Probe composition and kit for screening genetic disease pathogenic gene carriers and preparation method of probe composition and kit
A disease-causing gene and composition technology, which is applied in the field of probe composition for the screening of genetic disease-causing gene carriers, can solve the problems of inappropriate selection of probe capture regions, limited screening of diseases, and high detection costs, achieving Ease of popularization and clinical application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0045] In a second aspect, in some embodiments, the present invention provides a method for preparing a probe composition for genetic disease-causing gene carrier screening, comprising:
[0046] Target capture region selection step, selecting respective target capture regions according to each target gene;
[0047] Probe design step, designing probes according to the target capture region, the capture probes for the non-homologous region of the disease-causing gene in the target capture region are all the same length, and the capture probes for the partial homology region of the disease-causing gene in the target capture region The length of the needle is 110-120nt, and the probe composition for the screening of genetic disease-causing gene carriers is obtained. The purpose of capturing probes in some homologous regions with a length less than 120 nt is to improve the specificity of the capture probes in these regions.
[0048] In some embodiments, after designing the probes,...
Embodiment 1
[0174] SMA-related gene testing
[0175] Using this kit and a commercial kit (Shanghai Wuseshi Medical Research Co., Ltd., Survival Motor Neuron 1 (SMN1) Exon Deletion Detection Kit (Fluorescence Quantitative PCR)) were used to test 418 cases of known clinical results. The samples were tested for SMA-related SMN1 gene exon 7 deletion mutation, based on this detection process as described in the following (1), based on the detection of commercial kits, and operated in full accordance with the instructions of commercial kits (qPCR method).
[0176] (1) Mutation detection process based on this kit
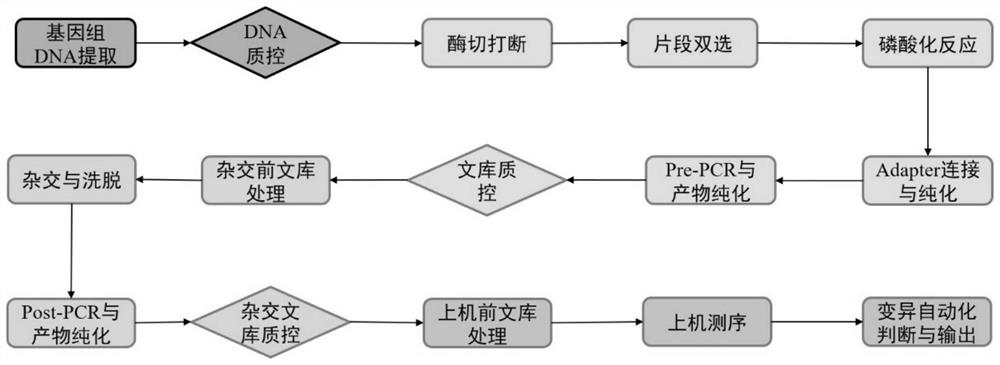
[0177] 1. Genomic DNA fragmentation
[0178] 1.1 According to the ratio in Table 2, prepare the amount of interruption reaction mixture required for the detection in a suitable centrifuge tube.
[0179] Table 2 interrupted reaction mixture
[0180]
[0181] 1.2 Take 5 μL of the interrupted reaction mixture and add it to the PCR tube (containing genomic DNA) in step 1.1, mix well...
Embodiment 2
[0278] Carrier Screening of 6006 Normal Population
[0279] Carrier screening was carried out on 6006 normal people using the same kit as in Example 1, and the variation detection process was as described in step (1) in Example 1.
