A bionic intestinal organ chip and its preparation method and application
An organ chip and chip technology, applied in the field of organ bionics, can solve the problems that the uniformity of the villi structure cannot be guaranteed, the inconvenience of experiment data statistics and result comparison, etc., achieve good reproducibility, and reduce the difference in intestinal tissue structure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
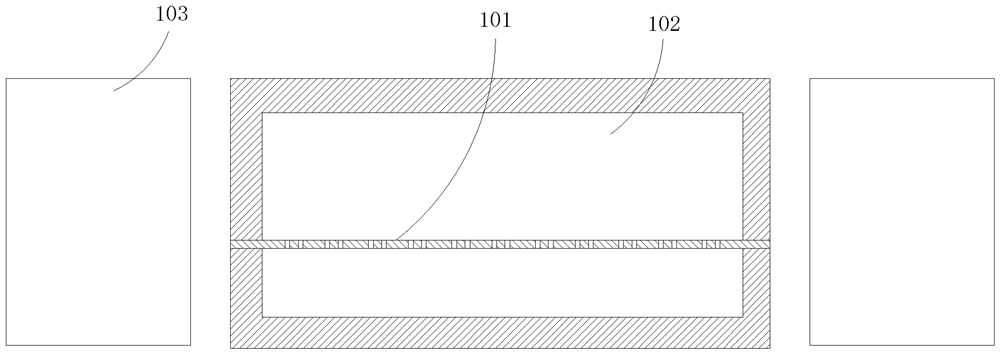
[0025] This embodiment provides a bionic intestinal organ chip. The bionic intestinal organ chip has a three-layer structure, which simulates the dynamic microenvironment in the intestinal tract and is used for dynamic cultivation of intestinal cells. It is suitable for intestinal diseases, drug screening, and food safety. And so on.
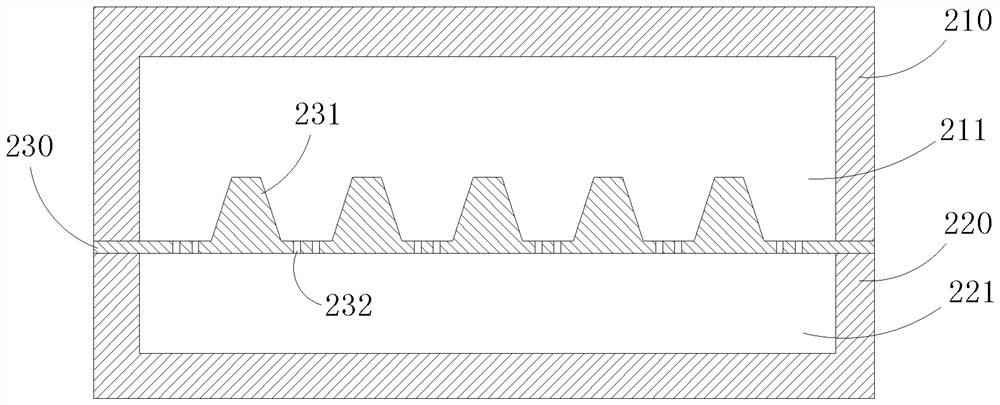
[0026] like figure 2 As shown, there is a fluid channel in the bionic intestinal organ chip of this embodiment. Specifically, the chip includes an upper chip 210 and a lower chip 220 . The lower surface of the upper chip 210 has an open upper fluid channel, the upper surface of the lower chip 220 has an open lower fluid channel, the porous membrane 230 is sealed between the upper chip 210 and the lower chip 220, and the porous membrane 230 is surrounded by the upper chip 210. The upper layer fluid channel 211 is synthesized, and the lower layer fluid channel 221 is surrounded by the porous membrane 230 and the lower layer chip 220 . Several ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a bionic intestinal organ chip. The preparation method mainly adopts soft lithography technology to prepare the bionic intestinal organ chip in the first embodiment above.
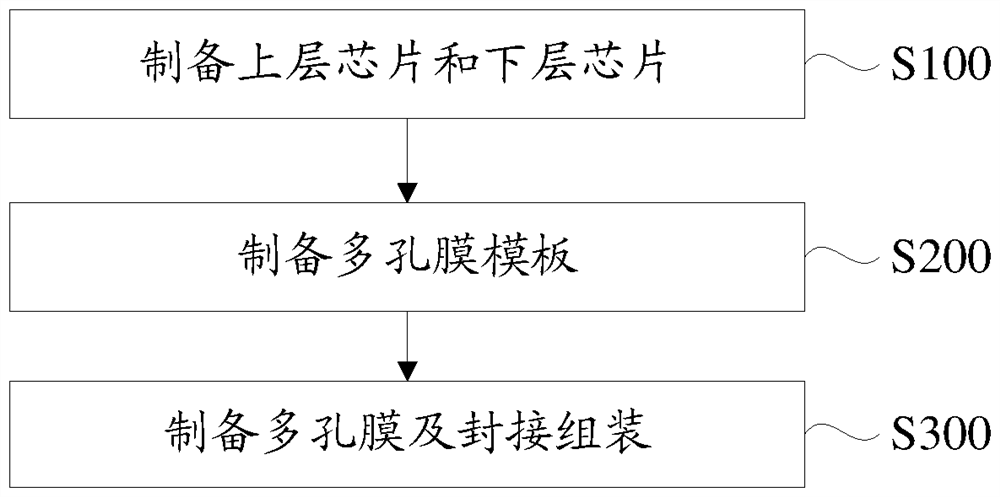
[0034] like image 3 As shown, the preparation method of the bionic intestinal organ chip of this embodiment mainly includes the following steps:
[0035] S100: preparing an upper chip and a lower chip;
[0036] S200: preparing a porous membrane template;
[0037] S300: preparing a porous membrane and sealing and assembling.
[0038] In step S300, a porous membrane is prepared by using a porous membrane template, and the porous membrane is sealed between the upper chip and the lower chip to form a bionic intestinal organ chip. Wherein, the produced porous membrane is distributed with several protrusions for simulating the structure of intestinal villi and several through holes for simulating the intestinal absorption function.
[0039] In the prepa...
Embodiment 3
[0086] This embodiment provides a method for preparing a bionic intestinal organ. This preparation method is carried out through the bionic intestinal organ chip described in Example 1. This method is an application to the bionic intestinal organ chip.
[0087] In this example, three-dimensional intestinal microtissues were constructed and dynamically cultured in the bionic intestinal organ chip, such as Figure 8 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0088] S401: Sterilize the bionic intestinal organ chip;
[0089] Using 70% alcohol and ultraviolet rays to sterilize the bionic intestinal organ chip described in Example 1;
[0090] S402: injecting the extracellular matrix solution into the fluid channel, modifying the porous membrane, and cleaning the fluid channel after modification;
[0091] Inject the extracellular matrix (type I collagen, matrigel, etc.) solution from the inlet of the upper chip into the channel to modify the PDMS porous membrane, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com