Compact and firm single-degree-of-freedom bionic joint and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of bionic joints and manufacturing methods, applied in the field of robotics, can solve problems such as energy consumption, deformation, tensile resistance, and small torsion resistance, and achieve the effects of improving manufacturing efficiency, reducing manufacturing costs, and high impact resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
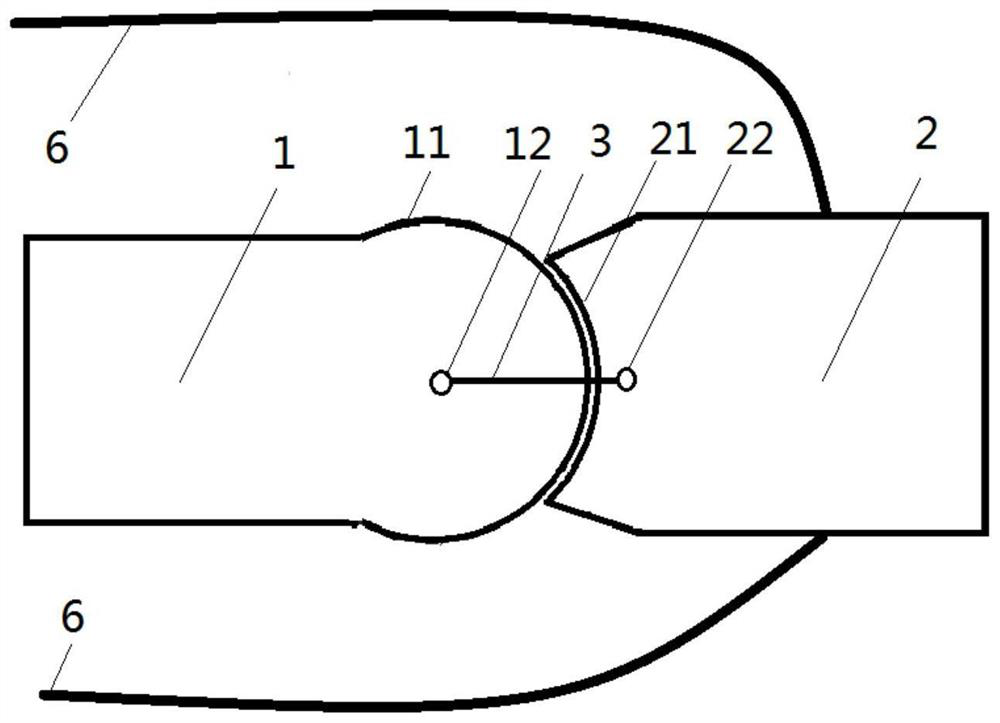
[0059] Reference attached figure 1 , with figure 1 is a side view showing a 1-DOF bionic joint.
[0060] The joint includes a first joint part 1, and the first joint part 1 includes a convex curved surface 11 and a first through hole 12, and the first through hole 12 is located on the central axis of the convex surface.
[0061] The second joint member 2 includes a convex curved surface 21 and a second through hole 22, and the second through hole 22 is near the outer edge of the concave surface. The first joint part 1 and the second joint part 2 are made of light alloy material, and the surfaces of the convex curved surface 11 and the convex curved surface 21 are coated with Teflon material to reduce the coefficient of friction.
[0062] The connecting fibers 3 are arranged symmetrically on both sides of the joint and are made of Kevlar fibers. The Kevlar fiber is pre-soaked with waterproof and UV-resistant resin, and then repeatedly passes through the first through hole 12...
Embodiment 2
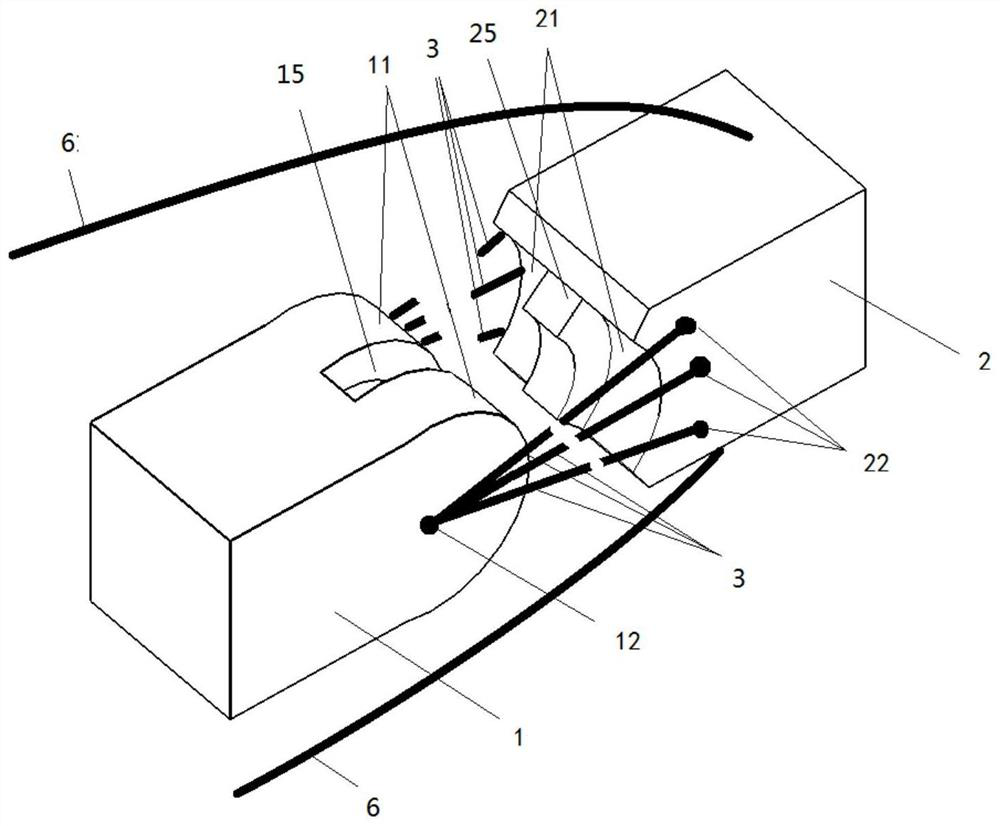
[0066] Reference attached figure 2 , with figure 2 is a 3D exploded view, (connectors cut off), showing a 1DOF joint with internal and external reinforcement.