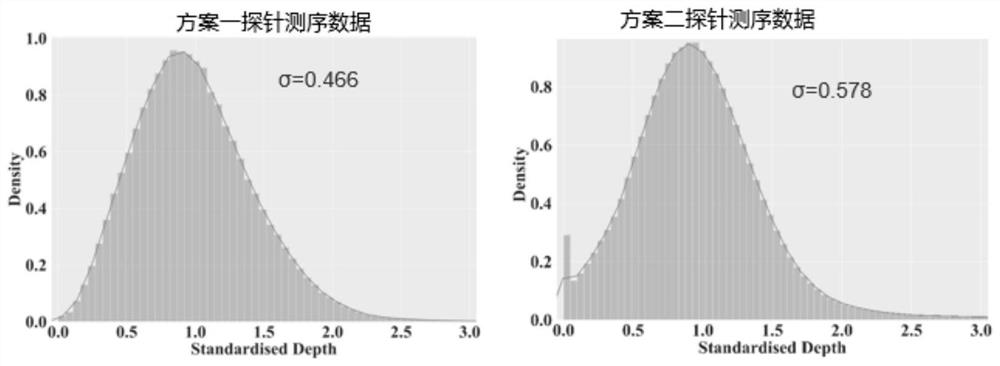
[0280] In the test samples, the depth and coverage of the target regions of the five genetic diseases were uniform, indicating that the probes had good capture uniformity, high on-target rate, and no GC preference.
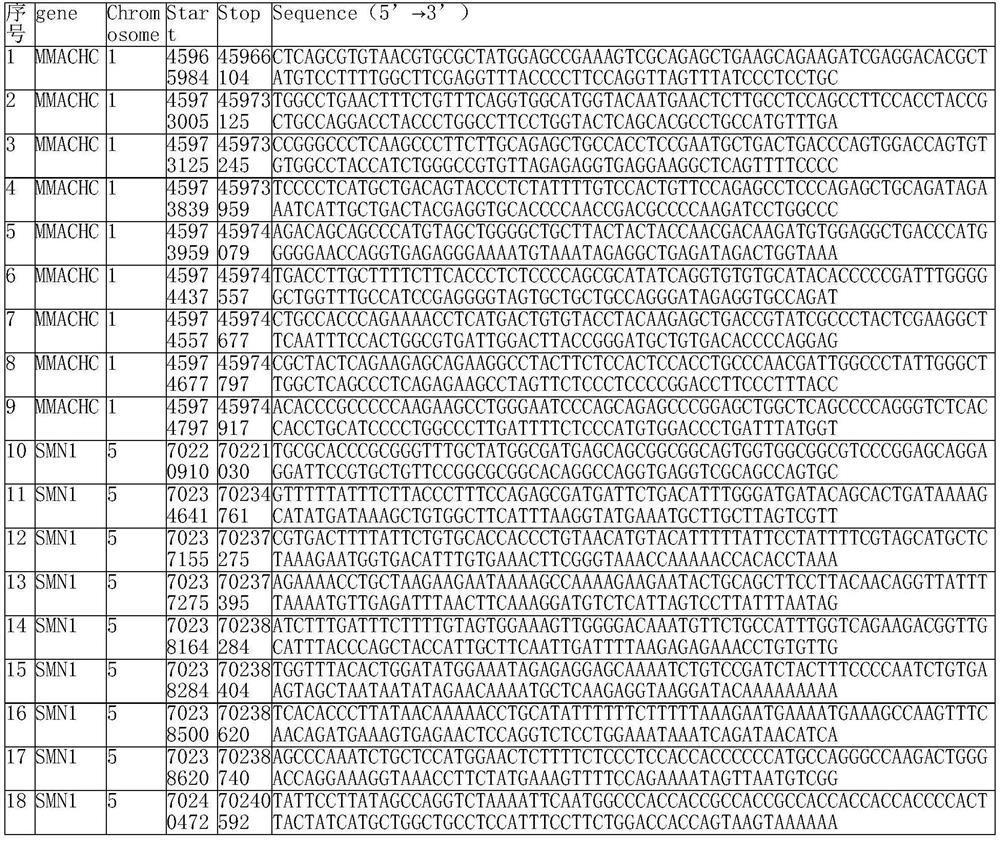
[0281] Among the 6006 normal samples, 122 samples were detected to carry pathogenic variants related to hepatolenticular degeneration, 99 samples to carry pathogenic variants related to cblC type of methylmalonic acidemia, and 87 samples to carry pathogenic variants related to SMA Variation, 217 samples carried pathogenic variants related to thalassemia (α+β).
[0282] If the traditional method is used to carry out carrier screening for the above five diseases, it is necessary to use a combination of three methods (qPCR method + sange...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com