Targeted nanomedicine for overcoming drug resistance caused by tumor hypoxia based on MRI guidance and its preparation method and application
An imaging-guided, nano-drug technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of short metabolic lifespan of small molecule drugs, poor targeting of SeD-1b, and lack of recognition ability, so as to overcome the problem of drug resistance and achieve good targeting. , the effect of cheap treatment of cancer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
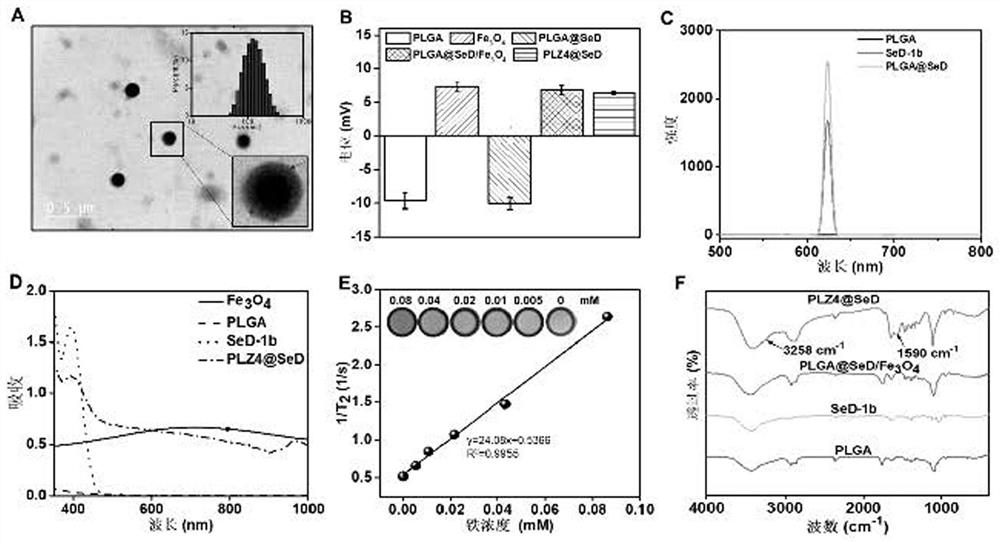
[0076] Example 1: Preparation of targeted nanomedicine
[0077] (1) Preparation of raw materials:
[0078] 1) Preparation of 3.5 mM Tween-80: Weigh 5 g of Tween-80, and use 1 L of secondary water to prepare an aqueous solution of Tween-80 with a concentration of 3.5 mM.
[0079] 2) Prepare 1.05mM Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticle-acetone dispersion: Weigh 0.2436g Fe 3 O 4 The nanoparticles were dispersed in 1L of acetone.
[0080] 3) Preparation of 20 mM PLGA-acetone dispersion: Weigh 20 g of PLGA (lactic acid LA: glycolic acid GA=50:50, Mn=13000) and disperse it in 1 L of acetone.
[0081] 4) Preparation of 0.65 mM SeD-1b solution: Weigh 24.375 mg of SeD-1b (SeD-1b is prepared according to Example 1 in the patent "201610127128.3") and dissolve it in 10 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide.
[0082] 5) Preparation of 20 mg / mL PLZ4 solution: Weigh 20 g of polypeptide PLZ4 powder and dissolve it in 1 L of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with a pH of 7.4 and a concentration of 0.01 M.
[0083] (2...
Embodiment 2
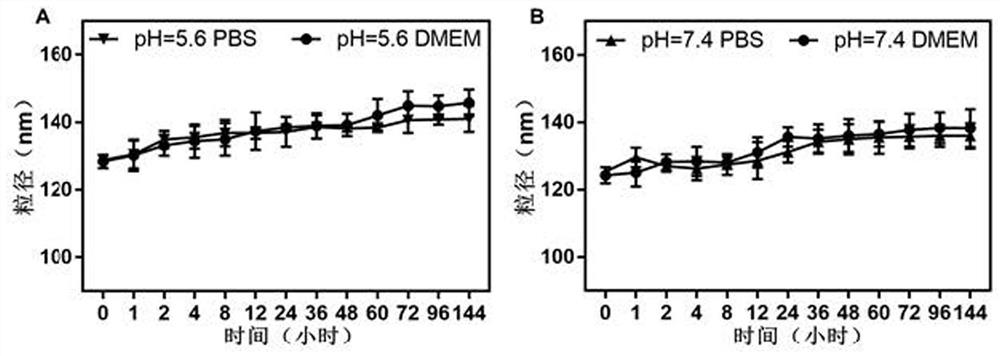
[0110] Example 2: In vitro stability study of targeted nanomedicines
[0111] The preparation method of the targeted nanomedicine PLZ4@SeD nanoparticles used in this example is the same as the preparation method described in Example 1 of this application.
