Method for detecting nonmetallic inclusions in steel
A technology for non-metallic inclusions and detection methods, applied in the field of smelting, can solve problems such as crushing, time-consuming, and complicated extraction process of inclusions, and achieve the effect of avoiding re-precipitation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The steel detected in this embodiment is CLAM steel, and the method for detecting non-metallic inclusions in the steel comprises the following steps:
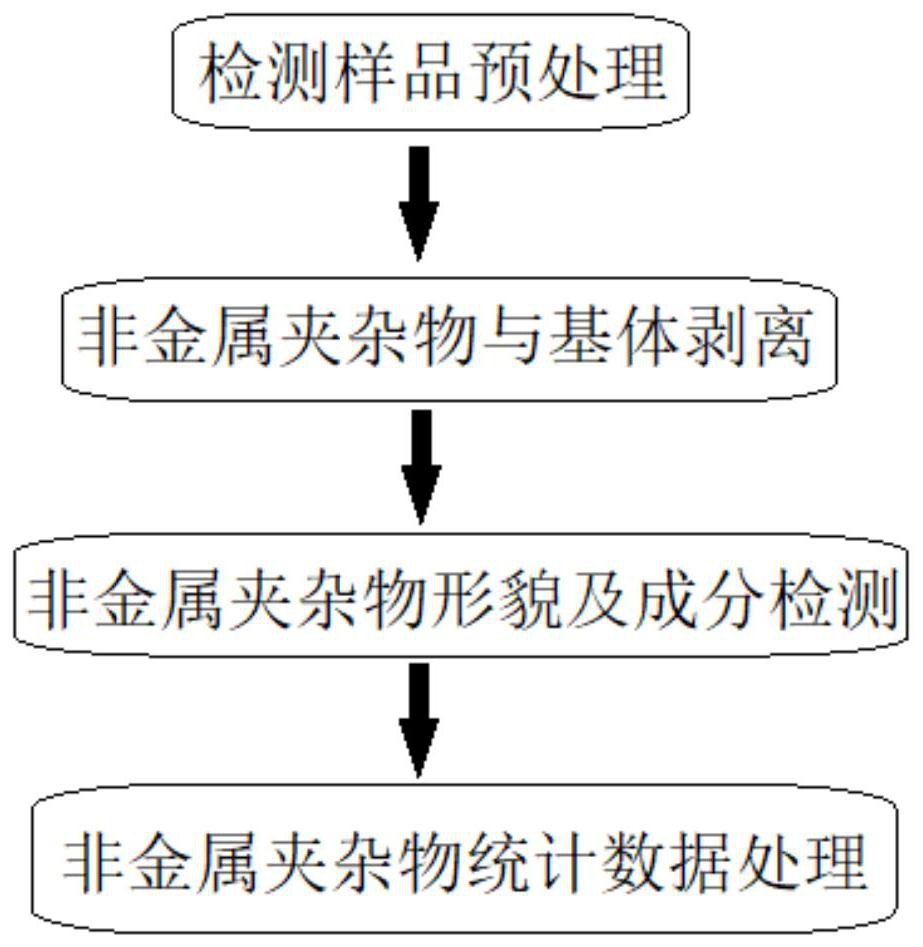
[0041] (1) Test sample pretreatment
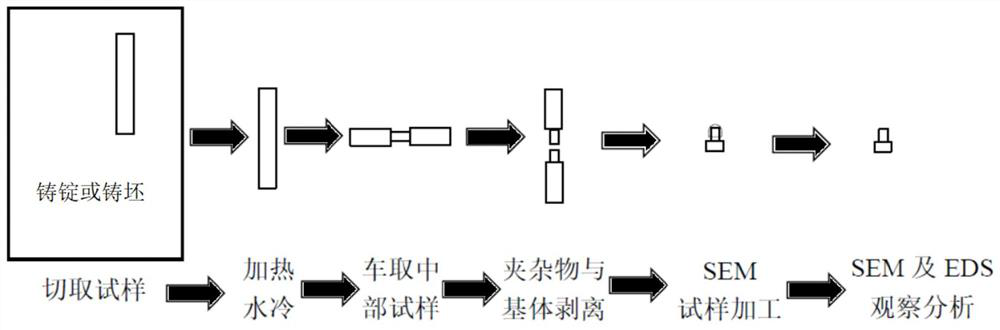
[0042] The sample is selected from the ingot of CLAM steel, and the diameter d is cut from the slab by wire cutting 1 = 1cm, length l 1 = 10cm round bar sample; place the round bar sample at 1100°C for 1.5h and then water-cool, and dry the sample as soon as possible after cooling; use a lathe to cut out the diameter d in the middle of the sample after cooling 2 = 5mm long l 2 = 5cm round bar sample, clean the round bar sample for use.
