Preparation method of microalgae edible oil
A technology for edible oil and microalgae, which is applied in the direction of fat oil/fat refining, fat oil/fat production, fat production, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient decolorization reaction, and achieves reduction of operational complexity, simple and fast operation, and simplified processing operations. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1 Algae powder broken wall
[0020] (1) Ball milling to break the wall. Chlorella algae powder is milled for 3 hours using a planetary ball mill at a speed of 400-500rpm. The algal flour is then collected.
[0021] (2) High-pressure extrusion to break the wall. Extrude for 5-10 minutes under the pressure condition of 80-120MPa using a high-pressure extruder. The algal flour is then collected.
[0022] (3) High-speed homogenization and crushing. Use a high-speed crusher to crush the algae powder for 3-5 minutes at a speed of 10,000 rpm. The algal flour is then collected.
[0023] Microscopic examination of the algae powder showed no visible cell morphology after ball milling, but a small amount of cells could be seen after high-speed extrusion and homogenate crushing. Ball milling is therefore preferred.
Embodiment 2
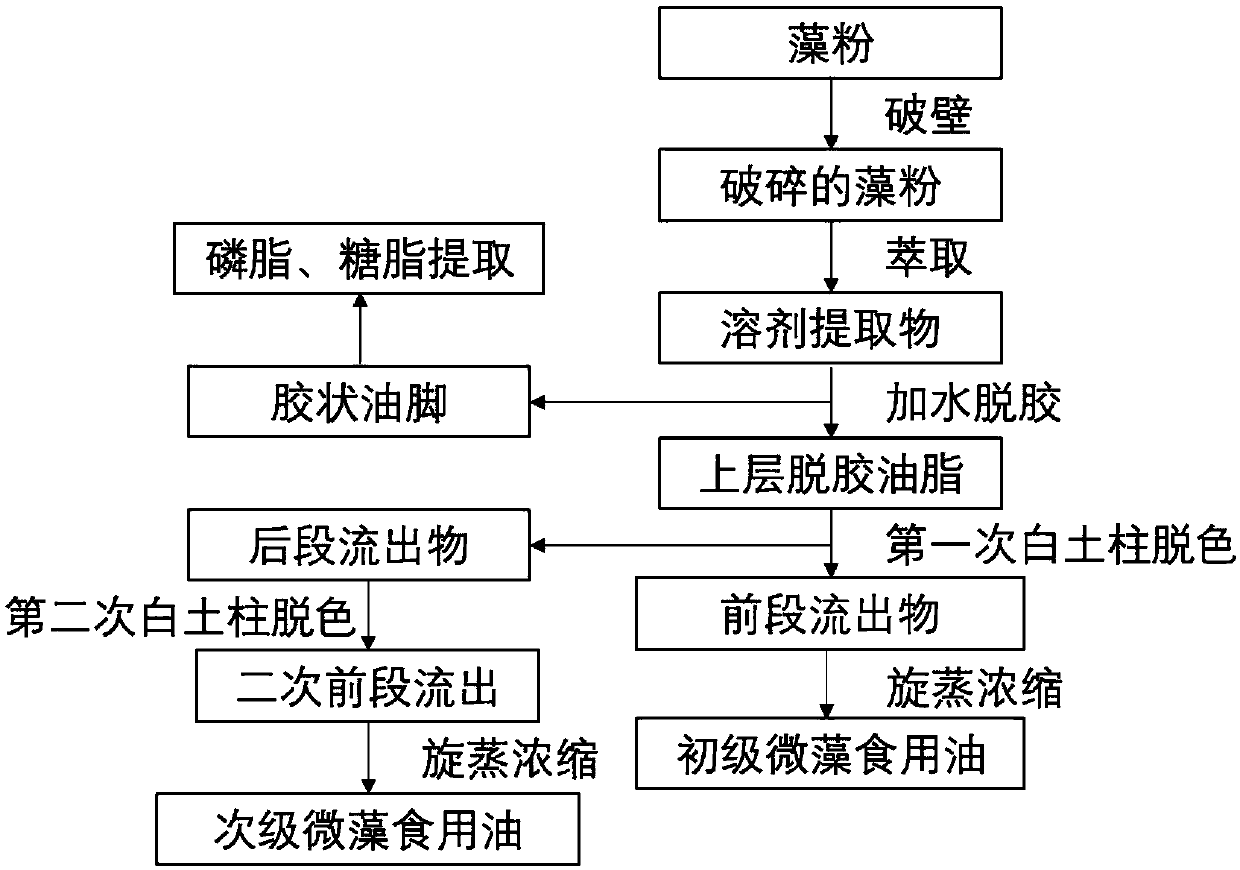
[0025] according to figure 1 The presented procedure was carried out for the preparation of edible oil from microalgae. Taking the ball-milled chlorella powder raw material obtained in Example 1 as an example, the oil was extracted. Use food-grade solvent ethanol to extract the algae powder, wherein the ratio of algae powder to solvent is 1g: 3-10mL. In order to avoid the loss of solvent during the extraction process, condensing and reflux extraction is adopted, the extraction temperature is 60° C., and the extraction time is 2 to 6 hours. The extraction process uses mechanical agitation for mixing.
[0026] After the extraction, the extract was filtered and the filtrate was collected. The filter cake was washed twice with the corresponding solvent. The target edible oil is obtained through degumming and activated clay decolorization.
Embodiment 3
[0028] according to figure 1 In the process described, the chlorella algae powder obtained by ball milling was extracted according to the extraction process described in Example 2, using hexane as a solvent, and the solvent phase was collected. Add hot water to the solvent phase at a ratio of 1:0.2~0.5 (oil:water, w / w), and stir for 1~6 hours at 60~80°C with condensing reflux to fully mix the oil and water for degumming treatment. The mixed system is then left to stand until the two phases are clearly separated. The upper oil phase is used for further clay decolorization treatment to obtain microalgae oil, and the lower colloidal oil bottom is collected for the purification of phospholipids and glycolipids.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com