[0067] The following methods are used to further restrict the range of motion of the joints, and strengthen the joints to increase the strength of the joints.
[0068] The first joint member 1 includes a convex curved surface 11 and a first through hole 12 , and the first through hole 12 is located on the central axis of the convex curved surface 11 .
[0069] The second joint part 2 includes a convex curved surface 21 and a second through hole 22 , and the second through hole 22 is near the edge of the concave curved surface 21 .
[0070] Grooves 15 are provided in the convex curved surface 11 , and ridges 25 are provided in the convex curved surface 21 . The groove 15 is in close contact with the ridge 25 , can slide freely, and can bear the horizontal tangential force of the second joint part 2 .
[0071] The ...
Embodiment 3
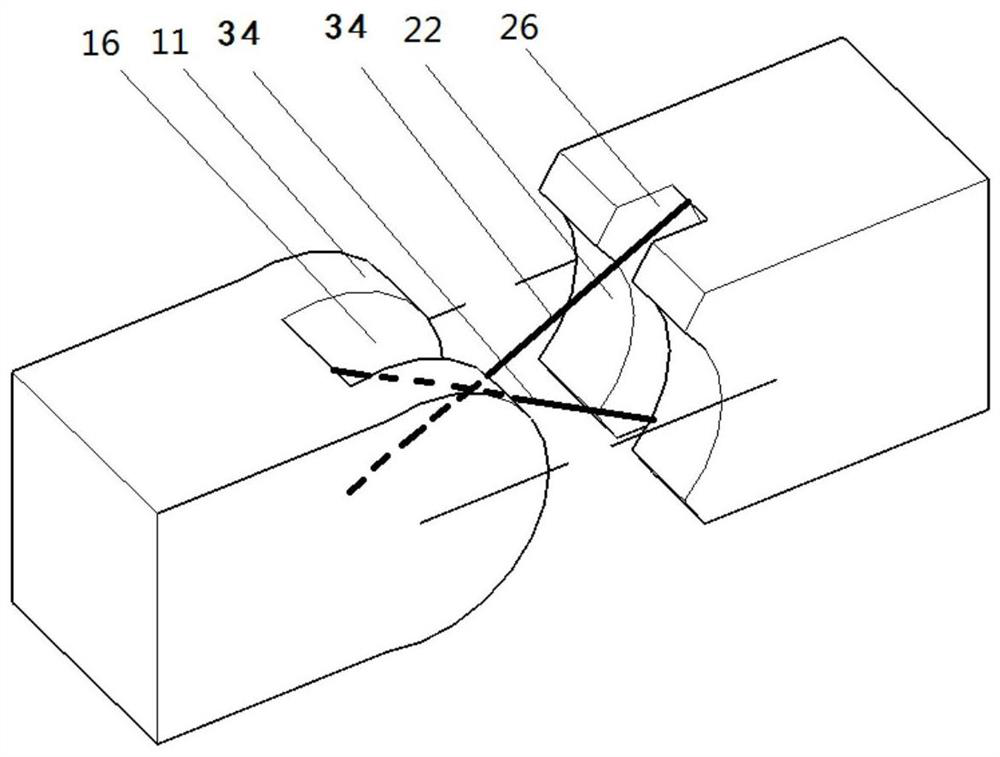
[0075] Reference attached image 3 , respectively remove part of the material at the corresponding positions of the two structural parts to form a depression, and add two connecting lines 34 of intersecting steps in the depression, the blocked connecting line 34 is marked with a dotted line, and the connecting line 34 is connected to the first joint part 1, the second The two joint parts 2 form a cross four-link mechanical structure, and the connecting line 34 is made of aramid fiber.
[0076] The joint adopting this design can withstand large tangential force, and can prevent the joint from translation when it is subjected to tangential force while retaining the rotation function.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com