Method for removing heavy metal cadmium in wastewater by using magnetic biomass charcoal, and applications thereof
A magnetic biochar and biochar technology, applied in the direction of alkali metal compounds, chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve problems such as poor connection stability, achieve retention of adsorption characteristics, Excellent cadmium recovery effect and increased recyclability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Biomass carbon materials, according to the following steps:
[0045] Step 1, washing the naturally dried wheat straw with water for 4 times, air-drying for 2 days, pulverizing with a pulverizer, and placing it in a drying container;
[0046] Step 2, take the wheat straw powder obtained in step 1, compact it, and cover the crucible; place it in a muffle furnace, raise the temperature to 400°C at a heating rate of 20°C / min, then carbonize for 4 hours, and cool down to Take out after room temperature;
[0047] Step 3, grinding the biochar obtained in step 2 through an 80-mesh sieve to obtain a biochar material (referred to as BC);
[0048] Step 4, prepare biochar material suspension (4.64g biochar, 300ml deionized water), mix with ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate solution (2g ferrous sulfate, 5.4g ferric sulfate, 200ml deionized water), use Stir with a magnetic stirrer at a constant speed, then add sodium hydroxide solution therein to adjust the pH of the reaction system ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is: the added mass (gram) of the raw material is biomass charcoal: ferrous sulfate: ferric sulfate=4.64:4:10.8, and the obtained magnetic biomass charcoal is denoted as MBC2;
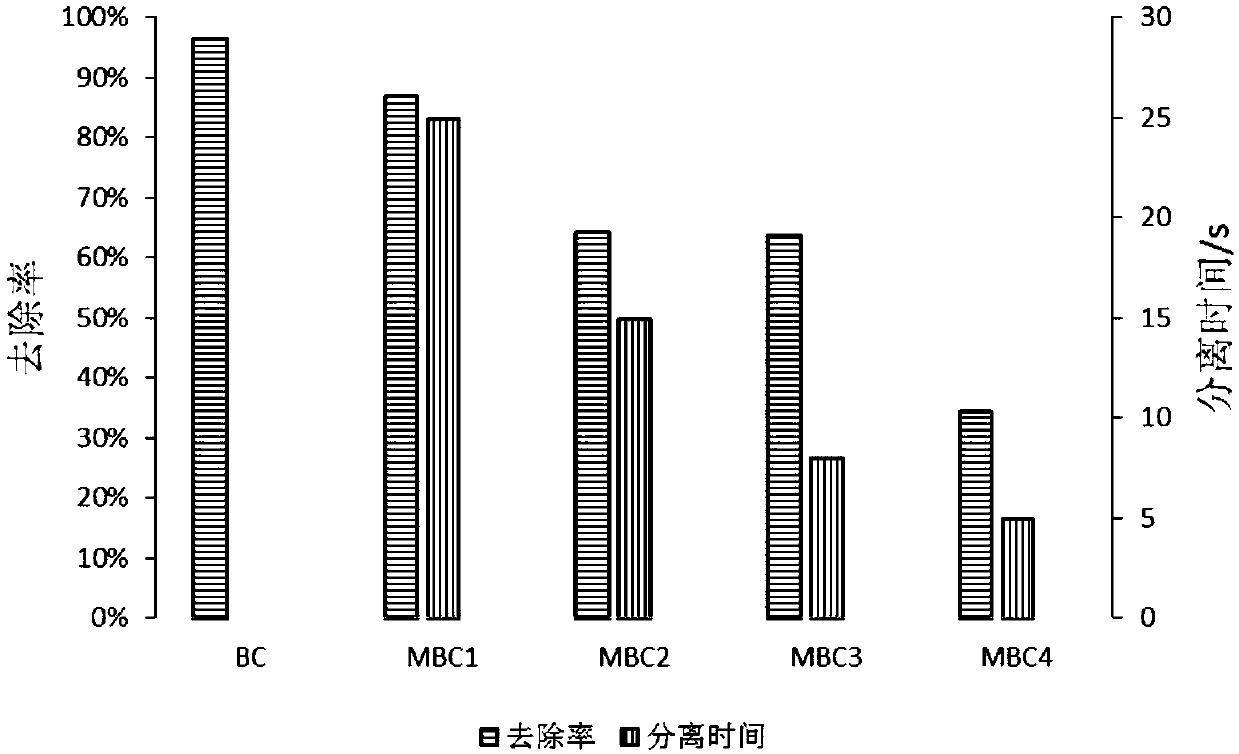
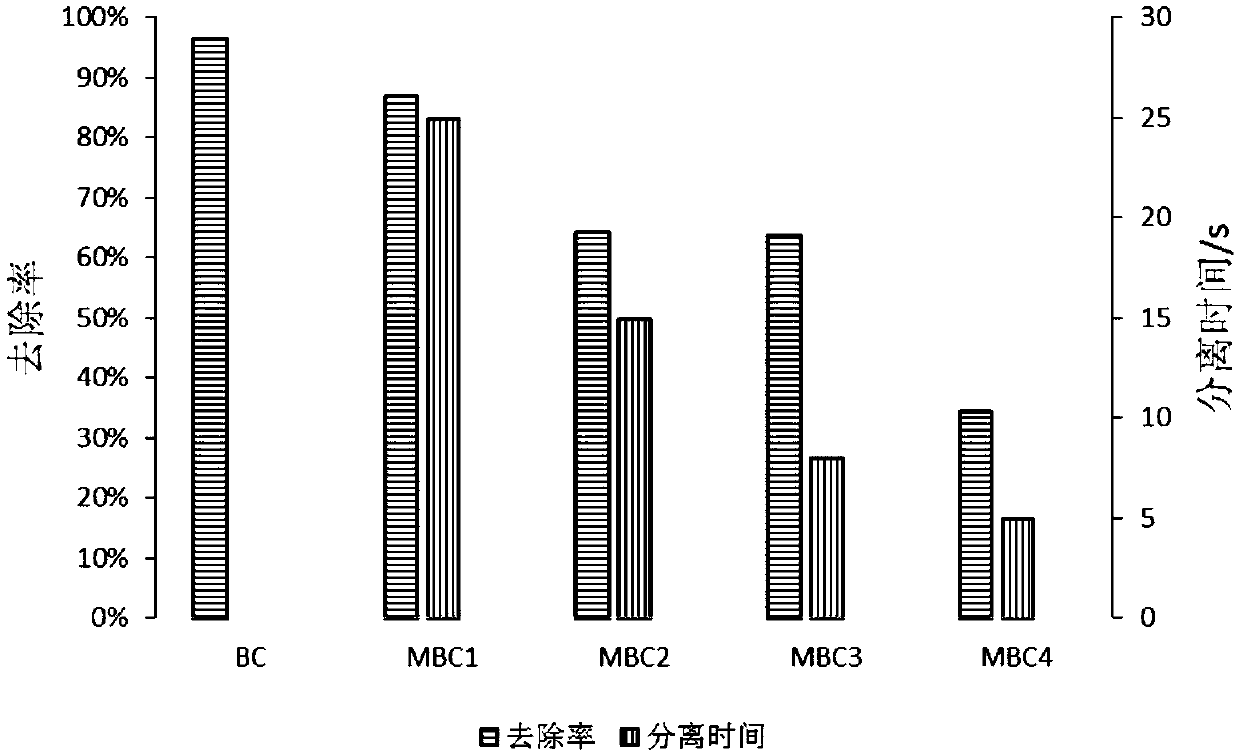
[0055] The initial concentration of cadmium solution is 11.11mg / L, the concentration of cadmium after adsorption equilibrium is 1.44mg / L, the removal rate is 64.35%, and the adsorption capacity is 14.3mg g -1 , the total separation time is 10-15s.
Embodiment 3
[0057] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0058] The added mass (gram) of the raw material is biomass charcoal: ferrous sulfate: ferric sulfate=2.32:4:10.8, and the gained magnetic biomass charcoal is denoted as MBC3;
[0059] The initial concentration of cadmium solution is 11.11mg / L, the concentration of cadmium after adsorption equilibrium is 3.96mg / L, the removal rate is 63.74%, and the adsorption capacity is 14.2mg g -1 , the total separation time is 8-10s.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com