055]Step (2): Place the cleaned semiconductor substrate in a 5% volume fraction HF solution at a temperature of 20°C for a immersion time of 1 min;
[0056]Step (3): Under the condition of temperature 20℃, directly immerse the corroded semiconductor surface in the configured chemical solution ① for surface passivation. The immersion time is 1 min, so that the semiconductor surface is transformed into the surface of the passivation layer, thereby preventing the semiconductor The surface is oxidized in the next reaction;
[0057]The configuration process of the chemical so...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com