Bacillus velezensis strain for soybean meal fermentation
A technology of Bacillus Velez and Bacillus, applied in the direction of bacteria, applications, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as single process and detection technology, affecting protein quality, and large differences in protein solubility and small peptide content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The isolation and screening of Bacillus veleisi strain DP-2, the specific steps are:
[0034] a. Isolation and purification of Bacillus in Douchi
[0035] Take 5g of Douchi sample into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 45mL sterilized normal saline (add 10% LB culture solution), shake and incubate for 30min, place the Erlenmeyer flask containing the sample solution in a water bath at 80°C for 20min, The sample solution was diluted 10 times with sterile physiological saline, and the appropriate dilution gradient suspension was spread on the plate of LB medium, 3 plates for each dilution, and cultured upside down at 37°C. After the colonies grow out, pick the strains with the morphological characteristics of Bacillus colonies, and separate and purify them by streaking.
[0036] b. Primary screening
[0037] The isolated and purified strains were planted on the screening plate with a sterilized toothpick, cultured upside down at 37°C for 18-24 hours, and the strains t...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Identification and Growth Curve Measurement of DP-2 Strain
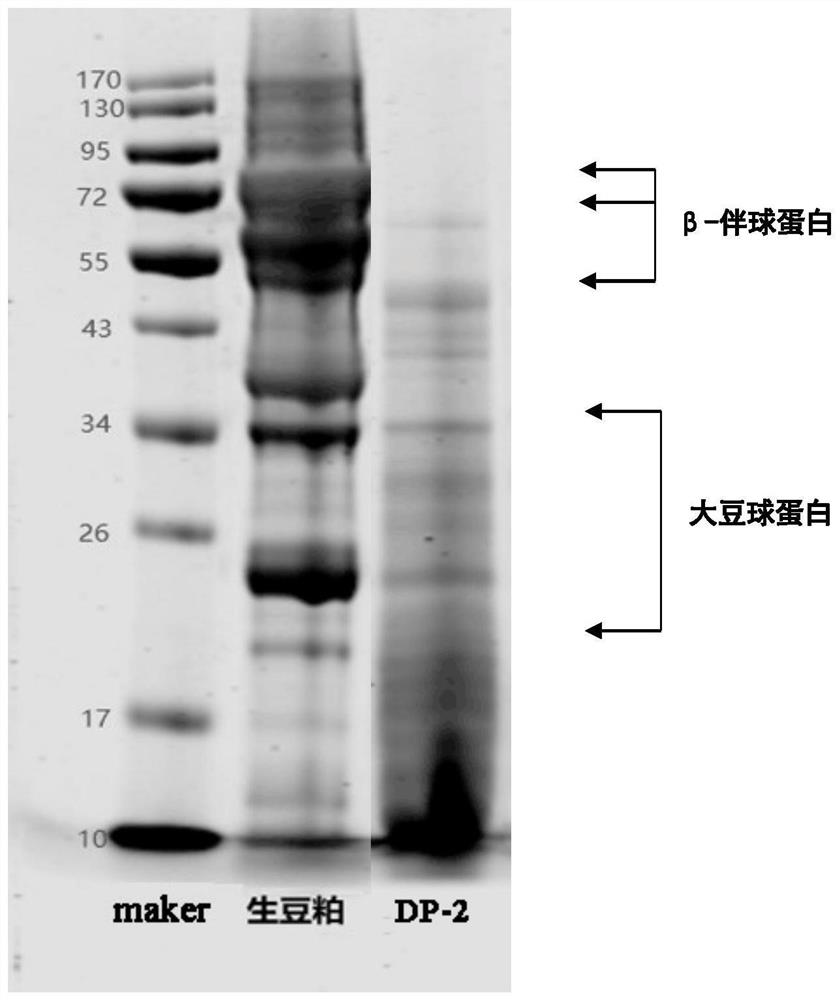
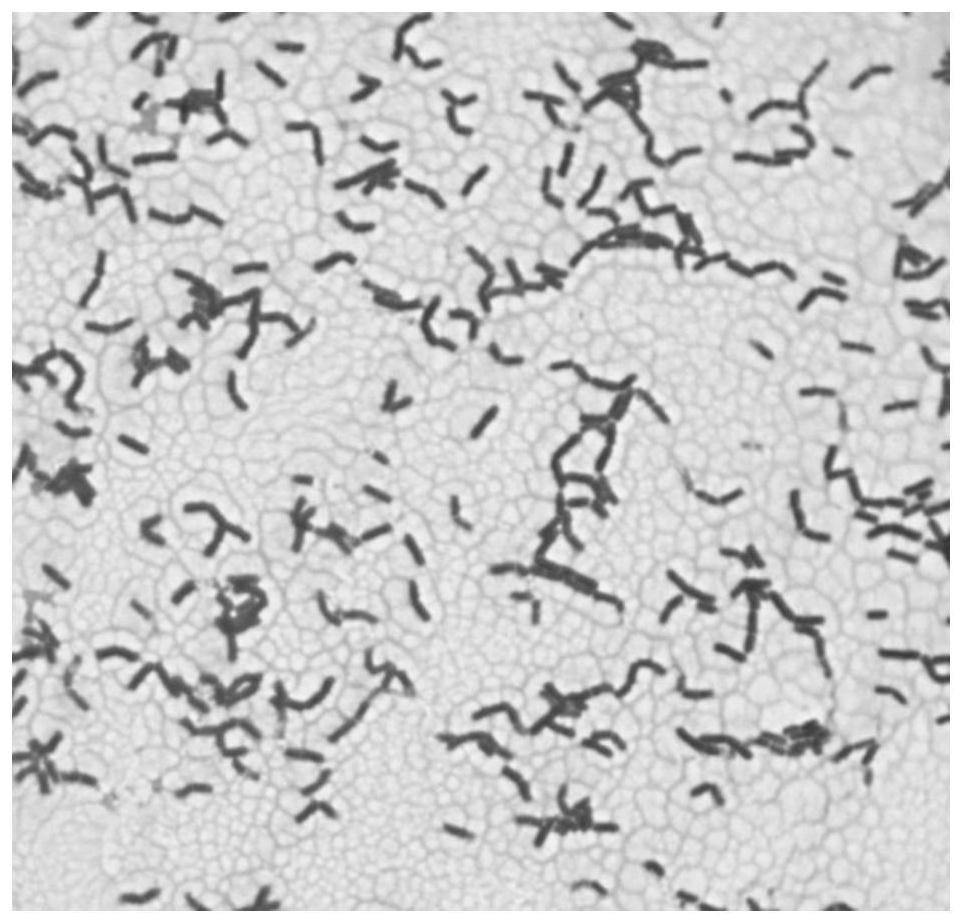
