Substrate for polymer brush formation, production method for substrate for polymer brush formation, and precursor liquid for use in production method for substrate for polymer brush formation
A technology of polymer brushes, manufacturing methods, applied in the field of precursor fluids, capable of solving problems such as without any research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
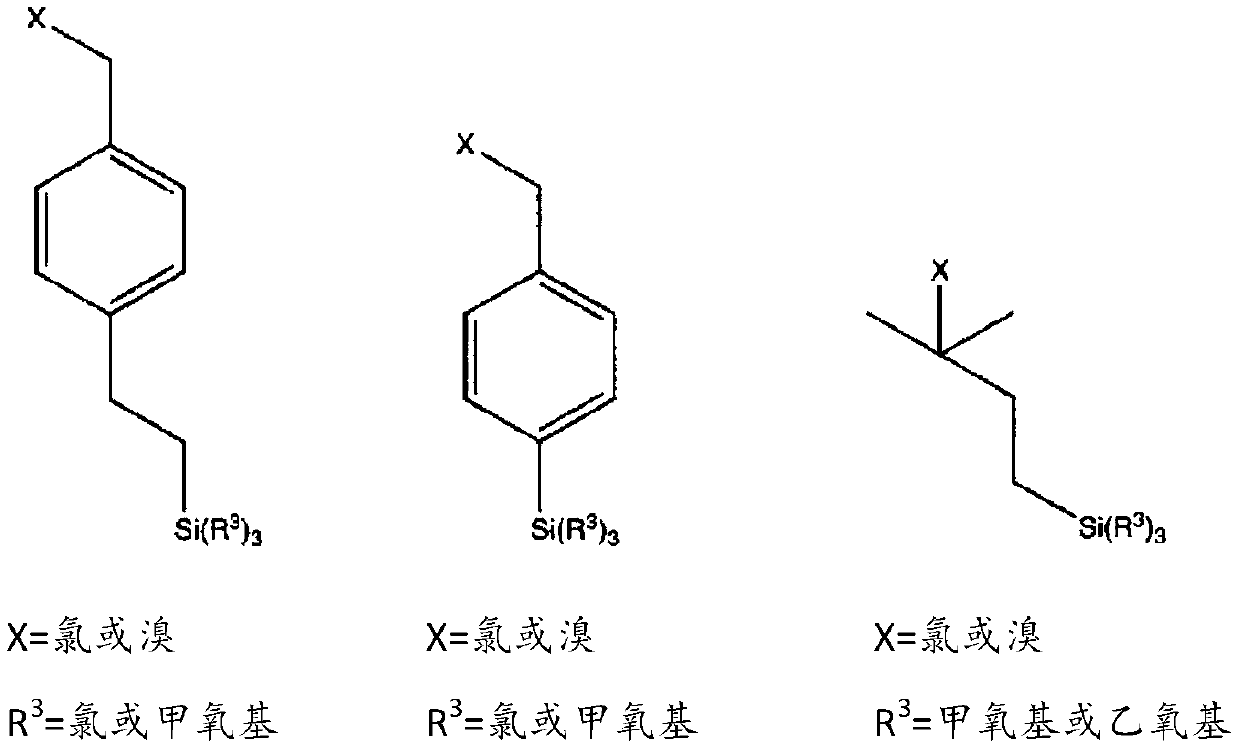
[0181] For a mixed solution of 0.01M HCl aqueous solution (1 volume part), TEOS (2.8 volume parts), EtOH (8 volume parts), add chloromethylphenylethyltrimethoxysilane (0.0088, 0.141, 0.564 volume parts: sequentially referred to as Example 1-1, 1-2, 1-3) or chloromethylphenyltrimethoxysilane (0.564 parts by volume: referred to as Example 1-4), and stirred at room temperature for 24 hours to prepare a precursor liquid. This precursor solution was dropped onto a silicon wafer, spin-coated (2000 rpm / 10 seconds), and dried at room temperature for 24 hours to form a polymerization initiation layer on the surface of the silicon wafer.
[0182] 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate (5.5 parts by volume), copper (II) chloride (4 parts by volume), N,N,N',N",N"-pentamethyldi Ethyltriamine (7 parts by volume), sodium ascorbate (1 part by volume), and water (1 part by volume) were mixed to prepare a polymerization solution. The aforementioned silicon wafer on which the polymerization initia...
Embodiment 2
[0189] For a mixed solution of 0.01M HCl aqueous solution (1 volume part), TEOS (2.8 volume parts), EtOH (8 volume parts), add chloromethylphenylethyltrimethoxysilane and phenyltriethoxysilane (0.5076 Parts by volume and 0.0564 parts by volume, 0.3948 parts by volume and 0.1692 parts by volume, 0.282 parts by volume and 0.282 parts by volume: successively referred to as Example 2-1, 2-2, 2-3), stirred at room temperature for 24 hours, and prepared the precursor liquid . This precursor solution was dropped onto a silicon wafer, spin-coated (2000 rpm / 10 seconds), and dried at room temperature for 24 hours to form a polymerization initiation layer on the surface of the silicon wafer.
[0190] 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate (5.5 parts by volume), copper (II) chloride (4 parts by volume), N,N,N',N",N"-pentamethyldi Ethyltriamine (7 parts by volume), sodium ascorbate (1 part by volume), and water (1 part by volume) were mixed to prepare a polymerization solution. The aforemen...
Embodiment 3
[0196] In this example, silicon wafers were formed using the polymerization initiating layers of Examples 1-3 above, and various polymer brushes were produced under the following conditions.
[0197] The aforementioned silicon wafer formed with the polymerization initiating layer was mixed with various monomers (parts by volume recorded in Table 3), copper (II) chloride (4 parts by volume), N, N, Immerse in the polymerization solution prepared by mixing N', N", N"-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (7 parts by volume), sodium ascorbate (1 part by volume), water or ethanol (1 part by volume) for 2 hours , forming polymer brushes on the substrate surface (Examples 3-1 to 3-16).
[0198] Table 2 shows the measurement results and appearance of the static contact angle with respect to water of the obtained polymer brush.
[0199] [table 3]
[0200]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com