Gene engineering high-yield strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes, method for increasing yield of epsilon-polylysine and application of streptomyces diastatochromogenes
A technology of Streptomyces chromogenes and polylysine, applied in the direction of genetic engineering, microorganism-based methods, applications, etc., can solve the problems of improving ε-polylysine, achieve production, and enhance diaminopimelic acid The effect of the pathway
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] A genetically engineered high-yield amylase strain Streptomyces chromogenes, the construction steps are as follows:
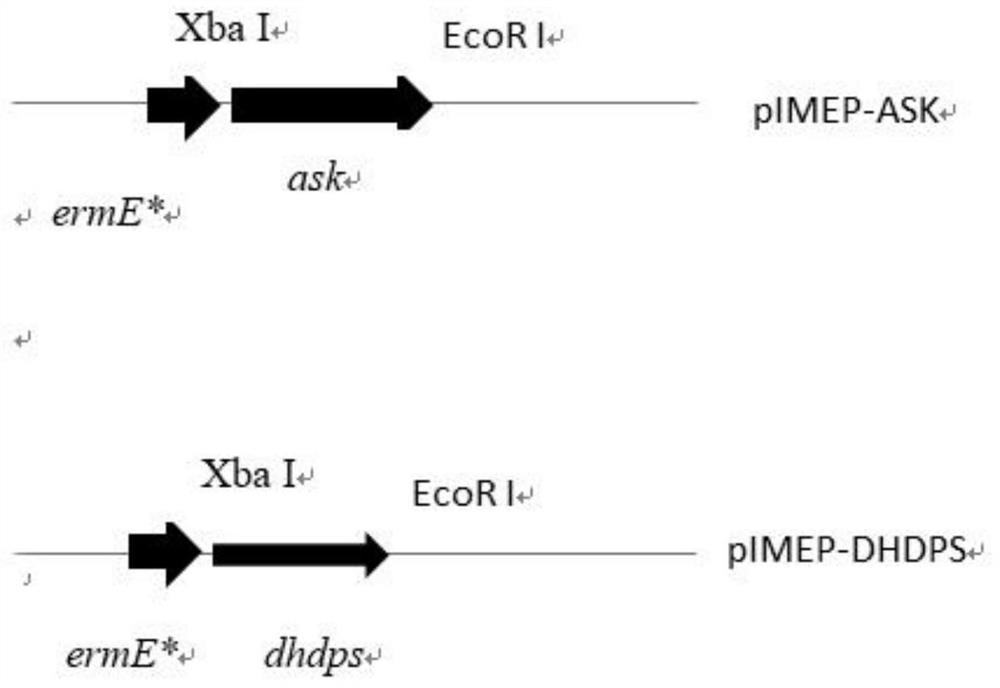
[0127] 1) Acquisition of aspartokinase gene (ask):
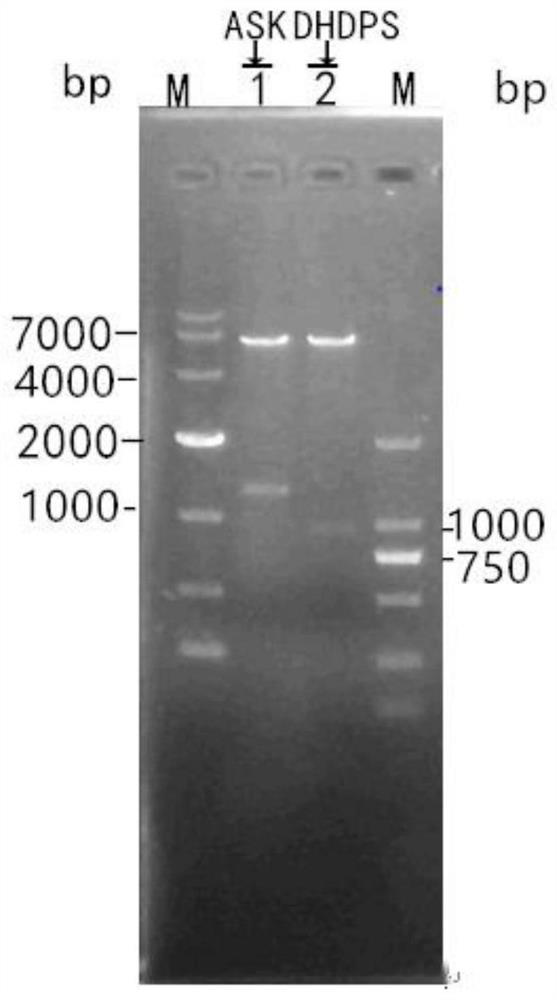
[0128] Using the amylase Streptomyces chromogenes genomic DNA as a template, use the primers ask-F / ask-R to amplify the full length of ask by PCR, and add an XbaI restriction site at the 5' end of the ask, and an EcoRI restriction site at the 3' end point. The gene size is 1272bp.