[0064] Bacterial strain DP-2 grows rapidly on the LB plate, and the colonies are milky white, opaque, with wrinkled edges, raised central part, easy to stir up, and sticky (such as figure 2 shown), and the shape of the bacteria was rod-shaped observed under the optical microscope (such as image 3 shown), morphologically identified as subspecies of Bacillus subtilis; identified by molecular biology as Bacillus Velez (such as Figure 4 shown); the growth and development curve of the strain is as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0065] Molecular biology identification is specifically as follows: use 16S rDNA universal primers: 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) to amplify the 16S rDNA of the target strain, and carry out the purified PCR product Sequencing, the sequencing results were Blast compared in the genbank nucleic acid sequence database to search for homologous sequences;...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Detect the protease-producing properties of the DP-2 strain. The specific steps are: after the DP-2 bacterial liquid is centrifuged at 3000r / min for 10 minutes to remove the bacteria, it is dialyzed with a 2KD dialysis bag for 24 hours (change the water 2-3 times in the middle), and the dialysis bag is taken out. The inner solution is freeze-dried (pre-freezing at -40°C for 540min, vacuuming at -40°C to 1500MT for 120min, first drying at 10°C at a vacuum of 200MT for 740min, at 25°C at a vacuum of 200MT for 1020min, and secondary drying at 20°C at a vacuum of 1020min 300MT dried for 120min and cooled to 0°C) and weighed to measure the activity of each protease in the lyophilized powder; the results are shown in Table 3;
[0069] Among them, the protease activity is detected according to the corresponding detection method of "GB / T 23527-2009 Protease Preparation".
[0070] Table 3 DP-2 bacterial liquid protease detection results
[0071] Enzyme activity Neut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com