Mode-locked fiber laser based on self-phase modulation
A fiber laser and self-phase modulation technology, applied in the field of ultrafast optics, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining high-power and wide-spectrum laser pulses, difficulty in obtaining wide-spectrum laser light sources, low laser damage threshold, etc., and achieve good environmental stability performance, simple structure, and the effect of improving single pulse energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
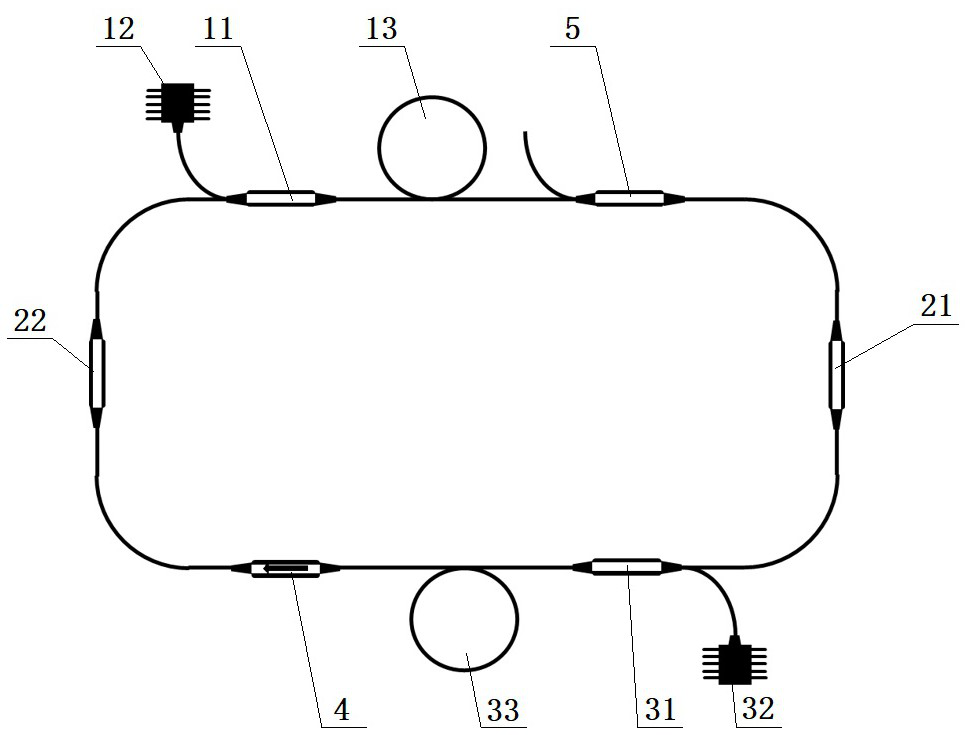
[0022] Such as figure 2 As shown, the mode-locked fiber laser based on self-phase modulation in this embodiment includes a first wavelength division multiplexer 11 arranged as a ring cavity, a first gain fiber 13, a long-wavelength bandpass filter 21, a second wave Division multiplexer 31, the second gain fiber 33, short-wavelength bandpass filter 22, fiber coupler 5 and fiber isolator 4, also include the first semiconductor laser 12 connected with the first wavelength division multiplexer 11 and The second semiconductor laser 32 connected to the second wavelength division multiplexer 31. The first semiconductor laser 12 sends laser pulses, and the first wavelength division multiplexer 11 couples the laser pulses into the first gain fiber 13, thereby broadening the spectrum while providing gain for the laser pulses. After the spectral filtering, the second wavelength division multiplexer 31, the second semiconductor laser 32, and the second gain fiber 33 amplify the laser pu...
Embodiment 2
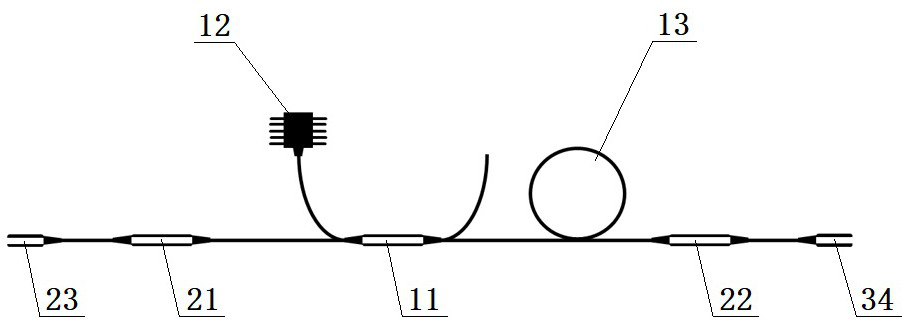
[0024] Such as image 3 As shown, the mode-locked fiber laser based on self-phase modulation in this embodiment includes a first fiber mirror 23, a long-wavelength bandpass filter 21, a first wavelength division multiplexer 11, and a first gain fiber arranged in sequence. 13. The short-wavelength bandpass filter 22 and the second fiber mirror 34 also include a first semiconductor laser 12 connected to the first wavelength division multiplexer 11, and the mode-locked fiber laser has a linear cavity inside. The first semiconductor laser 12 emits pulsed laser light, and the first wavelength division multiplexer 11 couples the pulsed laser light into the first gain fiber 13 to provide gain for the laser pulse while broadening the spectrum, and the long-wavelength bandpass filter 21 pairs the widened Spectral filtering, the first fiber mirror 23 reflects the laser pulse back into the linear cavity, the laser pulse is amplified again in the first gain fiber 13 and the spectrum is br...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the mode-locked fiber laser based on self-phase modulation in this embodiment includes a first fiber mirror 23, a bandpass filter 2, a first wavelength division multiplexer 11, a first gain fiber 13 and a first The second fiber mirror 34 also includes a first semiconductor laser 12 connected to the first wavelength division multiplexer 11 . The interior of the mode-locked fiber laser is a linear cavity. The maximum gain point of the first gain fiber 13 and the bandpass filter 21 have different central wavelengths. In this embodiment, the band-pass filter 2 is a single-chip band-pass filter. The laser pulse emitted by the first semiconductor laser 12 is coupled into the first gain fiber 13 through the first wavelength division multiplexer 11 to amplify and broaden the spectrum at the same time, and then pass through a bandpass filter to filter the broadened spectrum, and the first optical fiber reflects The mirror 23 reflects the laser puls...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com