Nano probe used for nucleolin cross-linking to induce tumor cell apoptosis, and preparation method and application of nano probe
A technology of tumor cell apoptosis and nano-probe, which is applied in the field of nucleolin crosslinking-induced tumor cell apoptosis nano-probe and its preparation, which can solve the problem of inability to selectively induce tumor cell apoptosis, probe degradation or Endocytosis, poor stability and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Preparation of nanoprobes for nucleolin cross-linking to induce tumor cell apoptosis
[0037](1) Glycol chitosan (GC) and succinimidyl ester-polyethylene glycol-cholesterol (chol, purchased from NANOCS, USA) were dissolved in PBS buffer with a concentration of 0.0067M and a pH of 7.4 In the method, the ethylene glycol chitosan solution with a concentration of 1.34 mg / mL and the succinimide ester-polyethylene glycol-cholesterol solution with a concentration of 5.00 mg / mL were obtained, and the two solutions were mixed in equal volumes and stirred at room temperature After reacting for 4 hours, the final reaction solution was transferred to a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 10KD, dialyzed in deionized water for 3 days, and freeze-dried to obtain an ethylene glycol chitosan-cholesterol compound. The mass fraction of cholesterol in the compound was 30 %;
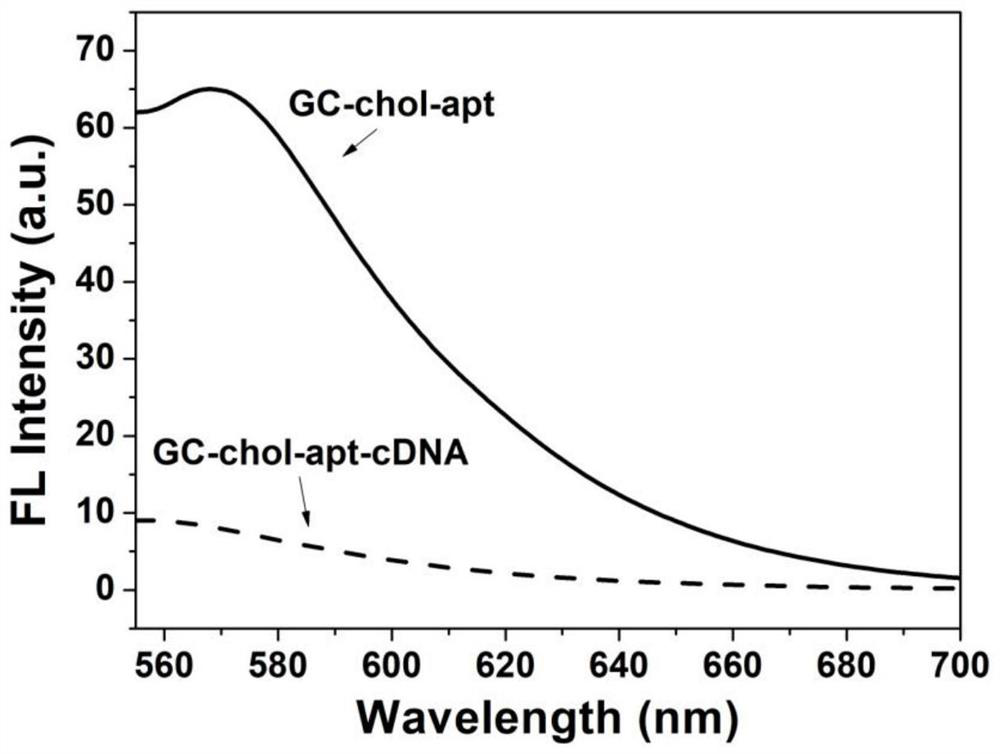
[0038] (2) The ethylene glycol chitosan-cholesterol compound and the A chain (apt, 5'-COOH-ttttttttttt...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Seed HEp-2 cells (human laryngeal carcinoma epithelial cells) in imaging dishes (1×10 4 per well), at 37°C and 5% CO 2 The culture medium was cultured for 24 hours under the condition of 24 hours, then the culture medium was aspirated, washed 3 times with PBS buffer, and then the GC-chol-apt-cDNA solution in Example 1 with a concentration of 60 μg / mL was added, and incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. After the incubation, wash off the unbound GC-chol-apt-cDNA with PBS, then add DiO cell membrane dye (5 μM), and incubate at 37°C for 25 min. After the incubation, wash off the unbound DiO cell membrane dye with PBS, and Fluorescence signals were collected using a confocal fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX-81). The result is as Figure 5 As shown, after GC-chol-apt-cDNA interacted with HEp-2 cells, Cy3 red fluorescence appeared, and it had a high co-localization phenomenon with Dio cell membrane dye, indicating that GC-chol-apt-cDNA could specifically interact with Nucleoli...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Validation of the ability of GC-chol-apt-cDNA to regulate nucleolin cross-linking and anchoring to the cell membrane
[0046] Seed HEp-2 cells (human laryngeal carcinoma epithelial cells) in imaging dishes (1×10 4 per well), at 37°C and 5% CO 2 Cultured under the condition of 24h, then aspirated the medium, washed 3 times with PBS buffer solution, then added the apt solution with a concentration of 60nM and the GC-chol-apt-cDNA solution in Example 1 with a concentration of 60μg / mL respectively, at 37°C Incubate for 0, 0.5, 2, 4, 6 hours. After the incubation, unbound apt and GC-chol-apt-cDNA were washed away with PBS, and fluorescent signals were collected using a confocal fluorescence microscope (Olympus IX-81). The result is as Figure 6 As shown, GC-chol-apt-cDNA can stay on the membrane for up to 6h, while the single Cy3-labeled A chain (apt) enters the cell after 0.5h.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com