Method for detecting mosapride citrate and five key impurities in preparation of mosapride citrate
A mosapride citrate and a key technology are applied in the detection field of mosapride citrate related substances, and can solve the problems of long analysis time, influence on the detection accuracy of impurities, baseline fluctuation and the like, and achieve good separation. , The effect of stable baseline and effective control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] The screening of embodiment 1 high performance liquid chromatography conditions
[0067] Preparation of system suitability solution: Weigh 10mg each of mosapride citrate related substances A~E, put them in five 20ml measuring bottles, add methanol to dissolve and dilute to the mark, shake well; then take 1ml each and place in the same 100ml To a measuring bottle, add 10 mg of mosapride citrate, add methanol to dissolve and dilute to the mark, shake well to obtain. (Containing mosapride citrate 1mg / ml, each impurity 5μg / ml).
[0068] HPLC conditions: mobile phase: 50mmol / L citric acid solution (adjust pH to 4.0 with sodium hydroxide solution)-acetonitrile (65:35), flow rate 1ml / min, detection wavelength 274nm, column temperature 40°C, sample injection Volume 10 μl.
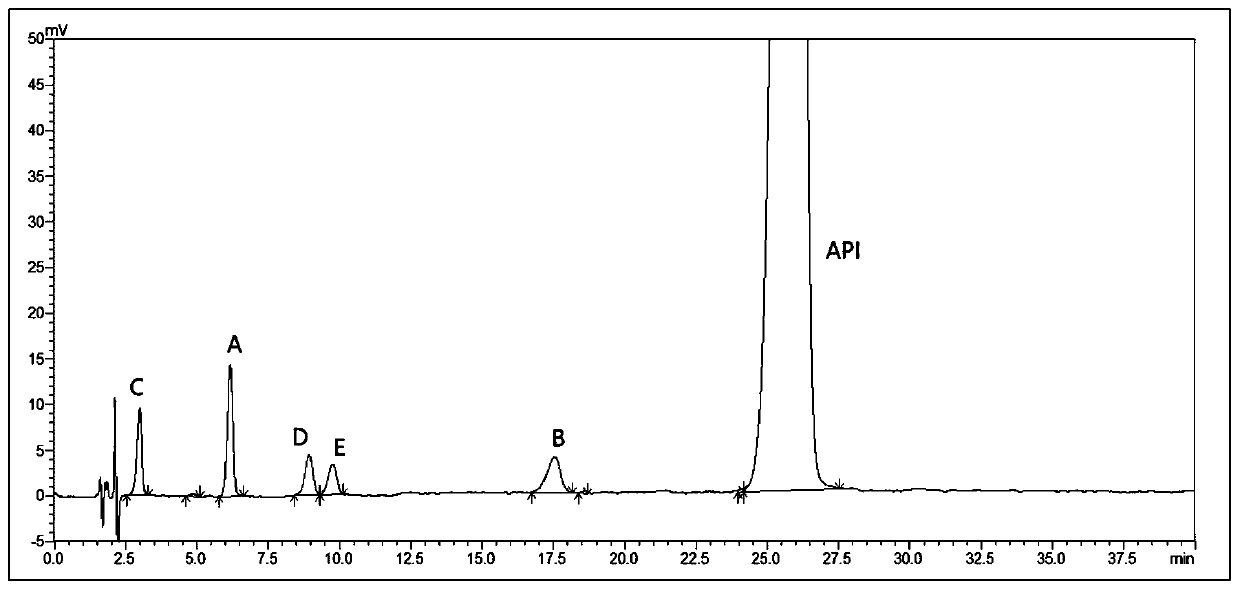
[0069] Take the system suitability solution and inject it for testing, the results are as follows: figure 1 As shown, impurity B and impurity E cannot be separated.
Embodiment 2
[0070] The screening of embodiment 2 high performance liquid chromatography conditions
[0071] HPLC conditions: mobile phase: 50mmol / L citric acid solution (adjust pH to 4.0 with sodium hydroxide solution)-methanol-acetonitrile (55:35:10), flow rate 1ml / min, detection wavelength 274nm, column temperature 40 ℃, the injection volume is 10 μl.
[0072] Prepare the system suitability solution according to the method in embodiment 1, sample injection detection, the result is as follows figure 2 As shown, all known impurities were detected, the baseline was stable, and the separation between impurities and main peaks and between impurities was good.
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3 Baseline comparison between this method and the gradient elution method
[0074] (1) Gradient elution method (Japanese Pharmacopoeia method):
[0075] HPLC conditions: mobile phase A: 0.03mol / L sodium citrate buffer (take 8.82g of trisodium citrate dihydrate, dissolve in 800ml of water, adjust the pH to 4.0 with dilute hydrochloric acid, add water to dilute to 1000ml obtained), mobile phase B: acetonitrile; column temperature 40°C, flow rate 1ml / min; detection wavelength 274nm, gradient elution as shown in the table below.
[0076]
[0077] (2) The patent method
[0078] HPLC conditions: mobile phase: 50mmol / L citric acid solution (adjust pH to 4.0 with sodium hydroxide solution)-methanol-acetonitrile (55:35:10), column temperature 40°C, flow rate 1ml / min, detection wavelength 274nm.
[0079] Prepare blank solution according to the method in embodiment 1, sample injection detects, and the result is as follows image 3 As shown, in the gradient method of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com