[0129] Where: ask-F:5'-GC TCTAGA GTGGGCCTTGTCGTGCAGAAGTACGG-3' horizontal line is the XbaI restriction site, and the boldface is the start codon;
[0130] ask-R: 5'-CCG GAATTC TCATCGCCCGGTGCCGCCGATG-3' horizontal line is the EcoRI restriction site, bold is the stop codon.
[0131] PCR reaction system and conditions: 5×PrimeSTAR GXLBuffer 10μL, dNTP mixture (2.5mM) 4μL, template (20ng / ul) 1μL, upstream and downstream primers ((10μM)) 2μL each, DMSO 2μL, PrimeSTAR GXLDNAPolymerase 1μL, supplemented with ultrapure wate...
Embodiment 2
[0140] A genetically engineered high-yield amylase strain Streptomyces chromogenes, the construction steps are as follows:
[0141] 1) Acquisition of dihydrodipicolinate synthase gene (dhdps):
[0142] Using amylase Streptomyces chromogenes genomic DNA as a template, use primers dhdps-F / dhdps-R to amplify the full length of dhdps by PCR, and add XbaI restriction site at the 5' end of dhdps, and EcoRI restriction enzyme at the 3' end location. The gene size is 897bp.
[0143] Where: dhdps-F:5’-GGC TCTAGA ATGGTTGATCGCACCCCCCTGGAGG-3' horizontal line is the XbaI restriction site, and the boldface is the start codon;
[0144] dhdps-R: 5'-CCG GAATTC The horizontal line at TCAGCCCAGGGCTGCCAGGTGC-3' is the EcoRI restriction site, and the stop codon is in bold.
[0145] PCR reaction system and conditions: 5×PrimeSTAR GXLBuffer 10μL, dNTP mixture (2.5mM) 4μL, template (20ng / ul) 1μL, upstream and downstream primers ((10μM)) 2μL each, DMSO 2μL, PrimeSTAR GXL DNAPolymerase 1μL, su...
Embodiment 3
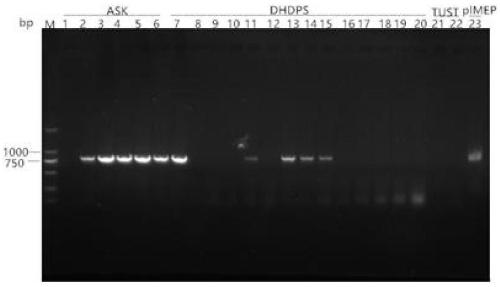
[0154] Verification of genetically engineered strains:
[0155] The genomic DNA of the genetically engineered Streptomyces was extracted, the primers aac-F / aac-R were designed and verified, and the apramycin resistance gene aac(3)IV was amplified with the genomic DNA of the genetically engineered Streptomyces as a template. The original strain genomic DNA was used as a negative control, and the plasmid pIMEP was used as a positive control. The results are shown in image 3 .
[0156] Among them, SEQ No.7aac-F: 5'-GTGCAATACGAATGGCGAAAAG-3'
[0157] SEQ No.8aac-R: 5'-TCAGCCAATCGACTGGCG-3'
[0158] PCR reaction system and conditions: 10X PCR Buffer 5μL, dNTPmixture (2.5mM) 4μL, template (20ng / ul) 1μL, upstream and downstream primers ((10μM)) 2μL, DMSO 2μL, TaKaRa Taq 1μL, add ultrapure water to 50 μL. PCR reaction conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min; denaturation at 95°C for 15 s, annealing at 62°C for 15 s, extension at 72°C for 60 s, 30 cycles in total, extension...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com