[0043] (2) Non-metallic inclusions are peeled off from the matrix
[0044] The pretreated round bar sample was subjected to tensile failure to peel the inclusions from the matrix and expose the inclusions.
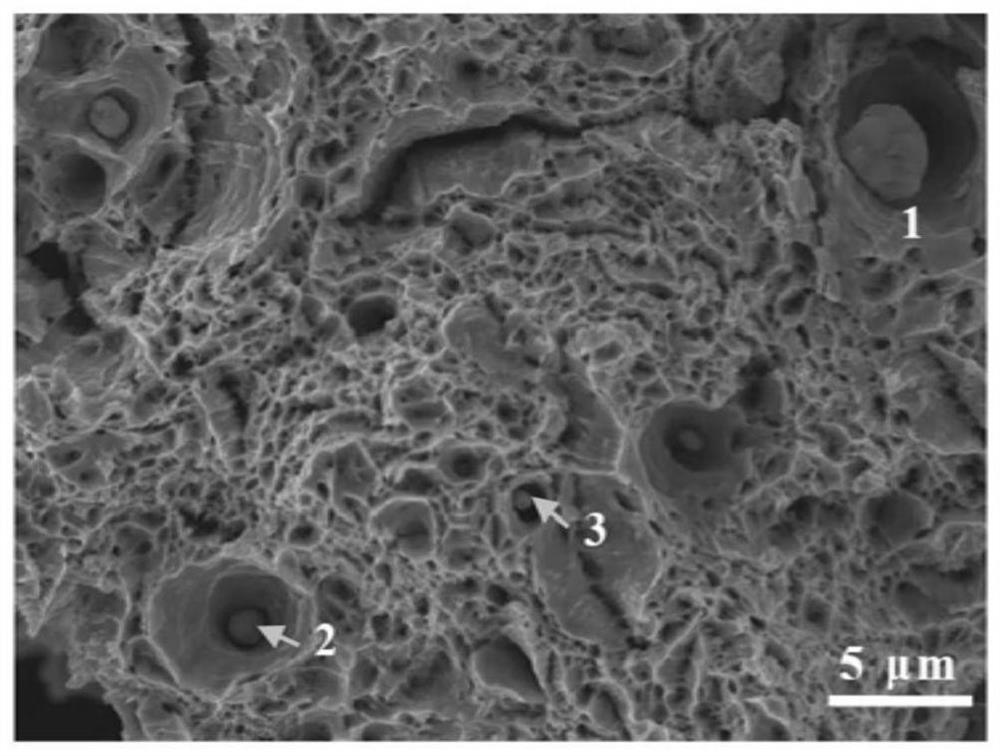
[0045] (3) Morphology and composition detection of non-metallic inclusions
[0046] The sample is processed into a size that can be placed in...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The steel detected in this embodiment is SCRAM, and the method for detecting non-metallic inclusions in the steel comprises the following steps:
[0055] (1) Test sample pretreatment
[0056] The sample is selected from the ingot of SCRAM steel, and the diameter d is cut from the billet by wire cutting 1 =1.5cm, length l 1 = 5cm round bar sample; place the round bar sample at 1200°C for 1.5h and then water-cool, and dry the sample as soon as possible after cooling; use a lathe to cut out the diameter d in the middle of the sample after cooling 2 = 3mm long l 2 = 1 for the round bar sample, clean the round bar sample for use.
[0057] (2) Non-metallic inclusions are peeled off from the matrix
[0058] The pretreated round bar sample was subjected to tensile failure to peel the inclusions from the matrix and expose the inclusions.
[0059] (3) Morphology and composition detection of non-metallic inclusions
[0060] The sample is processed into a size that can be pla...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The steel detected in this embodiment is ARAA steel, and the method for detecting non-metallic inclusions in the steel comprises the following steps:
[0069] (1) Test sample pretreatment
[0070] The sample is selected from the steel ARAA ingot, and the diameter d is cut from the ingot by wire cutting 1 =1.25cm, length l 1 = 7.5cm round bar sample; place the round bar sample at 1150°C for 1.25h and then water-cool, and dry the sample as soon as possible after cooling; use a lathe to cut out the diameter d in the middle of the sample after cooling 2 = 4.5mm long l 2 =1.25 for the round bar sample, clean the round bar sample for use.
[0071] (2) Non-metallic inclusions are peeled off from the matrix
[0072] The pretreated round bar sample was subjected to tensile failure to peel the inclusions from the matrix and expose the inclusions.
[0073] (3) Morphology and composition detection of non-metallic inclusions
[0074] The sample is processed into a size that ca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com