[0112] The mixed solutions for detecting the particle size of nanomedicine PLZ4@SeD nanoparticles were prepared according to the following methods:
[0113] Group A1: 1 mL of dialyzed PLZ4@SeD nanoparticle aqueous solution was mixed with pH=5.6, 0.01M phosphate buffer at a volume ratio of 1:2;
[0114] Group A2: 1 mL of dialyzed PLZ4@SeD nanoparticle aqueous solution was mixed with DMEM medium with pH=5.6 adjusted with hydrochloric acid in a volume ratio of 2:1;
[0115] Group B1: 1 mL of dialyzed PLZ4@SeD nanoparticle aqueous solution was mixed with pH=7.4, 0.01M phosphate buffer at a volume ratio of 2:1;
[0116] Group B2: 1 mL of dialyzed PLZ4@SeD nanoparticle aqueous solution was mixed with pH=7.4 DMEM medium at a vol...
Embodiment 3
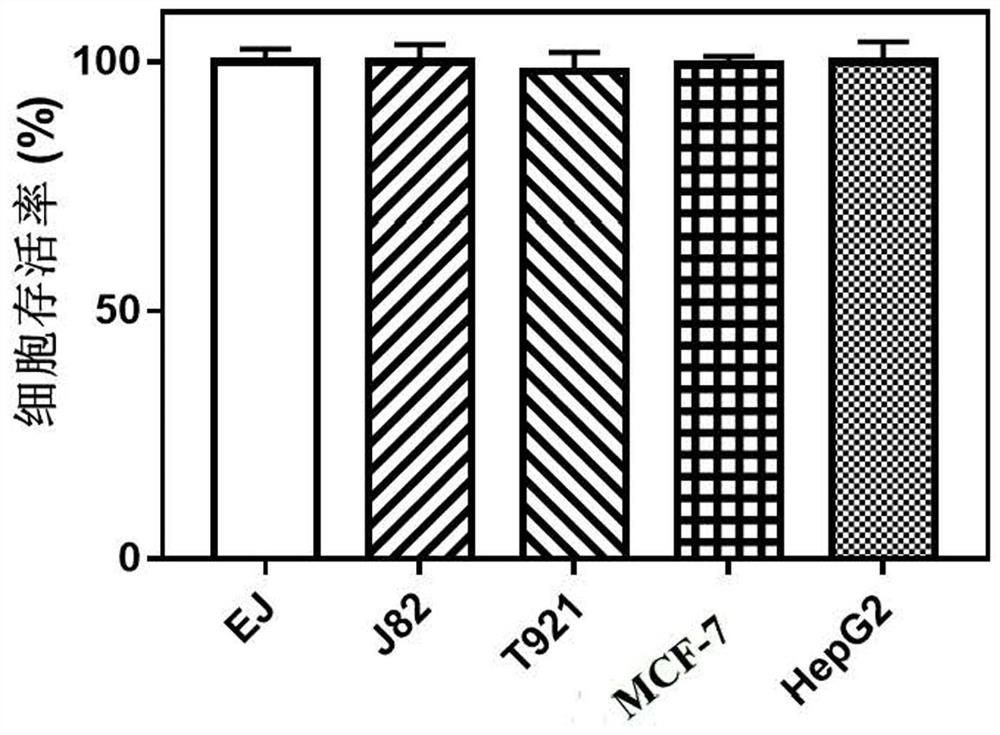
[0119] Example 3: Comparison of in vitro antitumor activity of targeted nanomedicines
[0120] The preparation method of the targeted nanomedicine PLZ4@SeD nanoparticles used in this example is the same as the preparation method described in Example 1 of this application.
[0121] Take the density of growth in logarithmic phase as 2×10 4 cells / mL of bladder cancer EJ cells, bladder cancer J82 cells, bladder cancer T921 cells, breast cancer MCF-7 cells, and liver cancer cells HepG2 cells were seeded in 96-well plates, 100 μL per well; Then, 100 μL of Fe diluted in DMEM medium was added to the first group of wells containing bladder cancer EJ cells, bladder cancer J82 cells, bladder cancer T921 cells, breast cancer MCF-7 cells, and liver cancer cells HepG2 respectively. 3 O 4 nanoparticles so that the final concentration is 0.08mmol / L. without Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles of bladder cancer EJ cells, bladder cancer J82 cells, bladder cancer T921 cells, breast cancer MCF-7 cells an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com